Overview
Voter apathy presents a formidable challenge for unions and democratic processes, marked by a pervasive lack of interest and motivation to participate in elections. This phenomenon stems from various causes, including disillusionment with candidates and a perceived ineffectiveness of voting. Understanding these underlying issues is crucial for union leadership. Furthermore, it is essential to implement targeted engagement strategies that can effectively revitalize participation.
- Education campaigns
- Simplifying the voting process
These are vital steps that can strengthen political advocacy and encourage active involvement. By addressing voter apathy head-on, unions can foster a more engaged electorate and ensure that their voices are heard in the democratic process.
Introduction
Voter apathy poses a significant threat to the democratic process, manifesting as a troubling disinterest among eligible voters that can skew election outcomes and diminish the collective voice of labor organizations. This disinterest not only undermines the electoral system but also challenges the very foundation of union representation.
As unions grapple with this phenomenon, understanding its root causes—ranging from disillusionment with political candidates to socioeconomic barriers—becomes essential for fostering a more engaged electorate.
What strategies can unions implement to not only combat this indifference but also reinvigorate participation in the electoral process?
It is imperative that union leadership takes decisive action to address these challenges and cultivate a more vibrant democratic participation among their members.
Define Voter Apathy and Its Significance
The concept of voter apathy meaning represents a significant challenge characterized by a lack of interest, enthusiasm, or motivation among eligible individuals to engage in the electoral process. This phenomenon frequently results in low participation in elections, disengagement from political discussions, and a general indifference toward election outcomes. For labor groups, the ramifications of electoral indifference are profound, directly impacting their capacity to mobilize participants for collective decision-making and advocacy efforts. When collective participants exhibit apathy, it undermines the democratic values that associations strive to uphold, thereby diminishing their overall impact and effectiveness.
Addressing disengagement among citizens is crucial for organizations aiming to ensure active participation in polls, which is essential for maintaining a robust and representative voice in the political arena. Case studies demonstrate that initiatives designed to boost engagement, such as educational campaigns and the implementation of online voting, can significantly improve turnout and cultivate a more active membership. By prioritizing strategies to combat electoral disinterest, organizations can enhance their democratic processes and advocate more effectively for the interests of those they represent.
