Overview
The article emphasizes the critical role of various voting systems in union elections, highlighting their importance in ensuring fair representation and active participation among union members. It details distinct voting methods, including plurality, majority, and ranked choice voting. Furthermore, it underscores the necessity of secure and compliant processes, alongside the adoption of technology to enhance accessibility and engagement in the electoral process. By understanding these systems, union leadership can foster a more inclusive and effective electoral environment.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of voting systems is essential for union leaders who aim to foster fair and effective electoral processes. Various methods are available—from plurality to ranked choice voting—each offering unique advantages and challenges that significantly impact member participation and representation.
How can union leaders navigate these complexities to ensure compliance, security, and inclusivity in their elections? This guide delves into the fundamental principles of voting systems, providing insights and strategies designed to empower unions in their electoral endeavors.
Explore the Fundamentals of Voting Systems
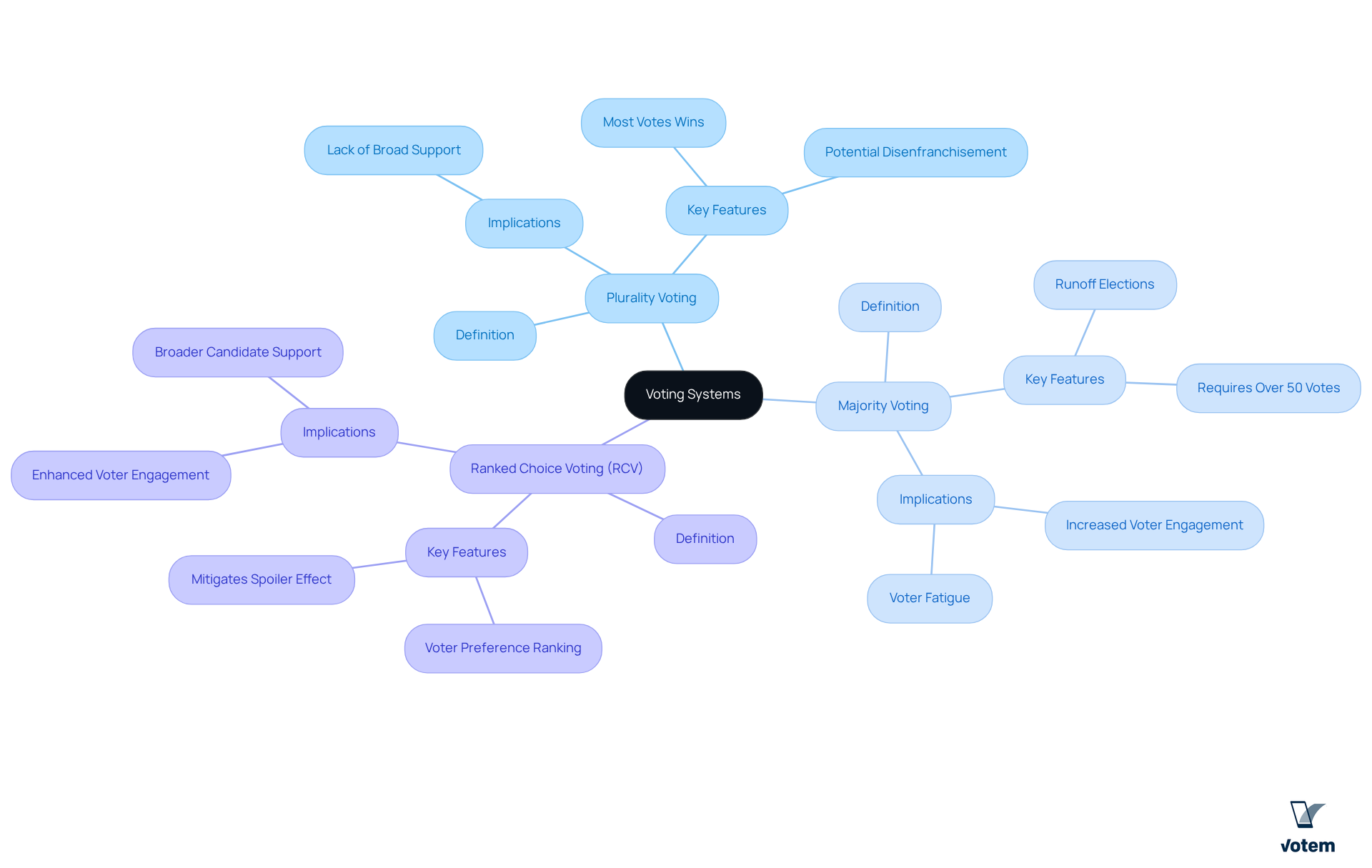
Voting systems serve as the foundational structures that dictate how votes are cast, counted, and ultimately transformed into electoral results. The primary types include:
- Plurality Voting: In this system, the candidate with the most votes wins, regardless of whether they achieve an outright majority. This method can lead to outcomes where a candidate wins without broad support, potentially disenfranchising a significant portion of the electorate.
