Overview
The rank voting system presents significant advantages for unions, notably enhanced electoral participation, improved representation, and a reduction in negative campaigning. By encouraging broader candidate appeal, ranked choice voting not only increases voter turnout but also alleviates concerns regarding wasted votes. Furthermore, it cultivates a more inclusive environment, ultimately resulting in leadership that more accurately reflects the diverse perspectives of union members. This approach fosters a stronger connection between leadership and the membership, paving the way for more effective advocacy and representation.
Introduction
The evolution of voting systems has ignited a critical dialogue regarding the effectiveness of traditional methods compared to innovative approaches such as ranked choice voting (RCV). This system not only enhances voter engagement but also promises a more democratic and representative electoral process, particularly within labor unions. By delving into the multifaceted benefits of RCV, unions can unlock new avenues for member participation and leadership representation.
However, how can unions effectively implement ranked choice voting to surmount historical challenges and cultivate a more inclusive decision-making environment? This question invites union leadership to reflect on the transformative potential of RCV in reshaping their electoral processes.
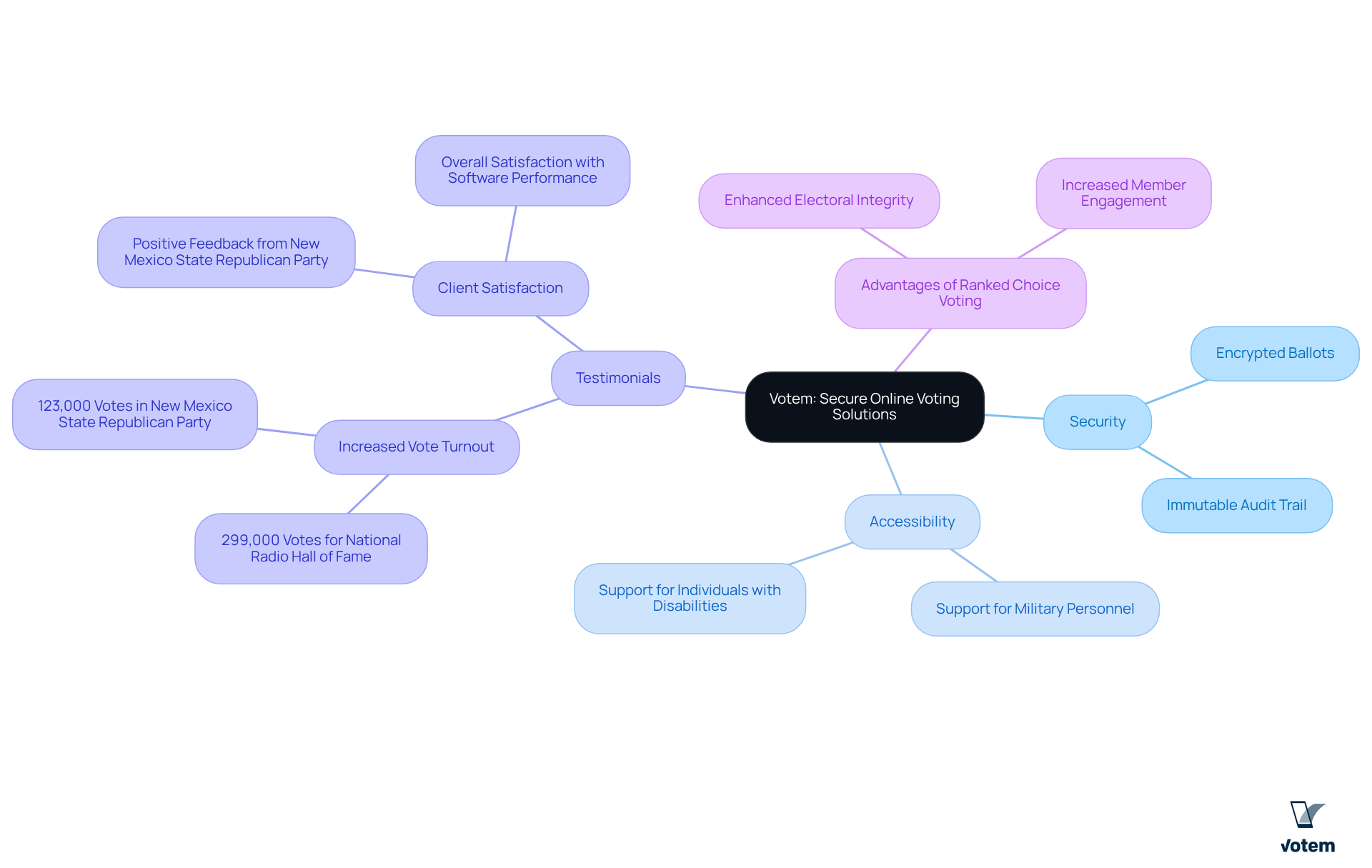
Votem: Secure Online Voting Solutions for Ranked Choice Elections
Votem’s CastIron platform provides a that utilize a rank voting system, ensuring the utmost security and compliance. Designed to meet the stringent requirements of regulated industries, Votem guarantees that every ballot is encrypted and that an immutable audit trail is maintained. This level of security is essential for organizations that must adhere to labor laws and uphold the trust of their members. By leveraging Votem’s technology, unions can streamline their election processes while ensuring transparency and accountability—critical elements in maintaining member confidence.
Furthermore, Votem’s innovative system significantly enhances accessibility for all eligible participants, including military personnel and individuals with disabilities. Testimonials from satisfied clients underscore this commitment:
- “Implementing Votem’s new, modern system allowed greater access for all qualified voters from military voters to voters with disabilities.”
- “Votem successfully handled the receipt of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, an increase over last year’s 126,000 votes received.”
- “The New Mexico State Republican Party was very pleased with Votem’s software performance and will use their services again in May for our State Party’s Quadrennial Election.”
- “Votem helped deliver 123,000 votes, more than double the turnout of the last election in 2015 and the highest number of votes since the election began 30 years ago!”
In addition, the combination of advanced technology and commitment to accessibility positions Votem as a leader in the electoral process. Union leadership should consider the advantages of adopting a rank voting system to enhance their electoral integrity and member engagement.
