Overview
The D’Hondt method serves as a pivotal mathematical formula in proportional electoral systems, facilitating the allocation of legislative seats in accordance with the votes garnered by political parties. This mechanism not only champions equitable representation but also underscores the complexities inherent in electoral dynamics.
While it is acknowledged that the method tends to favor larger parties, it simultaneously creates opportunities for smaller parties to secure representation. This duality enhances the overall inclusiveness and stability of the electoral process across various countries.
Ultimately, understanding the D’Hondt method is essential for grasping the nuances of electoral representation and its impact on democratic governance.
Introduction
The D’Hondt method, a mathematical formula devised by Victor D’Hondt in the late 19th century, is pivotal in shaping electoral systems worldwide. By translating votes into legislative seats, this method enhances proportional representation, ensuring diverse political voices resonate within government. However, while it promotes inclusivity, it also raises critical questions about the balance of power, often favoring larger parties at the expense of smaller ones. This duality significantly impacts the democratic process, prompting us to reflect on the lessons learned from its application across various countries.
Define the D’Hondt Method and Its Purpose
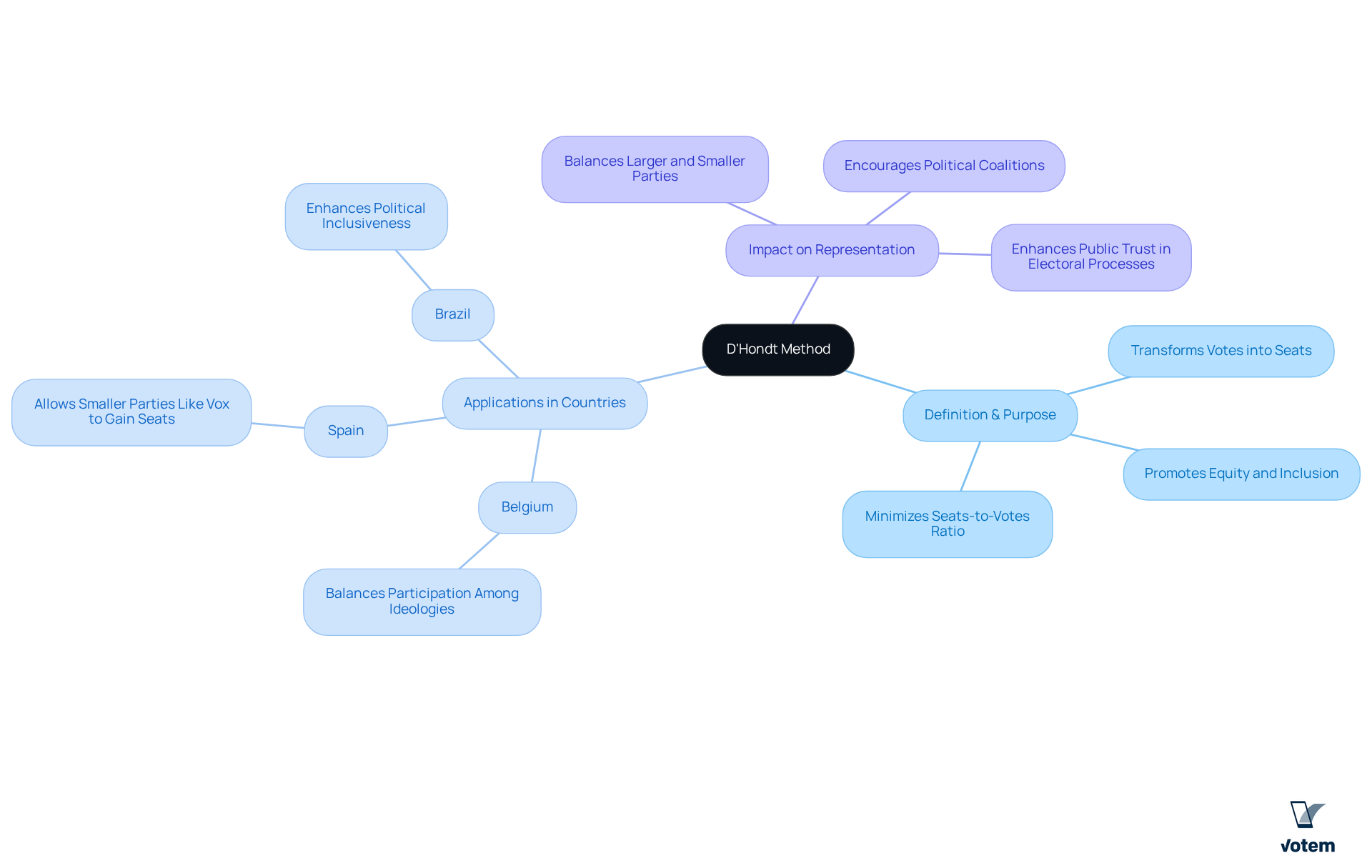
The d hondt method, created by Belgian attorney Victor D’Hondt in the late 19th century, serves as a crucial mathematical formula for the distribution of seats within proportional electoral frameworks. Its primary aim is to transform the votes garnered by political parties into a corresponding allocation of legislative seats through the d hondt method, thereby ensuring that this distribution accurately reflects each party’s overall vote share. The d hondt method promotes equity and inclusion within the electoral process by minimizing the largest seats-to-votes ratio and curbing political fragmentation, which proves especially beneficial in diverse political landscapes.