- Majority Voting: This approach requires a candidate to secure more than 50% of the votes to win. If no candidate meets this threshold, runoff elections are often necessary. While these can , they may also lead to voter fatigue.
- Ranked Choice Voting (RCV): RCV allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference, facilitating a more nuanced expression of voter choice. This mechanism can mitigate the spoiler effect, where a candidate’s presence in the race detracts from the chances of a more broadly supported candidate.
Understanding these voting systems is crucial for union leaders as they choose the most effective methods for their elections. By doing so, they can ensure fair representation and enhance participation, ultimately fostering a more democratic process within their organizations.
Examine Voting Systems Relevant to Unions
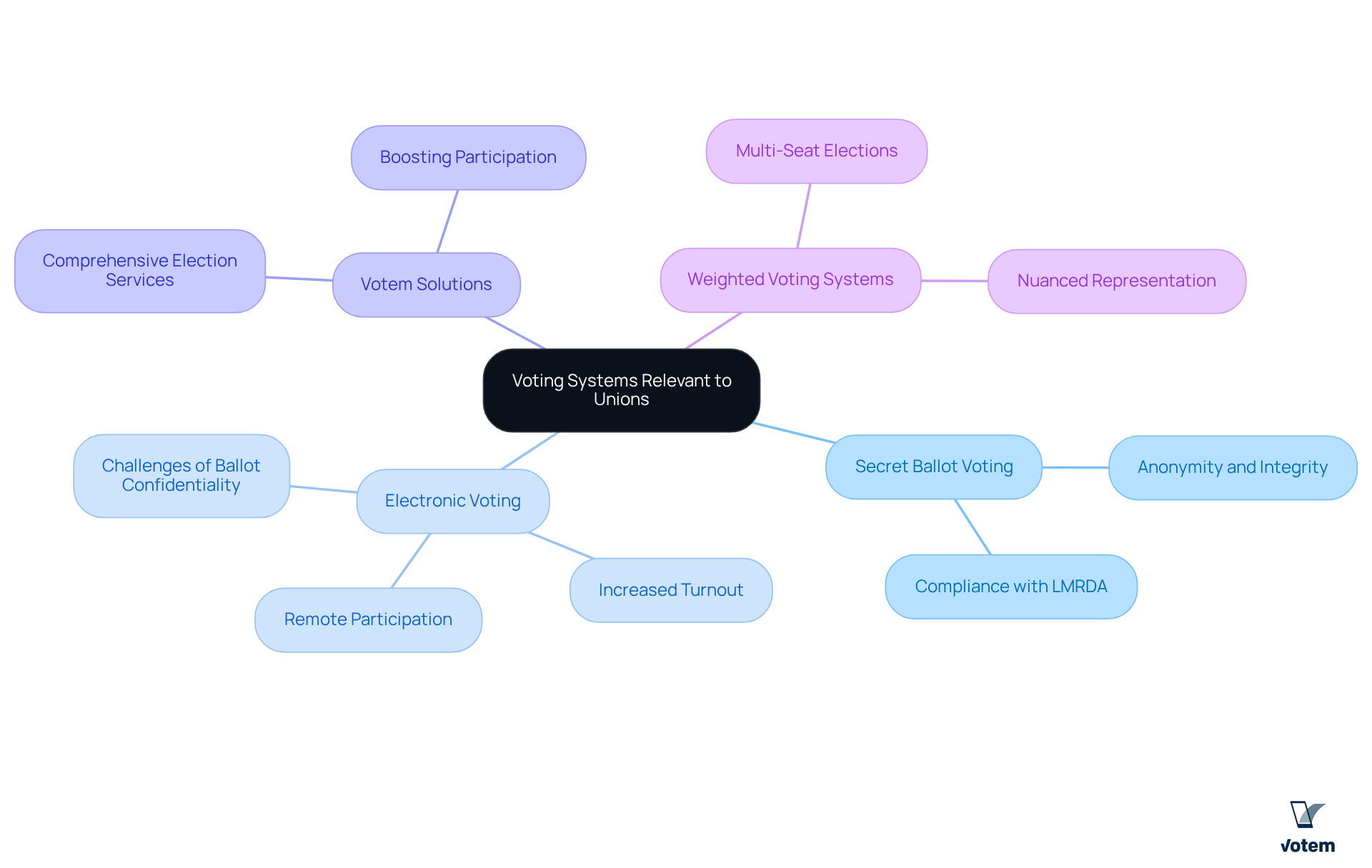
Unions frequently utilize specialized voting systems that are designed to meet their unique needs. Key systems include:
- Secret Ballot Voting: This method ensures voter anonymity, fostering a secure environment where members can express their preferences without fear of coercion. The Labor-Management Reporting and Disclosure Act (LMRDA) mandates secret ballots, reinforcing the integrity of the electoral process.