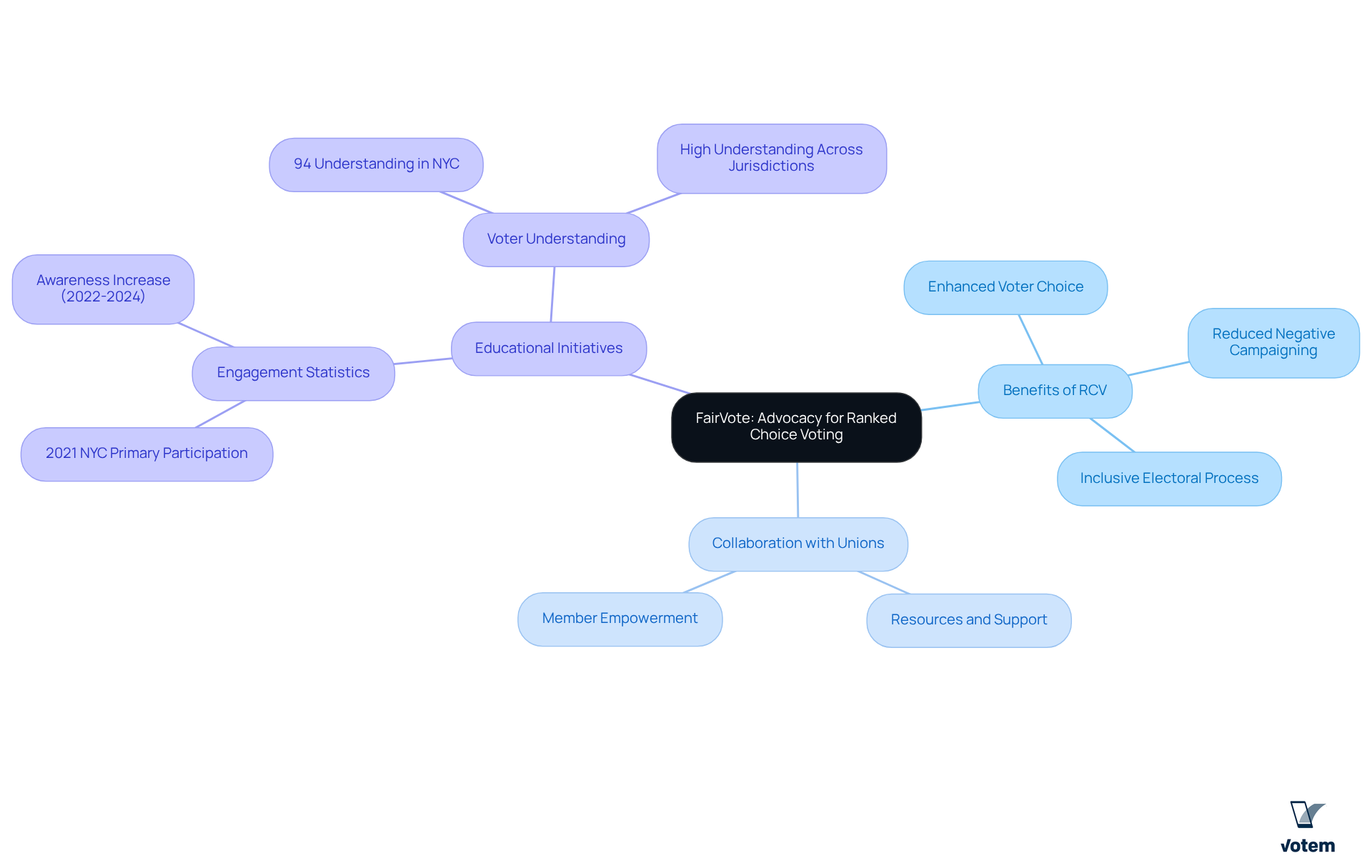
FairVote: Advocacy and Education for Ranked Choice Voting
FairVote spearheads the promotion of the rank voting system across the United States, focusing on educating both the electorate and policymakers about its numerous benefits. The rank voting system not only enhances voter choice but also reduces negative campaigning and fosters a more inclusive electoral process. For labor organizations, collaborating with FairVote opens doors to essential resources and support for advancing RCV adoption. This partnership not only improves electoral processes but also nurtures a more democratic environment for members.
Recent strides in RCV education have enabled FairVote to effectively engage with various unions, demonstrating how the rank voting system can enhance electoral participation and satisfaction. For instance, during the 2021 New York City mayoral primary, over 80 percent of Black, Latino, and Asian American participants utilized the rank voting system by ranking multiple candidates, illustrating RCV’s capacity to engage diverse electoral demographics. Furthermore, a study revealed that 94 percent of NYC electors reported a solid understanding of the rank voting system, underscoring the success of educational initiatives.
By leveraging FairVote’s expertise, unions can advocate for reforms that align with their objectives, ensuring their members’ voices are heard and represented in a more equitable manner. This is not just about voting; it’s about empowering your members and shaping a more . The time to act is now—partner with FairVote to transform the electoral landscape for the better.
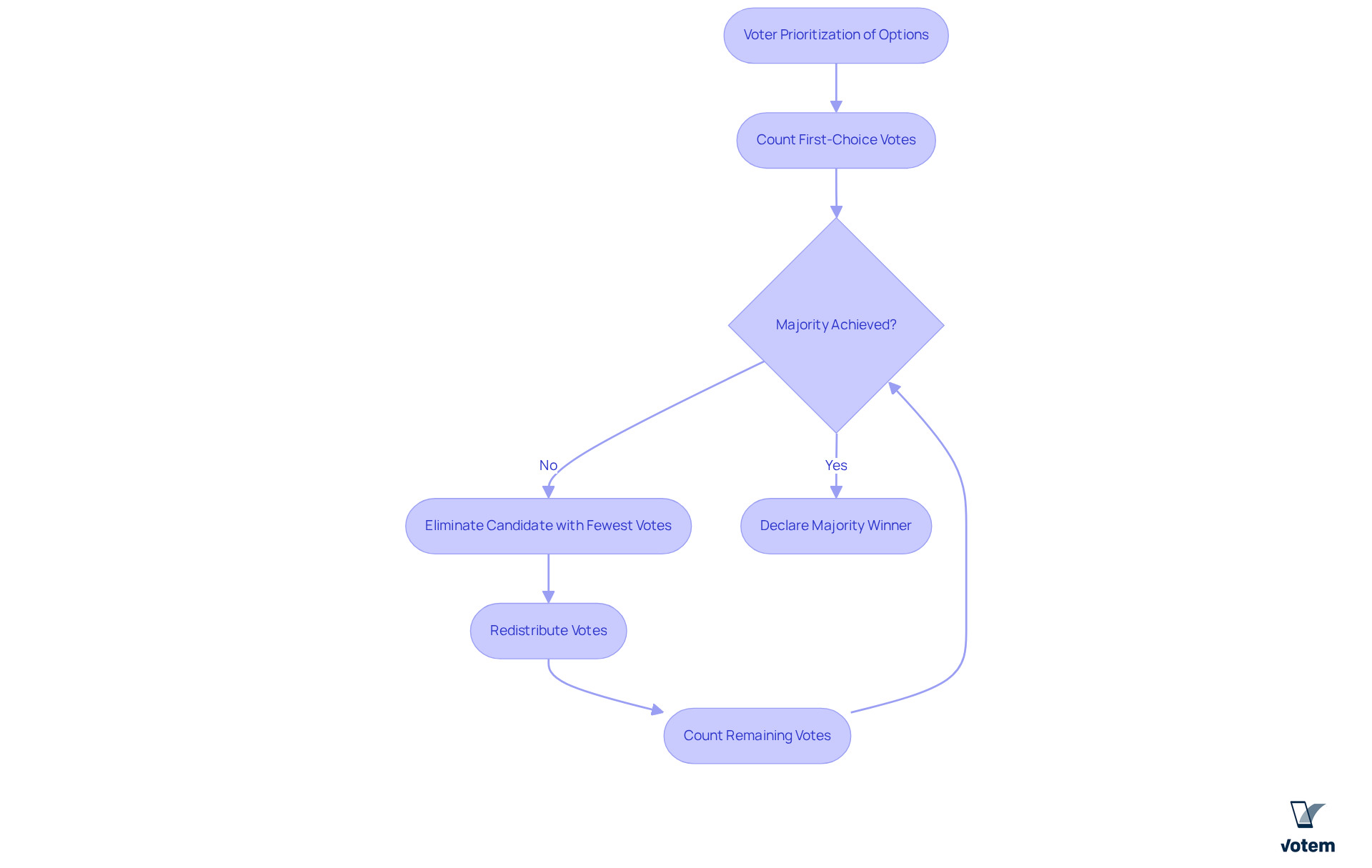
How Ranked Choice Voting Works: A Comprehensive Overview
The rank voting system allows individuals to prioritize their options according to preferences, rather than limiting them to a single selection. When no nominee secures a majority of first-choice votes, the individual with the fewest votes is eliminated, and their votes are redistributed to the remaining candidates based on voters’ subsequent preferences. This iterative process persists until a contender achieves a majority. The rank voting system not only ensures that the elected individual has broader support but also significantly mitigates the risk of vote splitting, making it an equitable and effective system for unions.