Furthermore, it is imperative for union leadership to recognize the challenges posed by the voter apathy meaning and to take decisive action. By fostering a culture of engagement and implementing targeted outreach efforts, unions can revitalize participation and strengthen their influence in the political landscape. The path forward is clear: through commitment to engagement strategies, labor organizations can not only elevate turnout but also reinforce their role as vital advocates for their members.
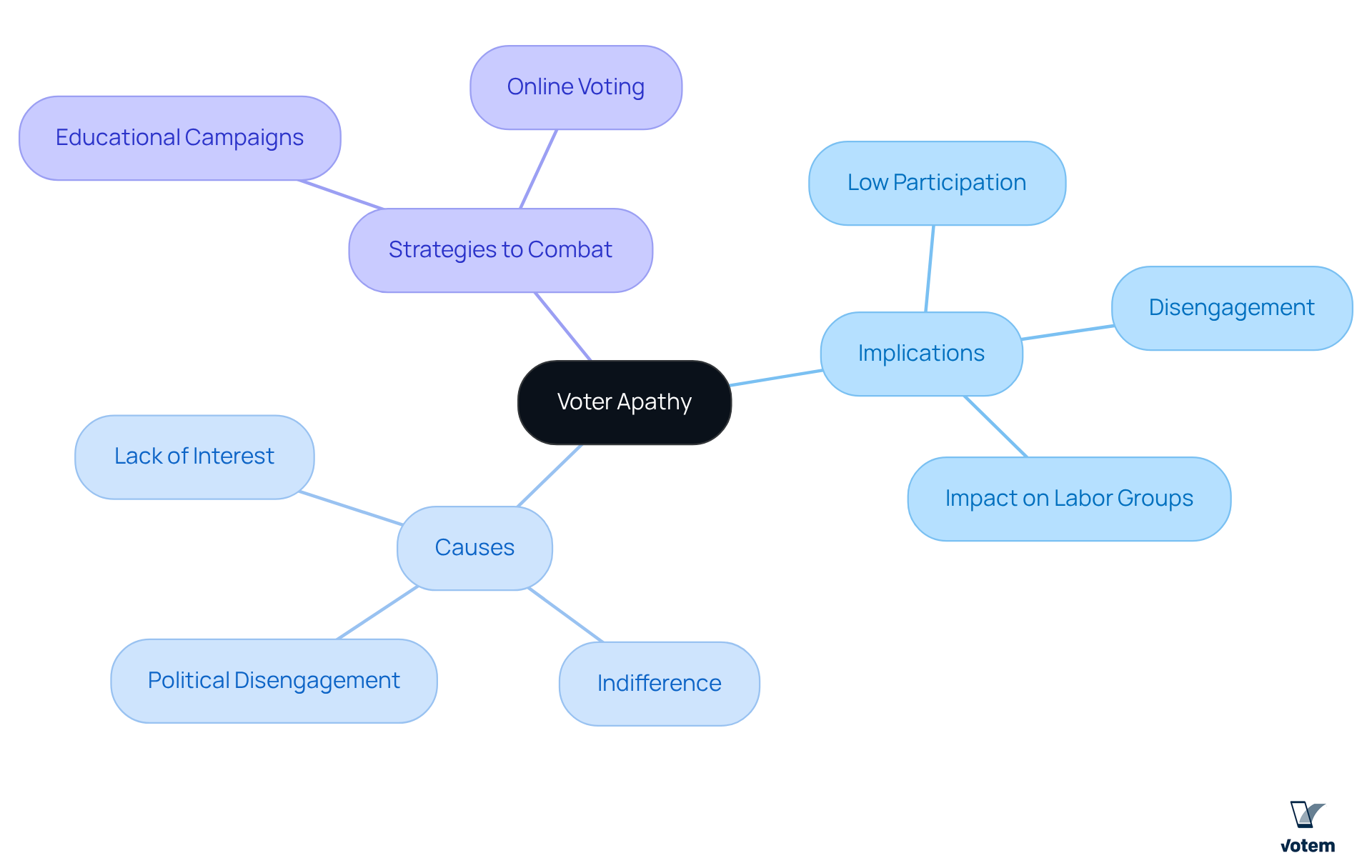
Identify Causes of Voter Apathy
Voter apathy is influenced by several interconnected factors that unions must understand to effectively engage their members.
-
Disillusionment with Political Candidates: A significant number of voters feel that candidates fail to represent their interests, diminishing their motivation to participate in elections. This sentiment is particularly pronounced among younger constituents, who often perceive a disconnect between their needs and the political agenda.
-
Perceived Ineffectiveness of Voting: Many individuals harbor the belief that their votes carry little weight, especially in larger contests where outcomes seem predetermined. This perception can lead to a sense of futility regarding the electoral process, further discouraging participation.
-
Barriers to Participation: Structural obstacles, such as complicated registration processes, limited access to polling locations, and restrictive voting laws, can significantly hinder electoral engagement. For labor participants, these obstacles may be intensified by work obligations and logistical issues, further complicating their ability to engage in voting.
-
Socioeconomic Factors: Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often face additional hurdles that impede their electoral participation. Time constraints due to work obligations, financial instability, and a lack of access to information about the electoral process can all contribute to lower turnout rates.
-
Ballot Fatigue: The regularity of polls can result in participant burnout, defined by sensations of overwhelm and detachment. With 62% of American adults indicating fatigue from voting, it is essential for organizations to acknowledge this trend and adopt strategies to rejuvenate interest among their members.
Understanding these causes is crucial for unions to develop targeted outreach and engagement strategies that effectively address voter apathy and encourage participation in the electoral process.