The practical applications of the d hondt method are evident in several countries, including Belgium, Spain, and Brazil, where it has been instrumental in advancing political inclusiveness. For instance, in Belgium, the d hondt method has successfully balanced participation among various political ideologies, enabling smaller groups, such as the Flemish Green Movement, to secure representation alongside larger factions. Similarly, in Spain, the d hondt method enables smaller parties like Vox to establish a presence while larger organizations maintain their influence.
Expert insights underscore the significance of the d hondt method in enhancing proportional representation. Although the d hondt method tends to favor larger parties, it still provides opportunities for smaller parties to gain seats, thus contributing to a more balanced electoral framework. The transparency of the d hondt method further , positioning it as a preferred choice for numerous electoral systems worldwide. Ongoing discussions and recent updates regarding the d hondt method continue to illuminate its role in fostering equitable outcomes, ensuring that electoral results genuinely reflect the will of the voters.
Contextualize the D’Hondt Method in Electoral Systems
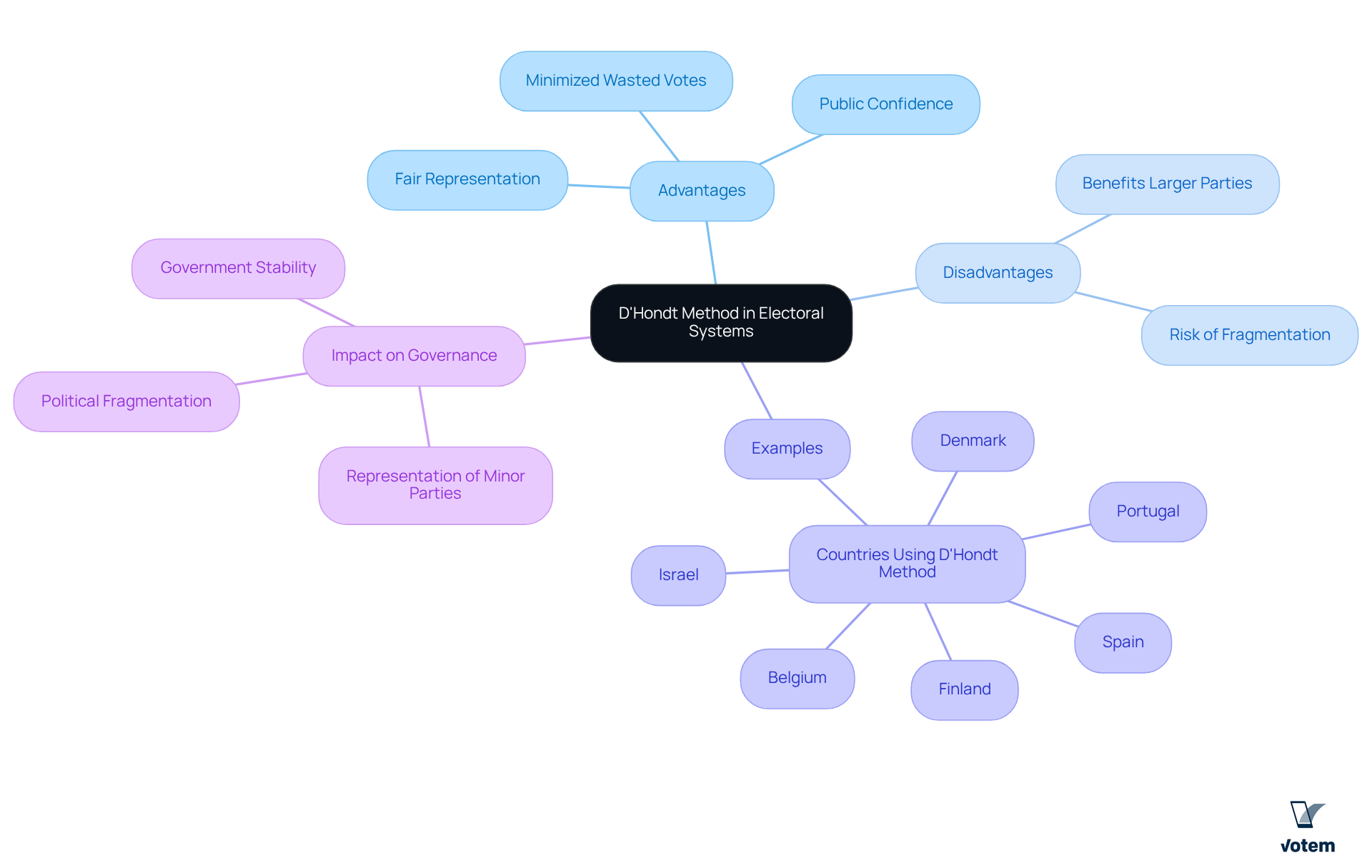