The success of RCV is evident across various jurisdictions. For instance, in New York City’s 2021 mayoral primary, an impressive 94% of respondents reported a solid understanding of RCV, underscoring the effectiveness of voter education initiatives. Furthermore, research indicates that RCV can enhance diversity among nominees; in California cities that adopted RCV, there was a notable nine-point increase in the percentage of candidates from racial or ethnic minority groups, as highlighted in a study by John et al. (2018).
Moreover, RCV has been shown to foster a more respectful political environment, encouraging candidates to engage with a broader electorate. As Horowitz stated, “under realistic conditions, preferential voting encourages coalition-building and accommodation and rewards political moderation and compromise.” This is particularly beneficial for groups, as it heightens the likelihood of consensus nominees succeeding, thereby promoting unity and cooperation within the organization. With nearly 90% of participants across various jurisdictions expressing a preference for majority winners—including 86% of registered individuals who believe it is crucial for the successful candidate to secure a majority of votes—the rank voting system aligns with democratic principles and the goals of organizations striving to effectively represent their members. Additionally, the rank voting system is currently employed in 51 jurisdictions across the United States, highlighting its increasing relevance and adoption.
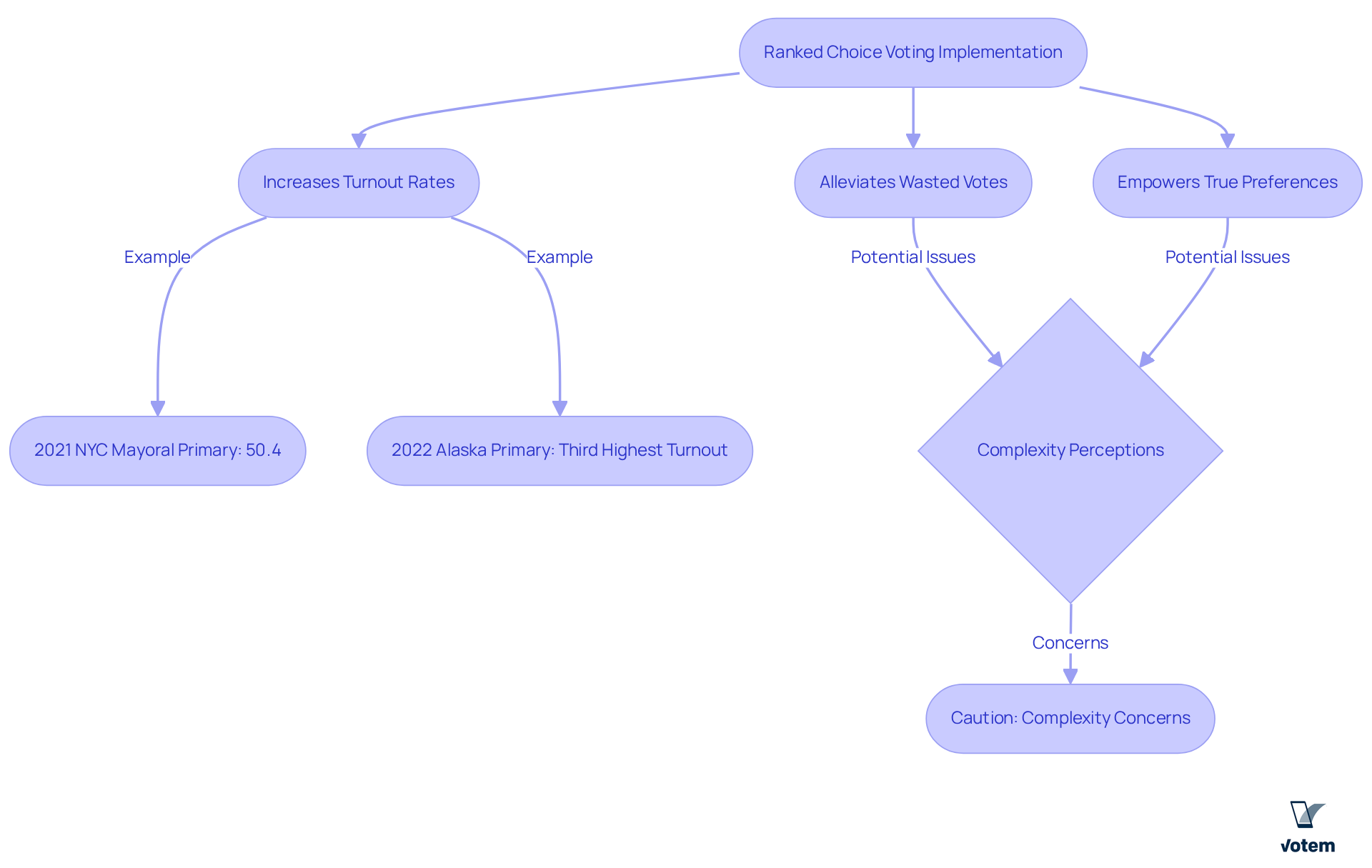
Increasing Voter Participation: The Impact of Ranked Choice Voting
Research indicates that the rank voting system can significantly enhance participation in union elections. By allowing participants to rank their preferences, the rank voting system alleviates the concern of wasting votes, thereby encouraging greater involvement in the electoral process. Unions that have adopted the rank voting system report notable increases in turnout rates, as members feel empowered to vote for their true preferences without the fear of splitting the vote among similar candidates.