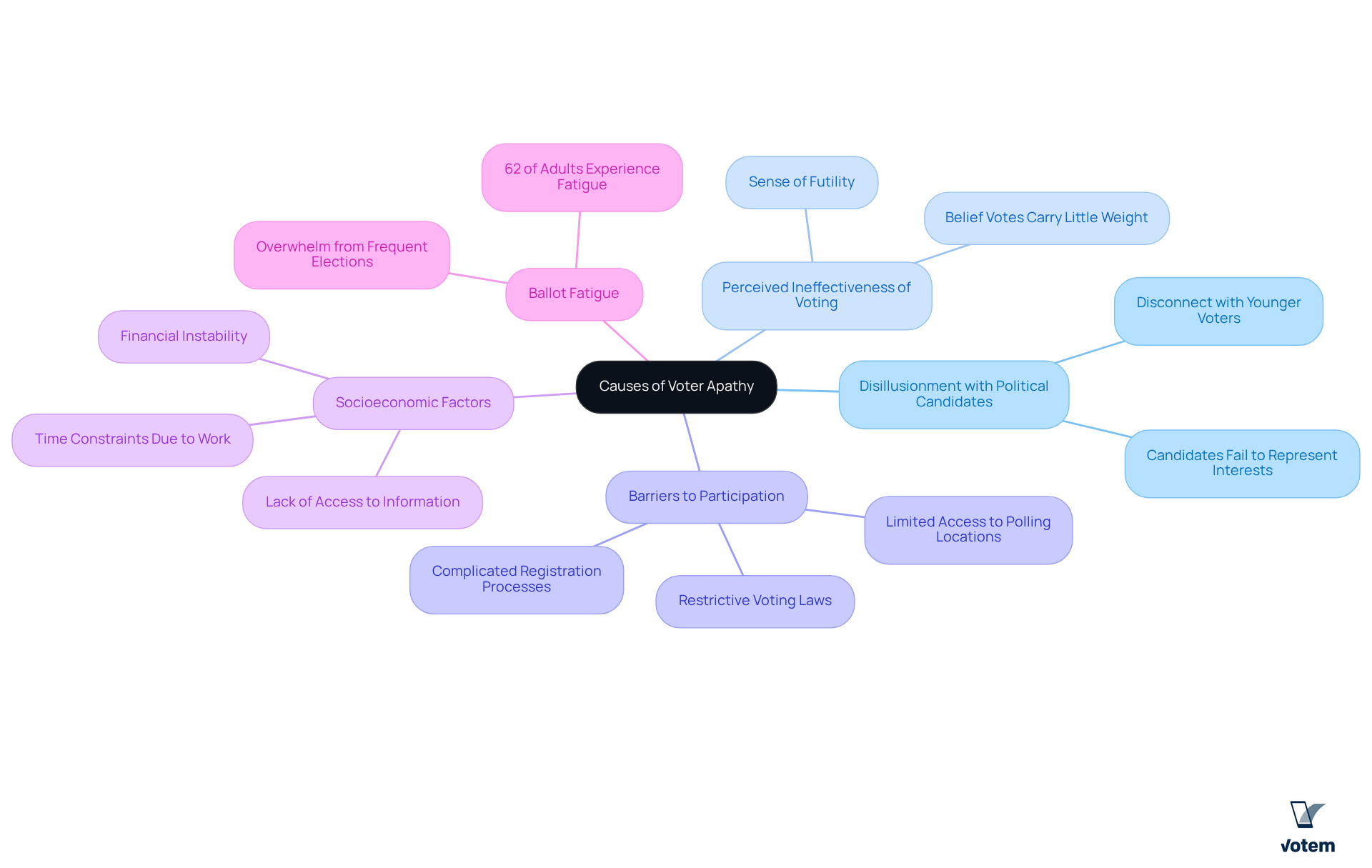
Examine Effects of Voter Apathy on Elections
Voter apathy significantly impacts elections, leading to several critical consequences:
-
Lower Voter Turnout: Apathy directly correlates with decreased participation, skewing election results and undermining the representativeness of elected officials. In recent elections, only 41% of adult citizens voted in all three national elections, highlighting a concerning trend of disengagement.
-
Weakened Democratic Processes: When substantial segments of the population abstain from voting, it undermines the legitimacy of the electoral system. This disengagement illustrates voter apathy meaning that governance fails to reflect the will of the people, as evidenced by the stark contrast in turnout rates among different demographic groups.
-
Diminished Labor Influence: For labor organizations, low electoral participation can result in less favorable policies and legislation. Elected officials may feel less accountable to a disengaged electorate, which can diminish the advocacy power of unions in shaping labor-related policies.
-
Increased Polarization: Apathy can exacerbate political polarization, as those who do participate may hold more extreme views. This dynamic can create a less collaborative political environment, making it challenging to achieve bipartisan solutions.
-
Erosion of Trust: Ongoing public indifference undermines confidence in the political system, complicating efforts to involve citizens in upcoming contests. A substantial segment of the electorate, particularly younger individuals, demonstrates doubt about the significance of elections, which highlights the voter apathy meaning, as only 27% consider the 2024 election to be the most crucial of their lifetime.
These effects highlight the pressing necessity for unions to actively tackle electoral apathy among their members, fostering a more engaged and representative electorate.