- Voting systems like electronic voting platforms are gaining traction due to their capacity to facilitate remote participation, significantly enhancing turnout and accessibility. Recent trends indicate that unions are increasingly adopting electronic voting systems, with organizations like the Teamsters planning to implement these voting systems for upcoming contract decisions, including the ABF contract selection expected to begin soon.
- Votem, a leader in internet-based ballot solutions, offers comprehensive election services that simplify the election process and strengthen voter confidence in voting systems. Their successful management of significant electoral events, such as handling 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, illustrates their capability to boost participation. Indeed, a clear majority of participants voted in the mail ballot on each of the last contracts for ABF, UPS Freight, and UPS, underscoring the effectiveness of these voting systems.
- This method of weighted voting systems is employed in scenarios where individuals possess different degrees of electoral influence, such as in multi-seat elections. It enables a more nuanced representation of stakeholder interests, ensuring that all voices are considered in decision-making.
While electronic ballot processes offer numerous advantages, it is crucial to address the challenges of preserving , as emphasized by the Office of Labor-Management Standards. By thoroughly understanding voting systems, union leaders can select approaches that not only comply with legal standards but also actively engage their members in electoral activities.
Implement Secure and Compliant Voting Processes
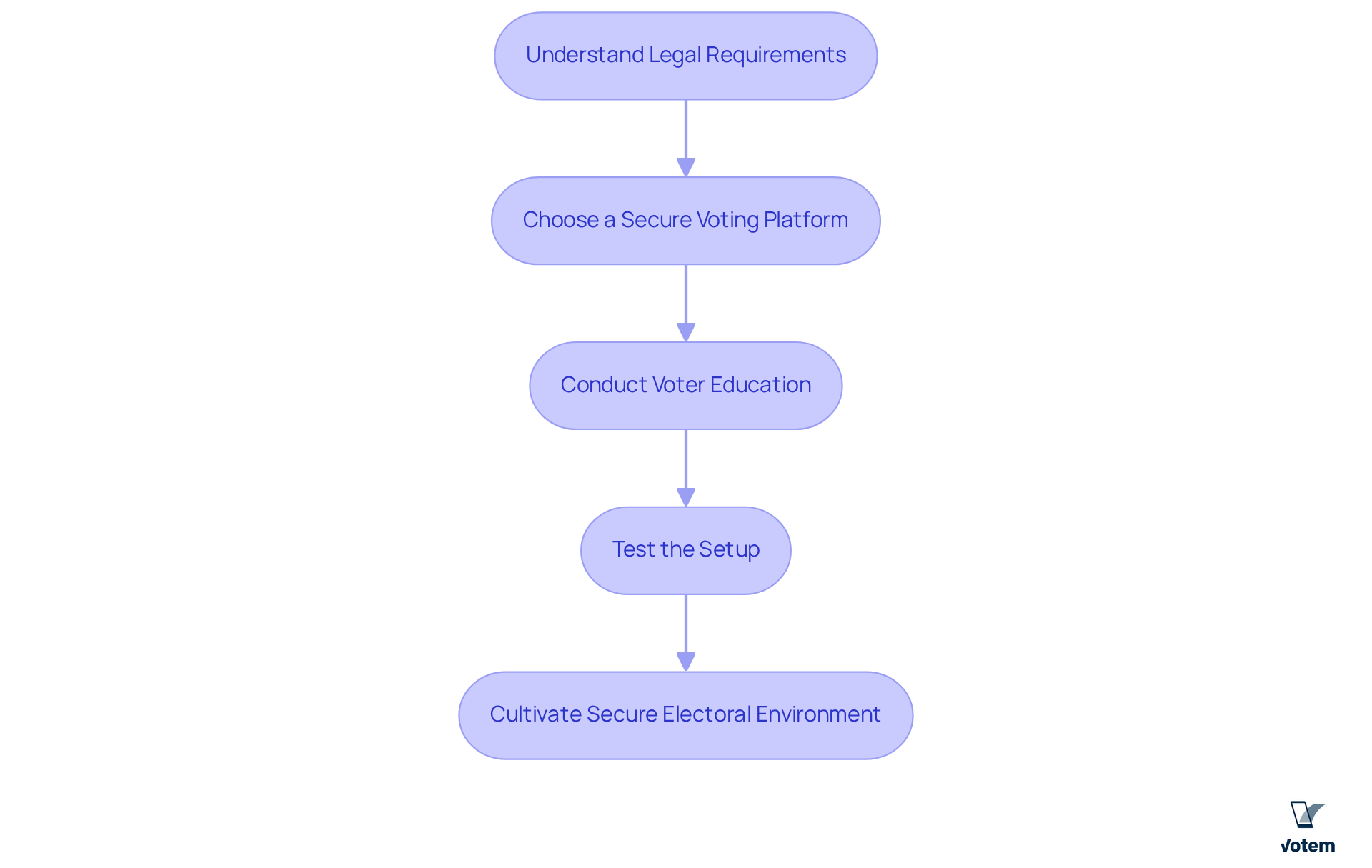
To establish secure and compliant voting processes, union leaders must take decisive steps:
- Understand Legal Requirements: Union leaders should familiarize themselves with the and other pertinent regulations governing union elections. This includes recognizing the necessity for confidential ballots and the rights of candidates to have observers present during both the election and tallying activities.
- Choose a Secure Voting Platform: It is essential to select platforms that utilize encryption technology to protect ballots both in transit and at rest. Ensure that the voting systems platform provides secure ballot storage, an immutable audit trail, and compliance with LMRDA standards, which mandate the preservation of all election records for at least one year.
- Conduct Voter Education: Informing members about the election system is crucial. Emphasize the security measures established to protect their voting systems. This transparency fosters trust and encourages participation, which is vital for a successful election.
- Test the Setup: Prior to the election, conduct a trial run of the voting mechanism to identify and resolve any potential issues. This practice not only guarantees system functionality but also allows observers to confirm the integrity of the procedure through test runs with practice ballots.
By adhering to these steps, unions can cultivate a secure electoral environment that promotes participation and supports effective voting systems while upholding democratic principles. Ultimately, this approach enhances the integrity of the election process.