For instance, in the 2021 New York City mayoral primary, Eric Adams secured his position with 50.4% support after eight rounds of the rank voting system, illustrating how the rank voting system can promote moderate candidates and bolster public participation. Furthermore, in 2022, Alaska achieved the third highest primary turnout in the United States, further substantiating the assertion that the rank voting system can lead to increased engagement.
This rise in participation not only results in more representative outcomes but also reinforces the collective voice of the organization, ensuring that the interests of all members are effectively represented in decision-making processes. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that in 2024, many voters rejected ranked-choice voting due to perceptions of complexity and confusion. As we approach 2025, the impact of the rank voting system on collective turnout rates remains a vital element in promoting democratic involvement within labor organizations.
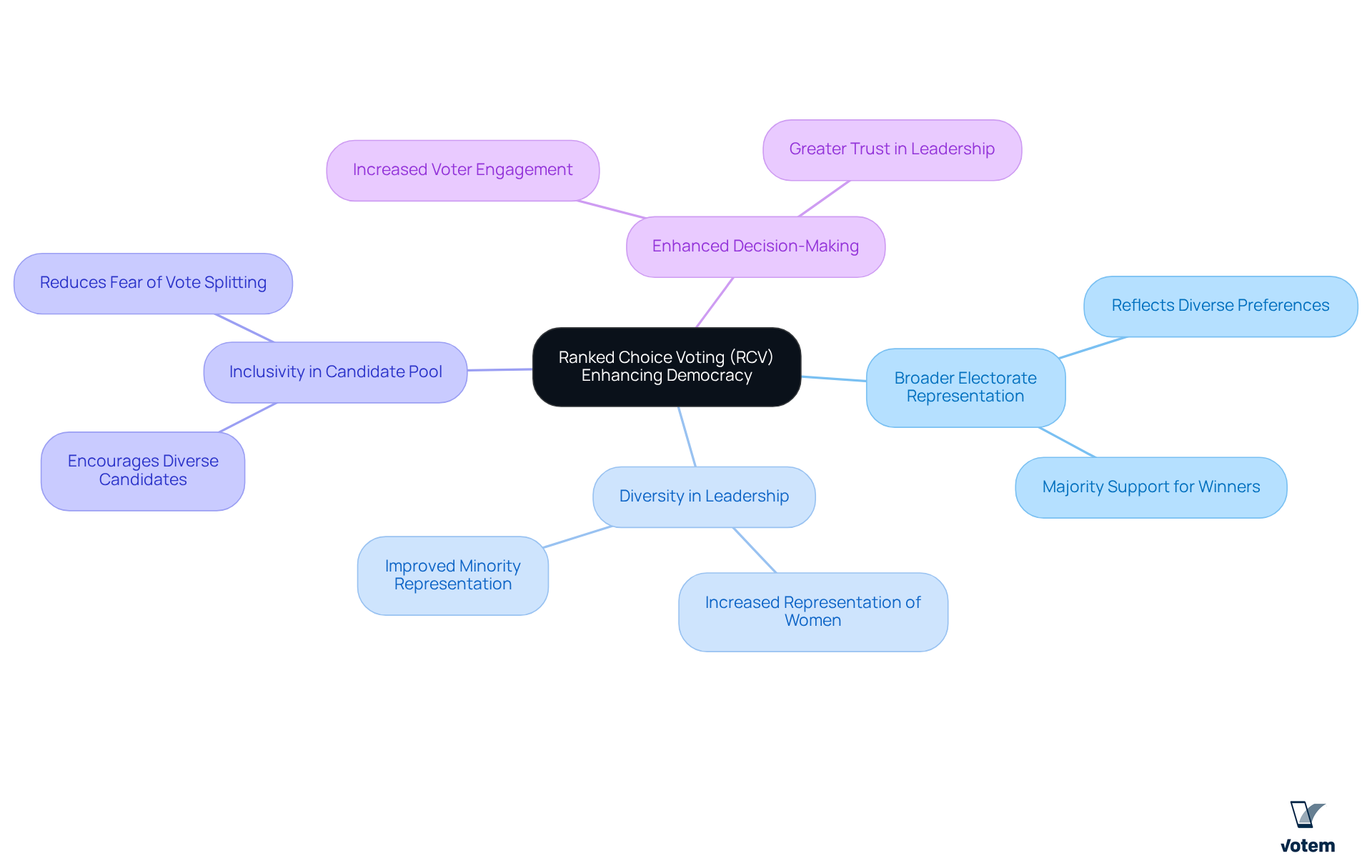
Representative Outcomes: How Ranked Choice Voting Enhances Democracy
The rank voting system significantly enhances democracy by ensuring that elected representatives reflect the preferences of a broader segment of the electorate. This rank voting system compels participants to , as they must seek second and third-choice votes to achieve success. For unions, this translates to leadership positions being filled by individuals who genuinely represent the diverse views of their members, fostering a more inclusive and democratic environment.
Notably, RCV has been associated with improved representation of women and minority individuals, effectively addressing historical disparities in leadership roles. Studies indicate that RCV can lead to a more diverse candidate pool, encouraging individuals from various backgrounds to run for office without the fear of vote splitting.
Furthermore, Votem’s versatile online voting platform enhances this process by providing accessible, secure, and transparent election solutions that support the rank voting system implementation. This inclusivity not only enhances the decision-making process within organizations but also bolsters member involvement and confidence in their leadership.
As RCV continues to gain traction, its potential to reflect the diverse preferences of union members becomes increasingly evident, paving the way for a more representative and equitable governance structure.