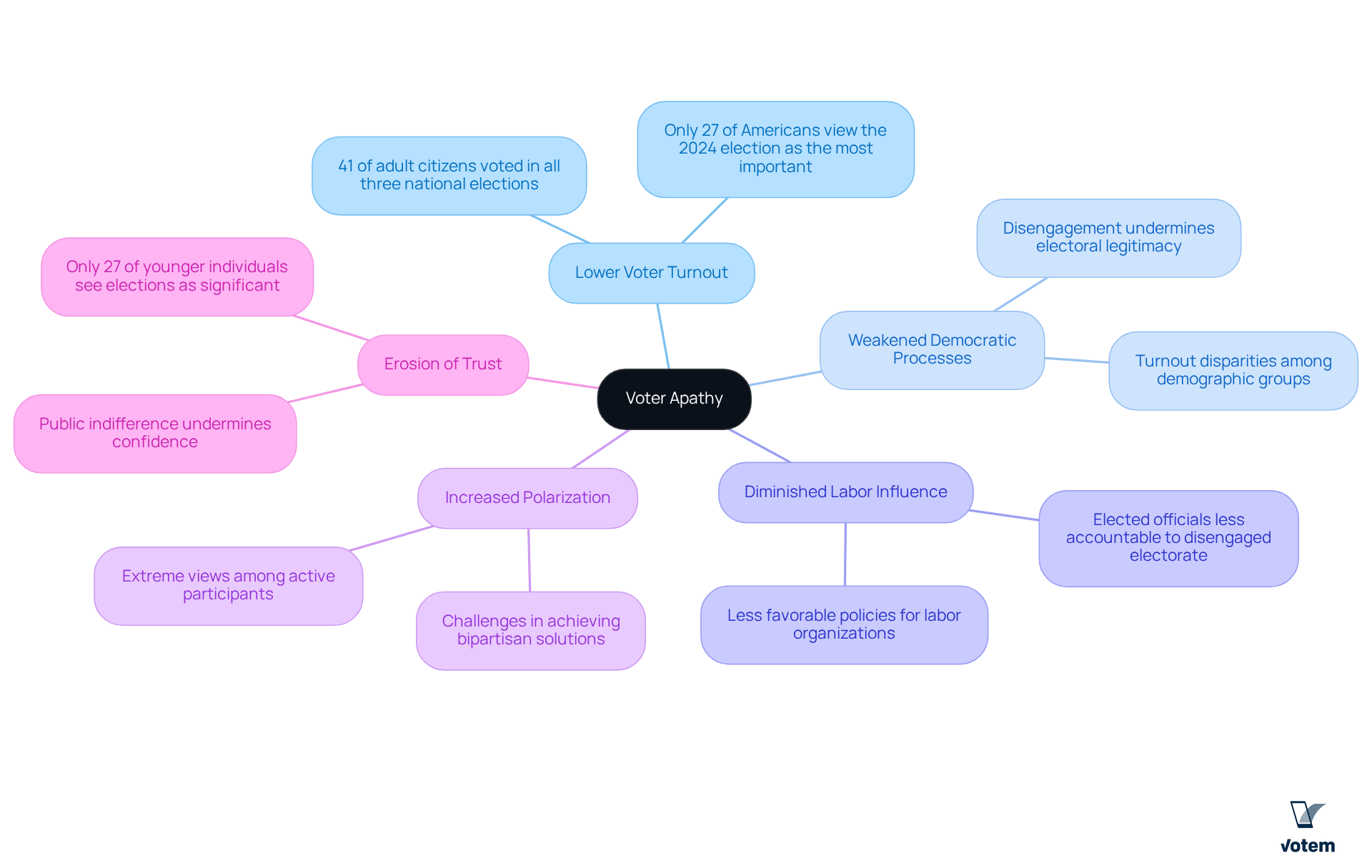
Differentiate Voter Apathy from Voter Suppression
Voter apathy and voter suppression, while both contributing to decreased voter turnout, represent distinct challenges that require tailored approaches.
The term voter apathy describes this phenomenon, which is characterized by a lack of interest or motivation to engage in the electoral process. It frequently stems from feelings of disillusionment, a belief that voting is ineffective, or a perception that candidates do not represent the individual’s values. Psychological factors, such as feelings of powerlessness and alienation, play a significant role in this disengagement. For instance, studies indicate that individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are less likely to vote due to limited access to information and a sense of disenfranchisement.