Leverage Technology for Enhanced Voting Accessibility
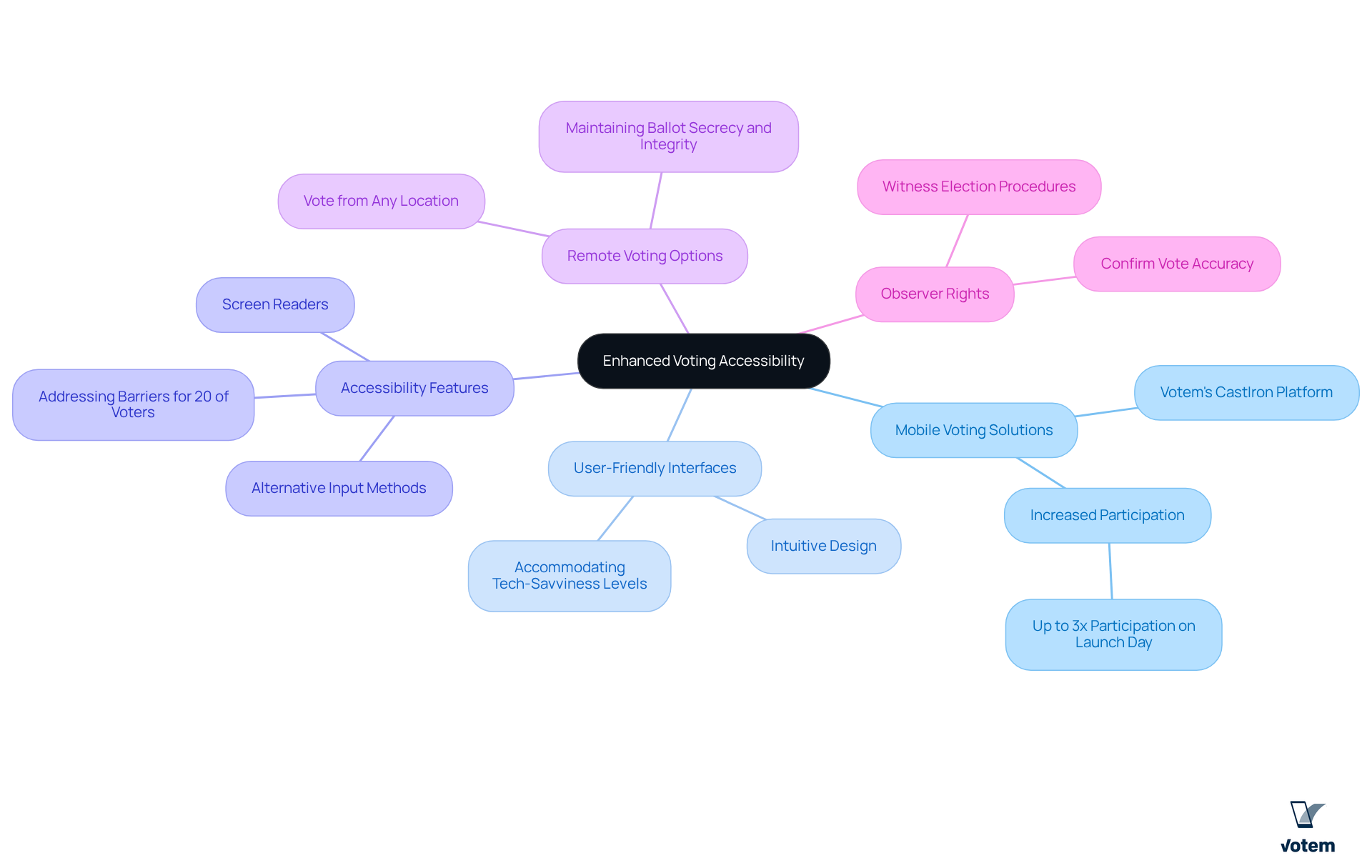
To enhance voting accessibility through technology, consider the following strategies:
- Mobile Voting Solutions: Implement Votem’s innovative CastIron platform, which enables members to vote via smartphones, significantly increasing convenience and participation. Research indicates that mobile-first balloting can increase participation by as much as three times on launch day, rendering it an essential resource for involving union participants.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Ensure that the platform is intuitive and easy to navigate, accommodating individuals of varying tech-savviness levels. Votem’s dedication to user-friendly design encourages participation, enabling everyone to engage without technological obstacles.
- Accessibility Features: Incorporate features that assist individuals with disabilities, such as screen readers and alternative input methods. Approximately 20 percent of potential U.S. voters face barriers to voting due to accessibility issues, highlighting the need for inclusive design in voting systems, a priority for Votem.
- Remote Voting Options: Enable participants to cast their votes from any location utilizing Votem’s secure and adaptable solutions, which are especially advantageous for individuals unable to attend face-to-face meetings. This flexibility not only enhances participation but also aligns with the requirements for maintaining ballot secrecy and integrity, as mandated by the LMRDA.
- Observer Rights: Ensure that participants have opportunities to witness aspects of the election procedure to confirm vote accuracy. Votem offers , which is crucial for establishing trust and adhering to legal obligations.
By leveraging Votem’s technology effectively and adhering to compliance standards, unions can create a more inclusive voting process that empowers all members to engage in their governance.