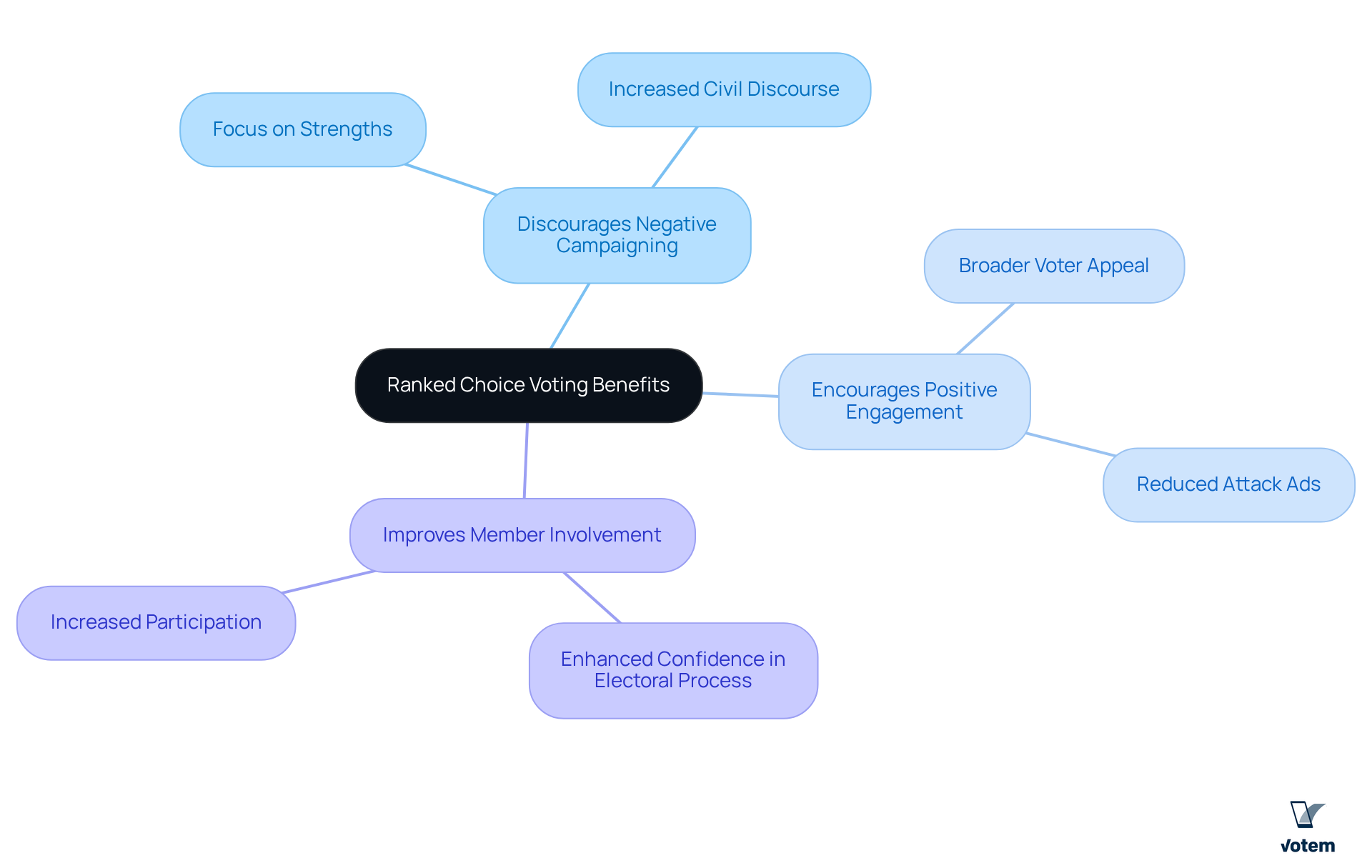
Discouraging Negative Campaigning: A Benefit of Ranked Choice Voting
One of the significant advantages of the rank voting system is its ability to discourage negative campaigning. Candidates are incentivized to appeal to a broader base of voters within the rank voting system, as they need to secure not only first-choice votes but also second and third choices. This dynamic encourages candidates to focus on their strengths and engage in more civil discourse, particularly within a rank voting system, ultimately reducing the prevalence of attack ads and negative rhetoric. Furthermore, for associations, promoting a positive campaigning atmosphere can significantly improve member involvement and confidence in the electoral process.
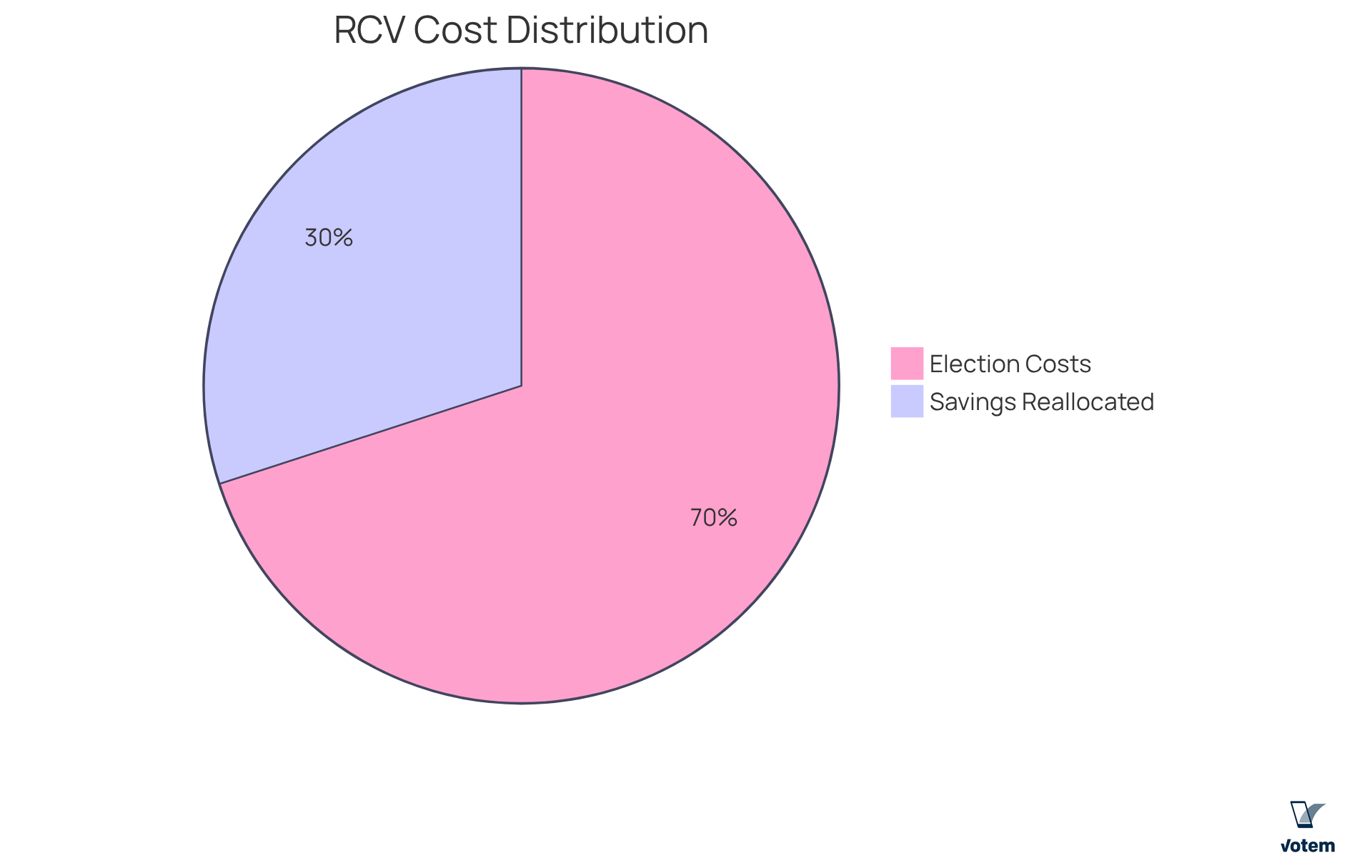
Cost Efficiency: How Ranked Choice Voting Saves Money
The rank voting system provides substantial cost savings for labor organizations by eliminating the need for separate runoff elections, which can be financially burdensome. This streamlined approach not only but also minimizes administrative costs and resource allocation.