Elector Suppression: In contrast, elector suppression involves intentional actions aimed at discouraging or preventing specific groups from exercising their voting rights. Tactics include:
- Implementing strict identification laws
- Reducing the number of polling locations
- Conducting aggressive registration roll purges
For example, over 21 million U.S. citizens lack qualifying government-issued photo identification, creating significant barriers to participation. Moreover, states with stringent identification regulations disproportionately impact individuals of color and those with low income, further entrenching systemic inequalities.
Comprehending these distinctions is vital for associations as they formulate strategies to engage their participants in relation to voter apathy. To address electoral indifference, organizations can introduce informative campaigns and involvement initiatives that connect with their members, promoting a sense of empowerment and link to the voting process. Conversely, tackling electoral suppression requires support for policy reforms and legal safeguards to guarantee fair access to voting for everyone. By acknowledging and tackling both electoral indifference and electoral obstruction, labor organizations can play a crucial role in increasing participation and representation in elections.
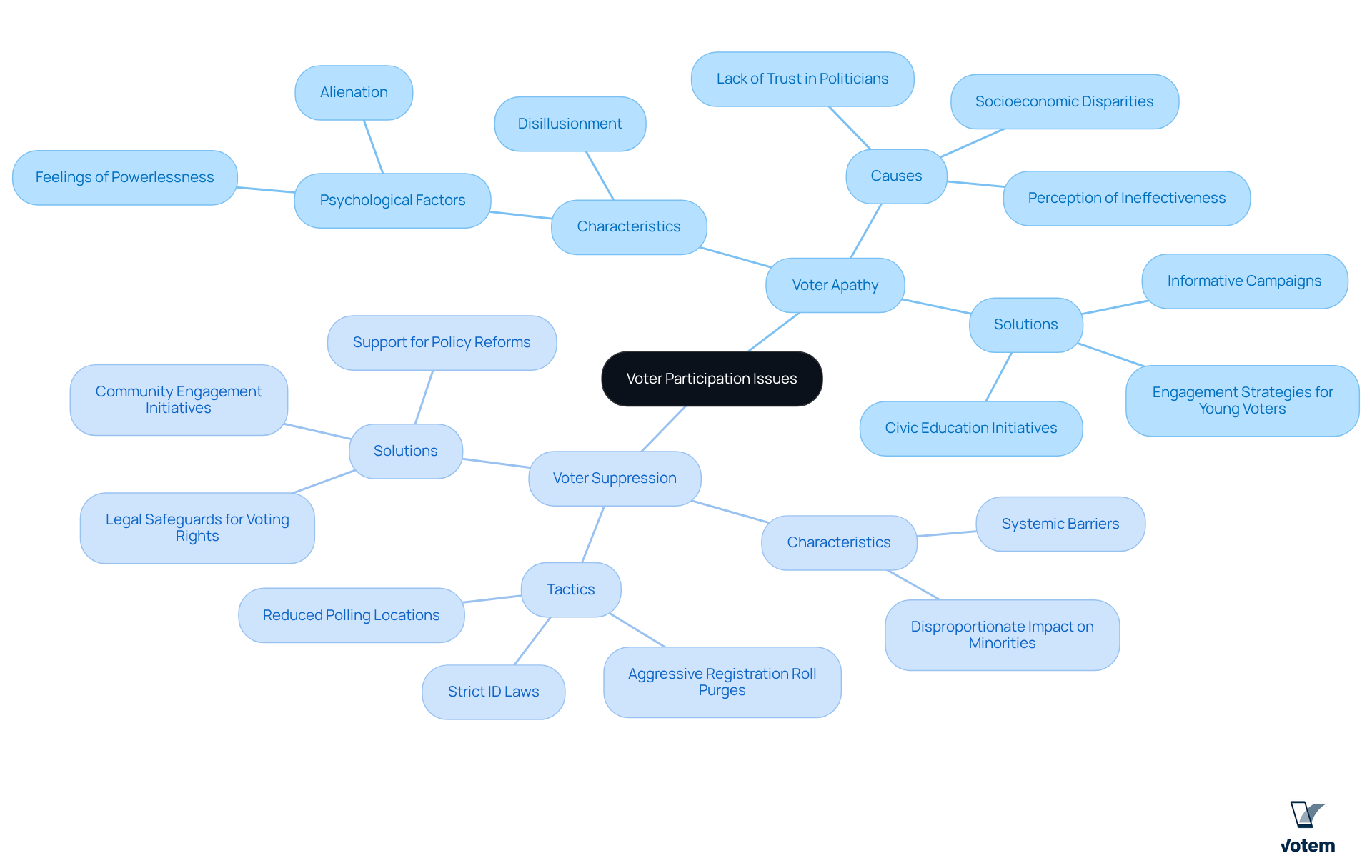
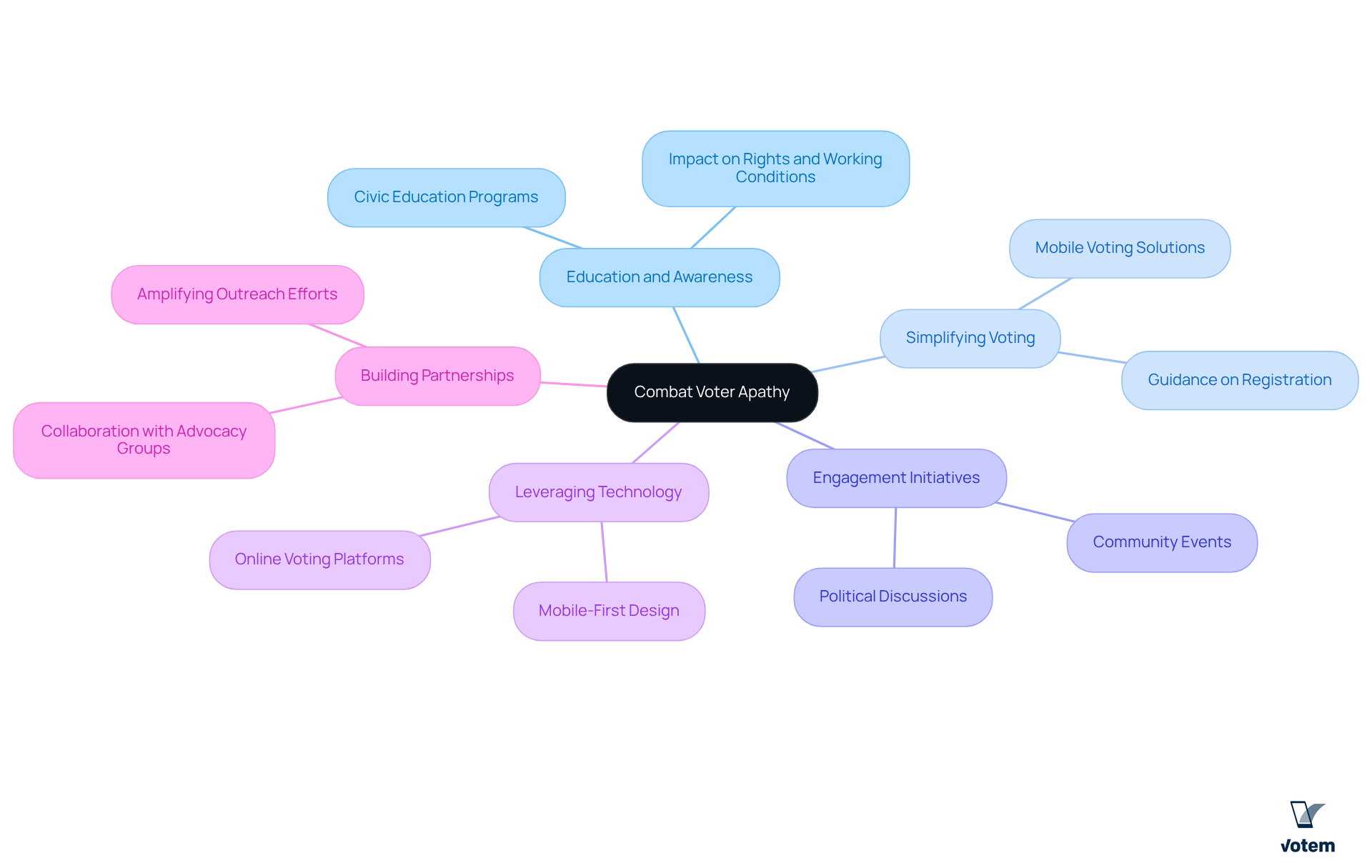
Implement Strategies to Combat Voter Apathy
To effectively combat voter apathy, unions can adopt several impactful strategies that not only inform but also empower their members:
-
Education and Awareness Campaigns: It is crucial to inform members about the significance of voting and its direct impact on their rights and working conditions. Research shows that civic education programs can significantly boost electoral participation, with informed individuals being more likely to engage in elections. Votem’s commitment to enhancing voter participation reinforces these essential messages.