The proportional representation system, which utilizes the d Hondt method, is a fundamental aspect of electoral frameworks that aim to allocate seats based on the votes submitted by the electorate. This approach is particularly crucial in multi-party systems, as it guarantees fair chances for representation among smaller parties. Nations such as Belgium, Spain, Portugal, Denmark, Finland, and Israel exemplify the broad endorsement of the proportional representation system in their parliamentary elections. By systematically distributing seats, the d Hondt method not only contributes to government stability but also mitigates the risk of extreme political fragmentation, which can hinder effective governance.
Furthermore, the clear nature of this system promotes public confidence in electoral processes, making it a preferred option for many countries seeking to balance involvement among various political entities. As Victor observed, this systematic approach minimizes wasted votes, thereby enhancing the democratic process. However, it is essential to recognize that while this system fosters diversity, it often benefits larger parties, potentially disrupting the overall equilibrium in multi-party frameworks. This duality presents both that must be navigated by union leadership.
Trace the Historical Development of the D’Hondt Method
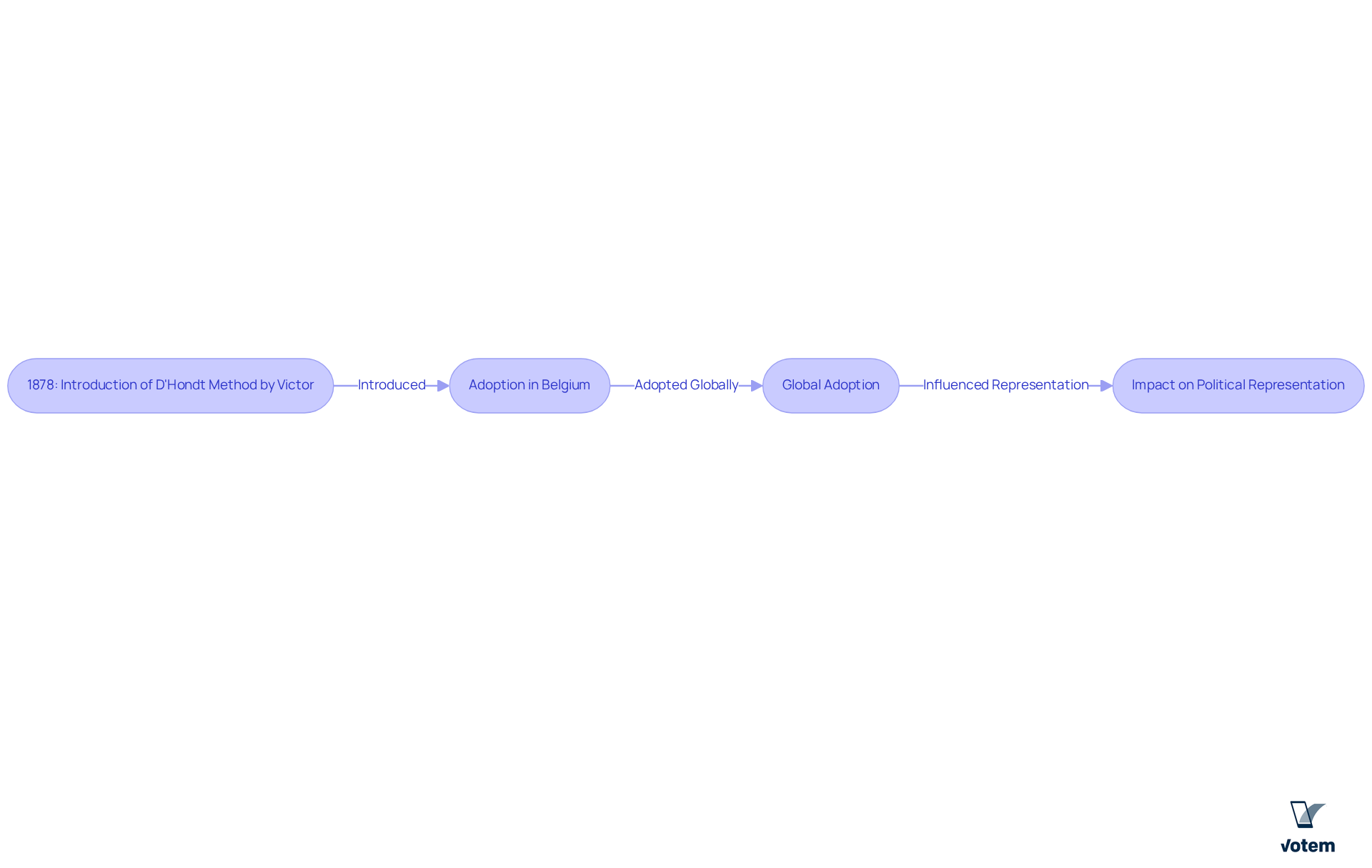
In 1878, Victor devised a system designed to provide a fair and effective mechanism for distributing parliamentary seats in Belgium. This within the Belgian parliament, addressing the complexities of inclusion in a multi-faceted society.