A case study from the National Education Association (NEA) illustrates this impact; by implementing RCV, they achieved a reduction in election costs by approximately 30%. This significant savings allows unions to reallocate funds toward member-focused initiatives instead of costly election logistics.
Furthermore, as leader Cathy Woolard states, ‘By adopting the rank voting system, we can enhance our financial efficiency, ensuring that more resources are directed toward programs that directly benefit our members.’ This highlights how RCV not only conserves financial resources but also empowers unions to invest in their core mission of effectively serving their members.
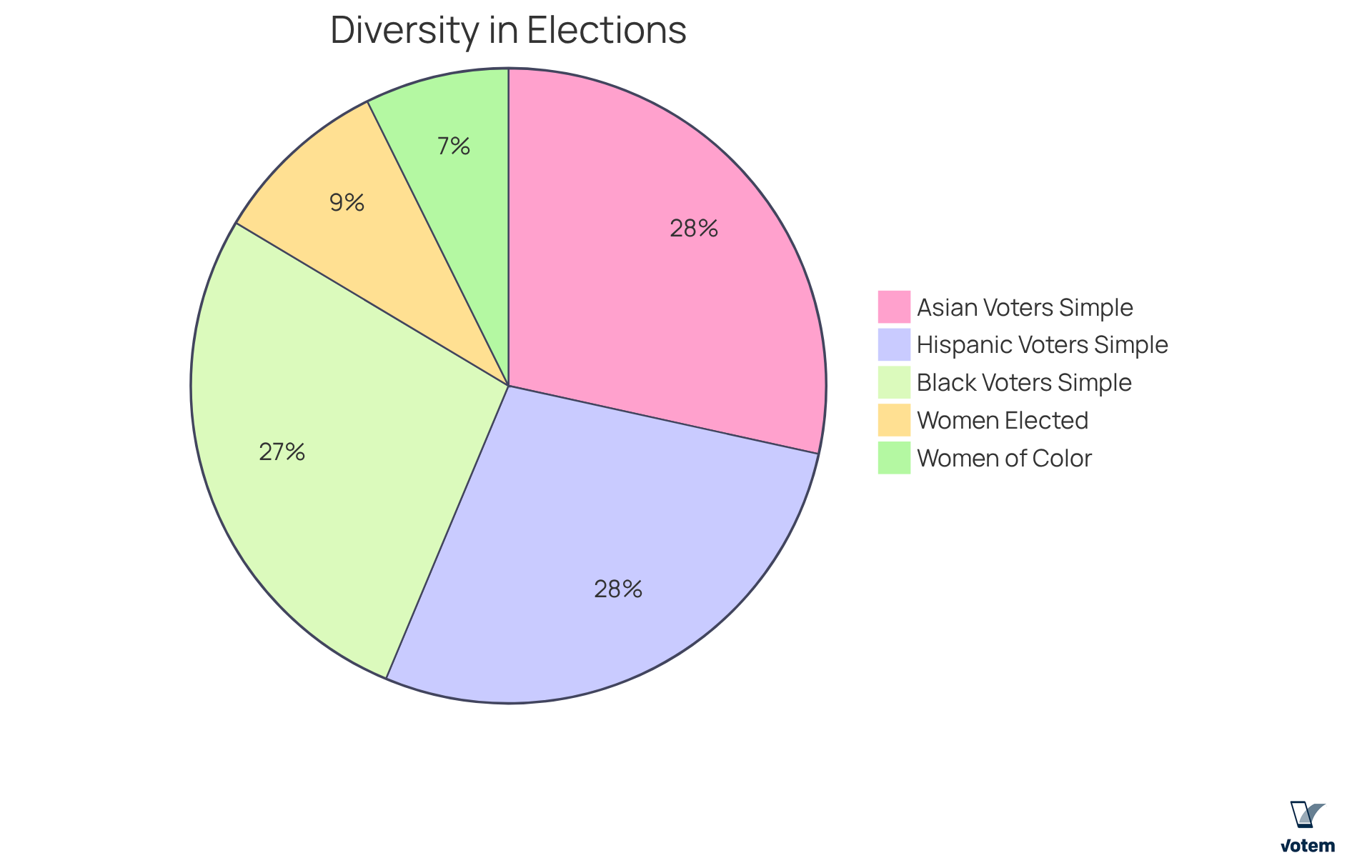
Promoting Diversity: Lowering Barriers for Candidates with Ranked Choice Voting
The rank voting system significantly enhances diversity by reducing barriers for individuals who have historically been underrepresented in leadership positions. By allowing voters to rank several individuals, the rank voting system promotes the election of candidates from diverse backgrounds, including women and people of color. This inclusivity is crucial for unions aiming to mirror the demographics of their membership and ensure that all voices are considered in decision-making processes.
For instance, in New York City’s first IRV elections in 2021:
- 31 women were elected to the city council, including 25 women of color, marking a historic shift towards equitable representation.
- In the Bay Area, cities utilizing RCV have seen candidates of color winning 62% of races since its implementation, compared to just 38% prior.
- Notably, 93% of Black participants, 95% of Hispanic individuals, and 97% of Asian residents in NYC found their ballot simple to complete in the 2021 rank voting system election, highlighting the accessibility of ranked choice voting.
Additionally, a 2020 study indicated that alternative ballot types, such as the rank voting system, are associated with smaller discrepancies in error proneness across demographics, reinforcing RCV’s reliability. Furthermore, 54% of Alaska Natives and 47% of non-Native individuals of color believed their ballot carried more influence under the new rank voting system, indicating a favorable view of RCV among various electoral groups. By embracing the rank voting system, organizations can create a more fair and representative leadership framework, ultimately resulting in improved outcomes for their members.