-
Simplify the Voting Process: Offering resources and assistance to help individuals navigate the voting process is essential. This includes guidance on registration and absentee voting options. Studies indicate that simplifying these processes can lead to increased turnout, with mobile voting solutions potentially boosting participation by three to five percentage points. Votem’s innovative online voting solutions simplify this process, enhancing accessibility for all participants, including those with disabilities.
-
Engagement Initiatives: Organizing events that promote political discussions and foster community among participants, such as town halls or candidate forums, can significantly enhance engagement. For instance, outreach initiatives have shown that personal interactions can greatly enhance voter turnout, especially among union members. By employing Votem’s technology, these discussions can be enhanced, effectively engaging participants.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilizing online platforms to facilitate discussions, share information, and mobilize members for upcoming elections is vital. Platforms like Votem’s have already demonstrated success in boosting participation, as evidenced by their management of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, an increase from the prior year’s 126,000 votes. This showcases the effectiveness of technology in modern electoral processes.
-
Build Partnerships: Collaborating with other organizations and advocacy groups can amplify efforts and reach a broader audience. By partnering with Votem, labor organizations can improve their outreach and establish a stronger support system for electoral participation, particularly in relation to mobile voting solutions during Covid-19.
By implementing these strategies and leveraging Votem’s innovative solutions, unions can effectively address voter apathy meaning and enhance participation in the electoral process, ultimately strengthening their collective voice.
Conclusion
Voter apathy stands as a formidable barrier to democratic participation, marked by a pervasive lack of interest and motivation among eligible voters. This disengagement significantly impacts not just individual electoral outcomes but also undermines the collective voice of unions and labor organizations that depend on active involvement to advocate effectively for their members. To tackle this pressing challenge, fostering a culture of engagement and implementing targeted strategies that encourage participation in the electoral process is essential.
Several key causes of voter apathy are highlighted, including:
- Disillusionment with candidates
- The perceived ineffectiveness of voting
- Socioeconomic barriers
These factors collectively contribute to lower voter turnout and diminish the influence of labor organizations in shaping policies that directly affect their members. Furthermore, it is crucial for unions to understand the distinction between voter apathy and voter suppression to tailor their approaches effectively. While apathy arises from a lack of interest, suppression entails intentional actions that obstruct access to voting.
Addressing voter apathy transcends merely increasing turnout; it is fundamentally about revitalizing democracy itself. Unions and labor organizations must prioritize education, simplify the voting process, leverage technology, and forge partnerships to cultivate a more informed and active electorate. By committing to these strategies, they can empower their members, enhance participation, and ultimately bolster their advocacy efforts within the political landscape. The call to action is unmistakable: combating voter apathy is vital for ensuring that every voice is heard and represented in the democratic process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is voter apathy and why is it significant?
Voter apathy refers to a lack of interest, enthusiasm, or motivation among eligible individuals to engage in the electoral process. It is significant because it leads to low participation in elections, disengagement from political discussions, and indifference toward election outcomes, which undermines democratic values and impacts organizations’ ability to mobilize participants for advocacy efforts.
How does voter apathy affect labor groups?
Voter apathy profoundly impacts labor groups by diminishing their capacity to mobilize participants for collective decision-making and advocacy. When members exhibit apathy, it weakens the overall impact and effectiveness of these organizations in upholding democratic values.
What strategies can organizations implement to combat voter apathy?
Organizations can enhance voter engagement through educational campaigns and the implementation of online voting. By prioritizing strategies to address electoral disinterest, they can improve turnout and cultivate a more active membership.
What are some causes of voter apathy?
Causes of voter apathy include disillusionment with political candidates, perceived ineffectiveness of voting, barriers to participation (such as complicated registration and limited access to polling), socioeconomic factors, and ballot fatigue.
How does disillusionment with political candidates contribute to voter apathy?
Many voters feel that candidates do not represent their interests, particularly younger constituents, leading to diminished motivation to participate in elections.
What role do structural barriers play in voter apathy?