As nations worldwide transitioned to more democratic voting systems, this approach gained traction due to its mathematical simplicity and effectiveness in promoting proportional allocation. Its implementation across various countries has facilitated the inclusion of diverse political forces, significantly contributing to the evolution of electoral frameworks.
Notably, the approach’s ability to balance representation—while slightly favoring larger groups—has established it as a cornerstone in the development of contemporary democratic practices.
Examine Key Characteristics and Mechanics of the D’Hondt Method
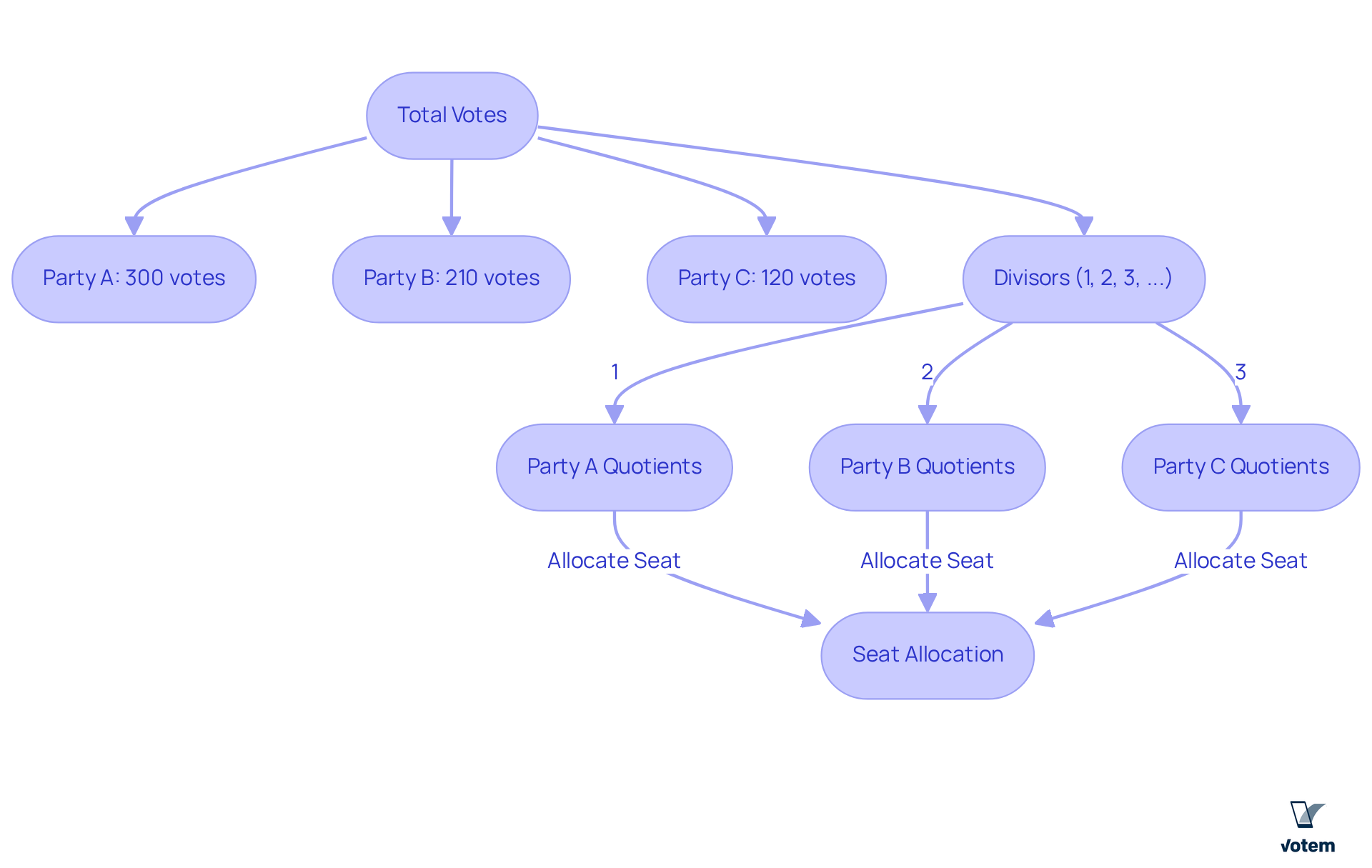
The d hondt method is a pivotal technique for assigning seats, achieved by dividing the total votes obtained by each group by a series of divisors (1, 2, 3, etc.). This generates quotients that determine seat distribution, continuing until all available seats are filled. Notably, this process tends to favor larger parties due to their higher vote totals. For instance, in a hypothetical election with 230,000 voters and 8 seats, if Party A receives 300 votes, Party B 210 votes, and Party C 120 votes, the allocation would reflect their respective quotients. Party A, possessing the greatest quotient, would secure the first seat, followed by Party B and then Party C, clearly demonstrating how the approach balances participation.
A significant feature of the d hondt method is its capacity to maintain a balance between proportional allocation and governmental stability. While it slightly favors larger groups, it still provides opportunities for smaller organizations to gain seats, contributing to a more inclusive political landscape. This balance is particularly evident in countries like Belgium, where smaller factions, such as the Flemish Green Party, successfully gain representation alongside dominant parties. Furthermore, the approach’s design reduces wasted votes compared to single-member plurality systems, ensuring that every vote contributes to the overall electoral outcome.
In practical applications, this voting system has been employed in various electoral frameworks globally, including the European Parliament and the Senedd elections in Wales. Its adaptability to secure online voting platforms, such as those offered by Votem, enhances transparency and public trust, making it a reliable choice for modern electoral processes. Votem’s mission to broaden access and strengthen confidence in elections aligns perfectly with the , ensuring that electoral processes are not only just but also accessible to all voters, including individuals with disabilities and military members.
Testimonials from clients highlight Votem’s impact:
- “Implementing Votem’s new, modern system which allowed greater access for all qualified voters from military voters to voters with disabilities was my greatest accomplishment in office.”