Global Adoption: Where Ranked Choice Voting is Implemented
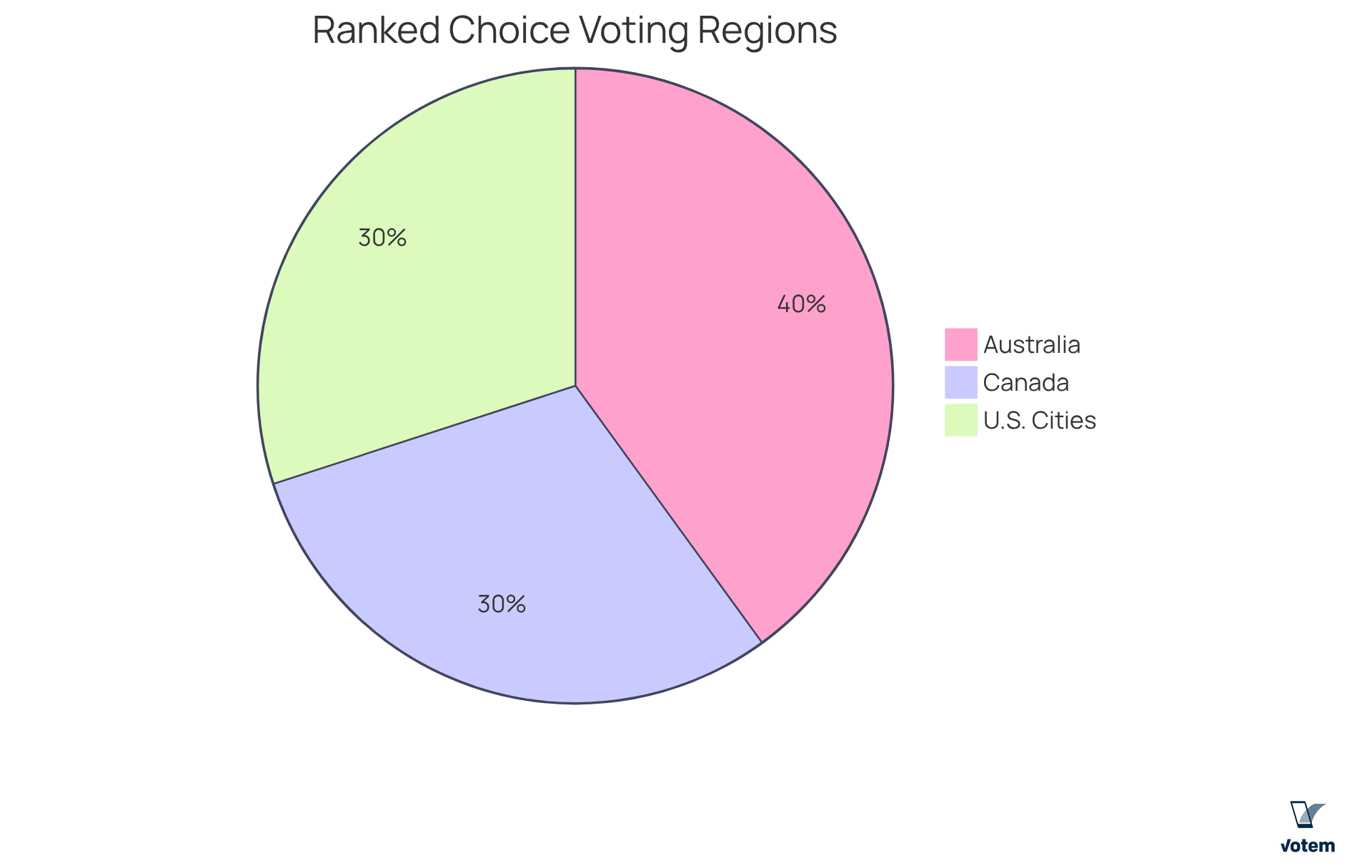
The rank voting system, referred to as ranked choice voting (RCV), has been successfully adopted in various jurisdictions worldwide, including Australia, Canada, and several U.S. cities. This global trend underscores the effectiveness of the in enhancing voter engagement and ensuring more representative electoral outcomes.
For organizations contemplating the implementation of the rank voting system, examining successful case studies from these regions can provide valuable insights into best practices and potential challenges.
Furthermore, understanding the global landscape of the rank voting system empowers unions to confidently advocate for its adoption, ensuring that they are well-prepared to navigate the complexities of electoral reform.
Empirical Research: Evidence Supporting Ranked Choice Voting
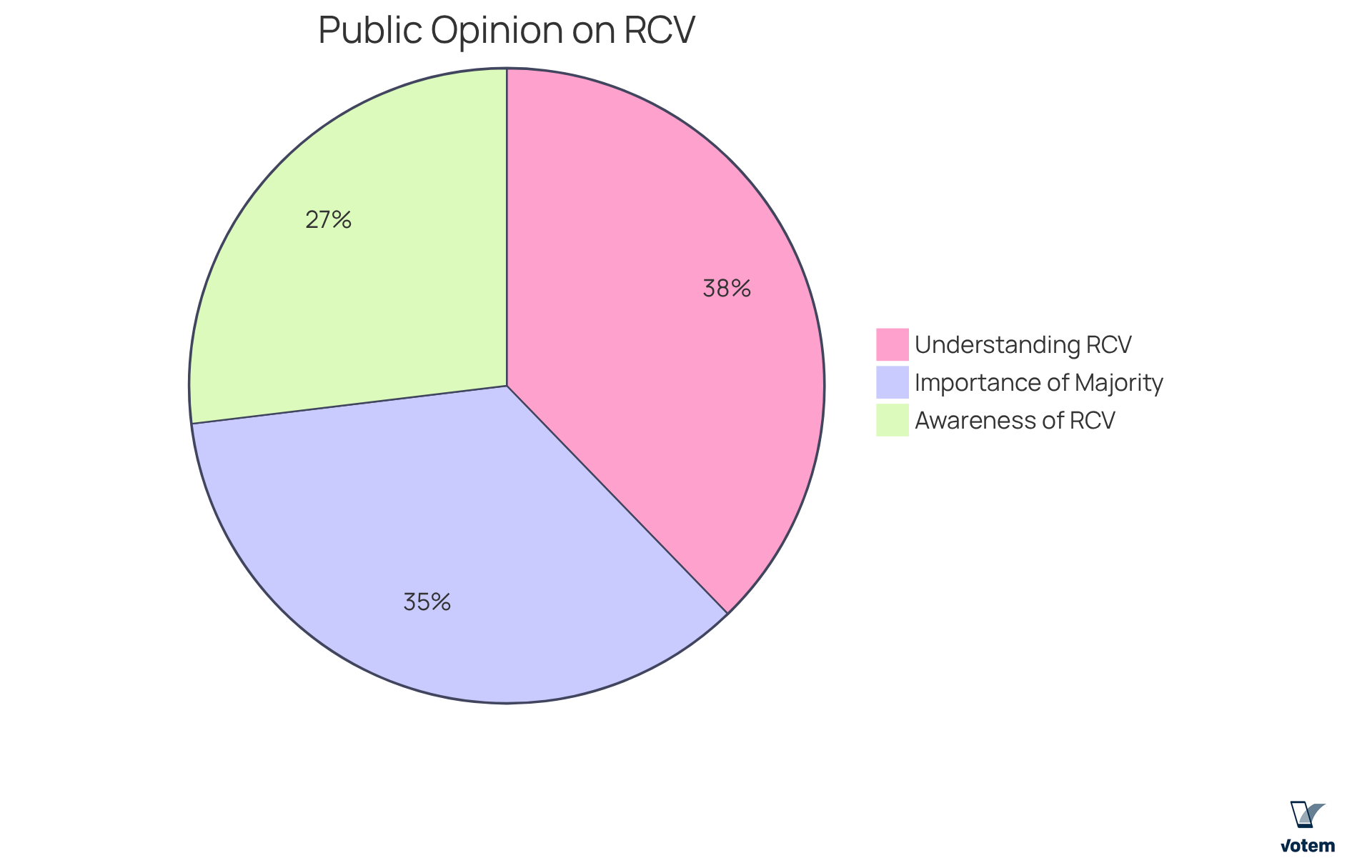
Comprehensive studies highlight the substantial benefits of the rank voting system, demonstrating its capability to increase participation, reduce negative campaigning, and improve overall representation. Jurisdictions that have implemented RCV often report elevated levels of electoral satisfaction and engagement. Notably, 94 percent of New York City respondents indicated they understood RCV extremely well, very well, or somewhat well. Furthermore, 67 percent of respondents had heard of RCV, showcasing a growing awareness and support among the public.