Structural barriers, such as complicated registration processes and limited access to polling locations, can hinder electoral engagement, especially for labor participants who may face additional challenges due to work obligations.
How do socioeconomic factors influence voter participation?
Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often experience time constraints, financial instability, and a lack of access to information about the electoral process, which can contribute to lower turnout rates.
What is ballot fatigue, and how does it affect voter engagement?
Ballot fatigue is a sensation of overwhelm and detachment caused by the regularity of polls. It affects voter engagement, with 62% of American adults indicating they feel fatigued from voting, highlighting the need for organizations to rejuvenate interest among their members.
List of Sources
- Define Voter Apathy and Its Significance
- While Other Voters Moved Away From the Democrats, Union Members Shifted Toward Harris in 2024 (https://americanprogressaction.org/article/while-other-voters-moved-away-from-the-democrats-union-members-shifted-toward-harris-in-2024)
- (PDF) Voters Apathy During Students’ Union Elections: Implication for Social Studies and Political Science Students (https://researchgate.net/publication/388441065_Voters_Apathy_During_Students’_Union_Elections_Implication_for_Social_Studies_and_Political_Science_Students)
- Dive into abstentionism: understanding voter apathy (https://eligovoting.com/dive-into-abstentionism-understanding-voter-apathy)
- Identify Causes of Voter Apathy
- 16 million workers were unionized in 2024: Millions more want to join unions but couldn’t (https://epi.org/publication/millions-of-workers-millions-of-workers-want-to-join-unions-but-couldnt)
- Dive into abstentionism: understanding voter apathy (https://eligovoting.com/dive-into-abstentionism-understanding-voter-apathy)
- ‘Democracy isn’t working’: Many young adults believe voting is not important, AP-NORC poll finds (https://pbs.org/newshour/politics/democracy-isnt-working-many-young-adults-believe-voting-is-not-important-ap-norc-poll-finds)
- Combat Election Fatigue: Strategies for Union Leaders to Engage Voters | Online Voting with Votem® (https://votem.com/combat-election-fatigue-strategies-for-union-leaders-to-engage-voters)
- Examine Effects of Voter Apathy on Elections
- Voter Turnout – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/resources/voter-turnout)
- Voter turnout, 2020-2024 (https://pewresearch.org/politics/2025/06/26/voter-turnout-2020-2024)
- Voter turnout, 2018-2022 (https://pewresearch.org/politics/2023/07/12/voter-turnout-2018-2022)
- An Unsettled Electorate: How Uncertainty and Apathy Are Shaping the 2024 Election – The Survey Center on American Life (https://americansurveycenter.org/research/an-unsettled-electorate-how-uncertainty-and-apathy-are-shaping-the-2024-election)
- Differentiate Voter Apathy from Voter Suppression
- Growing Racial Disparities in Voter Turnout, 2008–2022 (https://brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/growing-racial-disparities-voter-turnout-2008-2022)
- Block the Vote: How Politicians are Trying to Block Voters from the Ballot Box | ACLU (https://aclu.org/news/civil-liberties/block-the-vote-voter-suppression-in-2020)
- Voter Apathy Definition, Causes & Effects – Lesson | Study.com (https://study.com/academy/lesson/voter-apathy-definition-statistics-causes.html)
- Dive into abstentionism: understanding voter apathy (https://eligovoting.com/dive-into-abstentionism-understanding-voter-apathy)
- Implement Strategies to Combat Voter Apathy
- 7 Strategies to Engage Union Voters Effectively | Online Voting with Votem® (https://votem.com/7-strategies-to-engage-union-voters-effectively)
- 10 Ways to Increase Voter Turnout in the United States | Online Voting with Votem® (https://votem.com/10-ways-to-increase-voter-turnout-in-the-united-states)
- Labor Unions and Voter Turnout in the American States: Direct Versus Indirect Mobilization | State Politics & Policy Quarterly | Cambridge Core (https://cambridge.org/core/journals/state-politics-and-policy-quarterly/article/labor-unions-and-voter-turnout-in-the-american-states-direct-versus-indirect-mobilization/110FC7786622554F273C83C25683CABD)
- The Power of Voter Engagement: Key Strategies for Success (https://callhub.io/blog/political-campaign/voter-engagement-strategies)
- Strong Unions Need Strongly Informed Voters and Turnout | Educators for Excellence (https://e4e.org/blog-news/blog/strong-unions-need-strongly-informed-voters-and-turnout)