Conclusion
Mastering voting systems is crucial for union elections, as these frameworks dictate how members express their choices and how those choices translate into leadership and policy. By selecting the appropriate voting system, union leaders can significantly enhance democratic engagement, ensure fair representation, and foster a more inclusive environment within their organizations.
This article explored various voting systems, including plurality, majority, and ranked choice voting, each with unique implications for electoral outcomes. The emphasis on secure and compliant voting processes highlighted the necessity of legal adherence and the integration of technology to enhance accessibility. With advancements such as mobile voting solutions and user-friendly interfaces, unions can increase participation while maintaining the integrity of the electoral process.
The significance of adopting robust voting systems cannot be overstated. By prioritizing transparency, security, and accessibility, union leaders can empower their members, ensuring that every voice is heard and counted. As the landscape of voting continues to evolve, embracing these practices will be essential in shaping the future of union governance and engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are voting systems?
Voting systems are the foundational structures that dictate how votes are cast, counted, and transformed into electoral results.
What is Plurality Voting?
Plurality Voting is a system where the candidate with the most votes wins, regardless of whether they achieve an outright majority. This can result in a candidate winning without broad support, potentially disenfranchising a significant portion of the electorate.
How does Majority Voting work?
Majority Voting requires a candidate to secure more than 50% of the votes to win. If no candidate meets this threshold, runoff elections may be necessary. While this can increase voter engagement, it may also lead to voter fatigue.
What is Ranked Choice Voting (RCV)?
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference. This system facilitates a more nuanced expression of voter choice and can mitigate the spoiler effect, where a candidate’s presence detracts from the chances of a more broadly supported candidate.
Why is understanding voting systems important for union leaders?
Understanding these voting systems is crucial for union leaders as it helps them choose effective methods for their elections, ensuring fair representation and enhancing participation, which fosters a more democratic process within their organizations.
List of Sources
- Explore the Fundamentals of Voting Systems
- Jesuit Resource – Election Day Quotes (https://xavier.edu/jesuitresource/online-resources/quote-archive1/election-dayvoting)
- Voter Turnout – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/resources/voter-turnout)
- Ranked Choice Voting — Love Portland (https://loveportland.com/rcv-article-long)
- 45 Inspiring Quotes About Voting and Elections (https://shutterfly.com/ideas/inspiring-quotes-about-voting-and-elections)
- Examine Voting Systems Relevant to Unions
- IBT Intends to Use Electronic Voting on ABF and UPS Contracts (https://tdu.org/ibt_intends_to_use_electronic_voting_on_abf_and_ups_contracts)
- Electing Union Officers Using Remote Electronic Voting Systems (https://dol.gov/agencies/olms/compliance-assistance/tips/remote-electronic-voting-systems)
- allen.house.gov (https://allen.house.gov/news/documentsingle.aspx?DocumentID=5541)
- Implement Secure and Compliant Voting Processes
- Acting NLRB General Counsel Provides Guidelines for Expedited Union Elections | CDF Labor Law LLP (https://cdflaborlaw.com/blog/acting-nlrb-general-counsel-provides-guidelines-for-expedited-union-electio)
- Electing Union Officers Using Remote Electronic Voting Systems (https://dol.gov/agencies/olms/compliance-assistance/tips/remote-electronic-voting-systems)
- GAO-25-107297, LABOR ORGANIZATION OVERSIGHT: Department of Labor Should
Enhance Enforcement and Assistance Processes (https://files.gao.gov/reports/GAO-25-107297) - New union election rules yield much quicker elections – McAfee & Taft (https://mcafeetaft.com/new-union-election-rules-yield-much-quicker-elections)
- Leverage Technology for Enhanced Voting Accessibility
- Electing Union Officers Using Remote Electronic Voting Systems (https://dol.gov/agencies/olms/compliance-assistance/tips/remote-electronic-voting-systems)
- Jesuit Resource – Election Day Quotes (https://xavier.edu/jesuitresource/online-resources/quote-archive1/election-dayvoting)
- 45 Inspiring Quotes About Voting and Elections (https://shutterfly.com/ideas/inspiring-quotes-about-voting-and-elections)
- Innovations in Elections: Making Voting Accessible for Everyone (https://itif.org/events/innovations-elections-making-voting-accessible-everyone)
- ash.harvard.edu (https://ash.harvard.edu/articles/will-mobile-voting-defeat-gerrymandering-and-increase-participation)