For labor organizations, leveraging empirical evidence can significantly bolster their argument for RCV adoption. This evidence underscores RCV’s potential to enhance electoral outcomes and foster a more democratic atmosphere. Importantly, younger voters in RCV cities are found to be 9 percentage points more likely to vote, which highlights RCV’s positive impact on turnout. By grounding their advocacy in solid research, unions can effectively communicate the advantages of RCV to their members and stakeholders, fostering a deeper understanding of its transformative potential in the electoral process.
Moreover, RCV shifts elections from zero-sum contests to more positive campaigns, reinforcing the democratic principles that RCV aims to uphold. An impressive 88 percent of respondents believe it is very or somewhat important that the winning candidate has a majority of the votes. This statistic not only emphasizes the importance of majority support but also serves as a compelling call to action for union leadership to advocate for the adoption of RCV.
Conclusion
The rank voting system presents unions with a transformative approach to elections, fostering inclusivity and enhancing democratic engagement among members. By enabling voters to express their preferences more freely, this system not only increases participation but also ensures that elected leaders genuinely reflect the diverse views within the organization.
Several key benefits of the rank voting system have been highlighted. These include:
- Improved voter turnout
- Reduced negative campaigning
- Cost efficiency
- Enhanced representation of underrepresented groups
Secure online voting platforms, such as Votem, ensure that these elections are conducted transparently and securely. Additionally, organizations like FairVote provide essential advocacy and educational resources to support the adoption of this system.
As unions strive for greater member engagement and representation, embracing the rank voting system emerges as a vital step forward. By advocating for its implementation, unions can empower their members, promote a more inclusive electoral process, and ultimately strengthen the democratic foundations of their organizations. The time to act is now—unions should seize this opportunity to transform their electoral processes for the better, ensuring that every member’s voice is heard and valued.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Votem’s CastIron platform?
Votem’s CastIron platform is a secure online voting solution designed for conducting elections using a ranked choice voting system. It ensures ballot encryption and maintains an immutable audit trail for security and compliance.
How does Votem ensure security and compliance in elections?
Votem guarantees that every ballot is encrypted and that an immutable audit trail is maintained, which is essential for organizations that must adhere to labor laws and maintain the trust of their members.
What advantages does Votem’s technology provide to unions?
Votem’s technology streamlines election processes, enhances transparency and accountability, and significantly improves accessibility for all eligible participants, including military personnel and individuals with disabilities.
What are some testimonials about Votem’s services?
Clients have reported increased voter access, such as military and disabled voters, and notable increases in vote turnout, with examples including 299,000 votes received for the National Radio Hall of Fame and 123,000 votes for a state election.
What role does FairVote play in promoting ranked choice voting?
FairVote advocates for ranked choice voting (RCV) across the United States and educates the electorate and policymakers about its benefits, which include enhancing voter choice and reducing negative campaigning.
How does ranked choice voting work?
In ranked choice voting, individuals prioritize their preferences. If no nominee secures a majority of first-choice votes, the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated, and their votes are redistributed based on voters’ subsequent preferences until a majority winner is determined.
What are the benefits of ranked choice voting for unions?
RCV enhances electoral integrity, reduces vote splitting, encourages broader support for elected individuals, and fosters a more respectful political environment, which can lead to greater member engagement and satisfaction.
How has ranked choice voting been received in recent elections?
In the 2021 New York City mayoral primary, over 80% of diverse participants used the rank voting system, and 94% of electors reported a solid understanding of RCV, indicating successful voter education initiatives.
How does ranked choice voting contribute to diversity in elections?
Research indicates that RCV can enhance diversity among nominees, as seen in California cities where its adoption led to a nine-point increase in candidates from racial or ethnic minority groups.
How widespread is the use of ranked choice voting in the United States?
The rank voting system is currently employed in 51 jurisdictions across the United States, highlighting its growing relevance and adoption.
List of Sources
- FairVote: Advocacy and Education for Ranked Choice Voting
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- How Ranked Choice Voting Works: A Comprehensive Overview
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- Increasing Voter Participation: The Impact of Ranked Choice Voting
- The future of the instant runoff election reform | Brookings (https://brookings.edu/articles/the-future-of-the-instant-runoff-election-reform)
- Representative Outcomes: How Ranked Choice Voting Enhances Democracy
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- Ranked-Choice Voting – Center for Effective Government (https://effectivegov.uchicago.edu/primers/ranked-choice-voting)
- Cost Efficiency: How Ranked Choice Voting Saves Money
- FHWA – Center for Innovative Finance Support – Value Capture – Case Studies: Atlanta BeltLine Tax Allocation District (https://fhwa.dot.gov/ipd/value_capture/case_studies/atlanta_beltline_tax_allocation_district.aspx)
- Promoting Diversity: Lowering Barriers for Candidates with Ranked Choice Voting
- The Impact of Instant Runoff Voting on Representation for Women and People of Color | Unite America (https://uniteamerica.org/articles/the-impact-of-instant-runoff-voting-on-representation-for-women-and-people-of-color)
- Empirical Research: Evidence Supporting Ranked Choice Voting
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- Ranked-Choice Voting – Center for Effective Government (https://effectivegov.uchicago.edu/primers/ranked-choice-voting)