- “Votem successfully handled the receipt of 299,000 votes on behalf of the National Radio Hall of Fame, an increase over last year’s 126,000 votes received. Thank you for your efforts in every way!”
As the d hondt method continues to evolve, it remains a pivotal mechanism for achieving fair representation in diverse political environments.
Conclusion
The D’Hondt method serves as a cornerstone in the domain of electoral systems, offering a systematic approach to converting votes into legislative representation. This mathematical formula aims to ensure that seat distribution mirrors the diverse political landscape, fostering fairness and inclusivity in the electoral process.
Various aspects of the D’Hondt method have been examined, including its historical origins, practical applications across numerous countries, and its mechanics in seat allocation. While this method tends to favor larger parties, it simultaneously provides opportunities for smaller factions, contributing to balanced representation within multi-party systems. The transparency and efficiency of the D’Hondt method enhance public confidence in electoral outcomes, making it a preferred choice for many democracies globally.
Understanding the D’Hondt method is essential for grasping how electoral systems can accurately represent the electorate’s will. As nations continue to explore and refine their electoral frameworks, embracing methods like D’Hondt can pave the way for more equitable political environments. Engaging in discussions about electoral systems and advocating for fair representation empowers voters and enriches democratic processes, ensuring that every voice is acknowledged and counted.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the D’Hondt Method?
The D’Hondt Method is a mathematical formula developed by Belgian attorney Victor D’Hondt in the late 19th century, used for the distribution of seats in proportional electoral systems.
What is the purpose of the D’Hondt Method?
The primary purpose of the D’Hondt Method is to allocate legislative seats to political parties based on the votes they receive, ensuring that the distribution reflects each party’s overall vote share.
How does the D’Hondt Method promote equity in elections?
The D’Hondt Method promotes equity by minimizing the largest seats-to-votes ratio and reducing political fragmentation, which is particularly beneficial in diverse political environments.
In which countries is the D’Hondt Method used?
The D’Hondt Method is used in several countries, including Belgium, Spain, and Brazil, where it has helped enhance political inclusiveness.
Can you provide an example of the D’Hondt Method’s impact in Belgium?
In Belgium, the D’Hondt Method has facilitated balanced participation among various political ideologies, allowing smaller groups, such as the Flemish Green Movement, to gain representation alongside larger parties.
How does the D’Hondt Method function in Spain?
In Spain, the D’Hondt Method enables smaller parties like Vox to establish a presence in the legislature while still allowing larger organizations to maintain their influence.
Does the D’Hondt Method favor larger parties?
Yes, the D’Hondt Method tends to favor larger parties; however, it still provides opportunities for smaller parties to secure seats, contributing to a more balanced electoral framework.
Why is the transparency of the D’Hondt Method important?
The transparency of the D’Hondt Method enhances public confidence in electoral processes, making it a preferred choice for many electoral systems around the world.
Are there ongoing discussions about the D’Hondt Method?
Yes, there are ongoing discussions and updates regarding the D’Hondt Method that continue to highlight its role in fostering equitable electoral outcomes and ensuring that results reflect the voters’ will.
List of Sources
- Define the D’Hondt Method and Its Purpose
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method: Its Use in the Northern Ireland Assembly (https://niassembly.gov.uk/news-and-media/assembly-explained/understanding-the-dhondt-method-its-use-in-the-northern-ireland-assembly)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- D’Hondt method – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D’Hondt_method)
- Contextualize the D’Hondt Method in Electoral Systems
- D’Hondt formula | politics | Britannica (https://britannica.com/topic/dHondt-formula)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- D’Hondt method – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D’Hondt_method)
- Trace the Historical Development of the D’Hondt Method
- D’Hondt formula | politics | Britannica (https://britannica.com/topic/dHondt-formula)
- The D’Hondt Method and the scapegoat theory | Ideas for democracy (https://minsait.com/ideasfordemocracy/en/dhondt-method-and-scapegoat-theory)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- Examine Key Characteristics and Mechanics of the D’Hondt Method
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- Senedd election 2026: What is the D’Hondt formula and how does it work? (https://senedd.wales/senedd-now/senedd-blog/senedd-election-2026-what-is-the-d-hondt-formula-and-how-does-it-work)
- D’Hondt method – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D’Hondt_method)

