Overview
This article underscores best practices for union leaders concerning electoral systems, highlighting the critical importance of comprehending diverse voting methods to enhance representation and participation. By examining systems such as:
- First-Past-The-Post
- Proportional Representation
- Ranked Choice Voting
it illustrates their implications for voter engagement. Furthermore, it emphasizes the necessity for unions to actively advocate for fairer electoral reforms, ensuring that all members’ voices are effectively represented. This call to action is vital for union leadership as they navigate the complexities of electoral processes.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of electoral systems is crucial for union leaders who strive to ensure fair representation and advocate for their members’ interests. With a variety of systems in play—from First-Past-The-Post to Proportional Representation and Ranked Choice Voting—each presents unique challenges and opportunities that can significantly influence voter engagement and representation.
How can union leaders navigate these complexities to enhance participation and ensure their voices are heard in the political landscape? This article delves into best practices for mastering election systems, empowering union leaders to make informed decisions that foster democratic engagement and secure representation for all members.
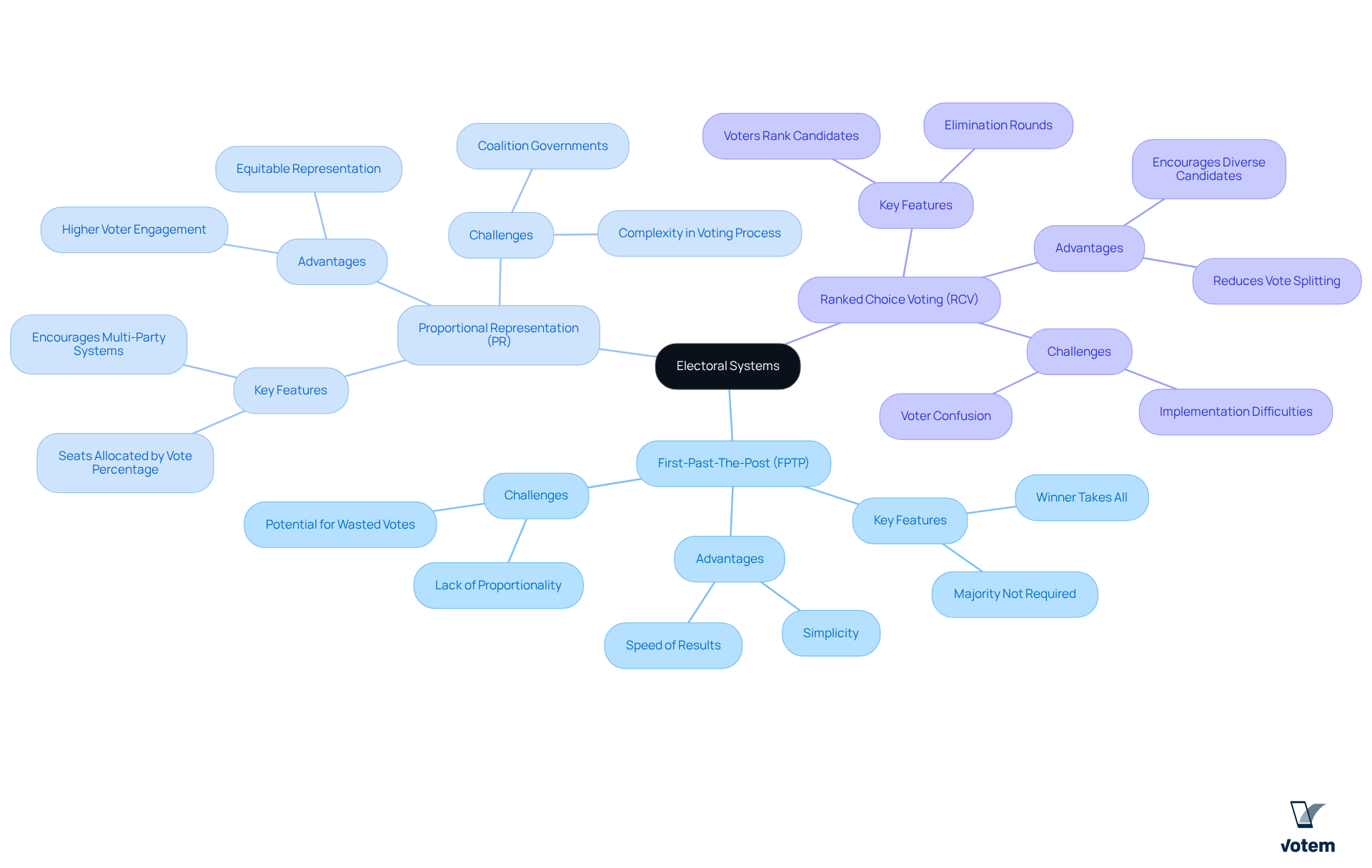
Explore the Fundamentals of Electoral Systems
Election systems serve as fundamental frameworks that dictate how votes translate into seats within legislatures or leadership positions in organizations. Understanding election systems is paramount for labor leaders, as they advocate for practices that align with their members’ interests and ensure fair representation.
The primary types of electoral systems include:
-
First-Past-The-Post (FPTP): In this system, the candidate with the most votes wins, often leading to a lack of proportional representation. This can result in situations where a candidate triumphs without securing a majority, exemplified by various elections where the winning candidate garnered less than half of the total votes cast.
-
Proportional Representation (PR): This system allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, thereby promoting equitable representation. Research indicates that nations employing PR systems consistently report higher electoral participation and greater civic engagement, as citizens perceive their involvement as having a direct impact on political outcomes.
-
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV): In this system, voters rank candidates in order of preference, which can alleviate the effects of vote-splitting. Evidence suggests that RCV can enhance participation in elections, increasing the likelihood of supporting minor candidates and fostering a more diverse candidate pool. For instance, in the 2021 New York City mayoral primary, 94% of respondents reported a solid understanding of RCV, underscoring the effectiveness of electoral education campaigns. However, challenges arose during the implementation of RCV in Santa Fe, NM, where a brief educational period for participants led to some confusion among the electorate.
The choice of election systems significantly influences union representation and participation, making it essential to consider the implications of each system thoughtfully. Furthermore, Votem’s innovative online voting solutions enhance accessibility, security, and transparency in polling processes, ensuring that they are auditable and safe. This advancement can further bolster electoral participation and confidence, as RCV has the potential to increase the number of candidates running for office, thereby diversifying the political landscape.
Examine Canada’s Electoral Systems and Their Implications
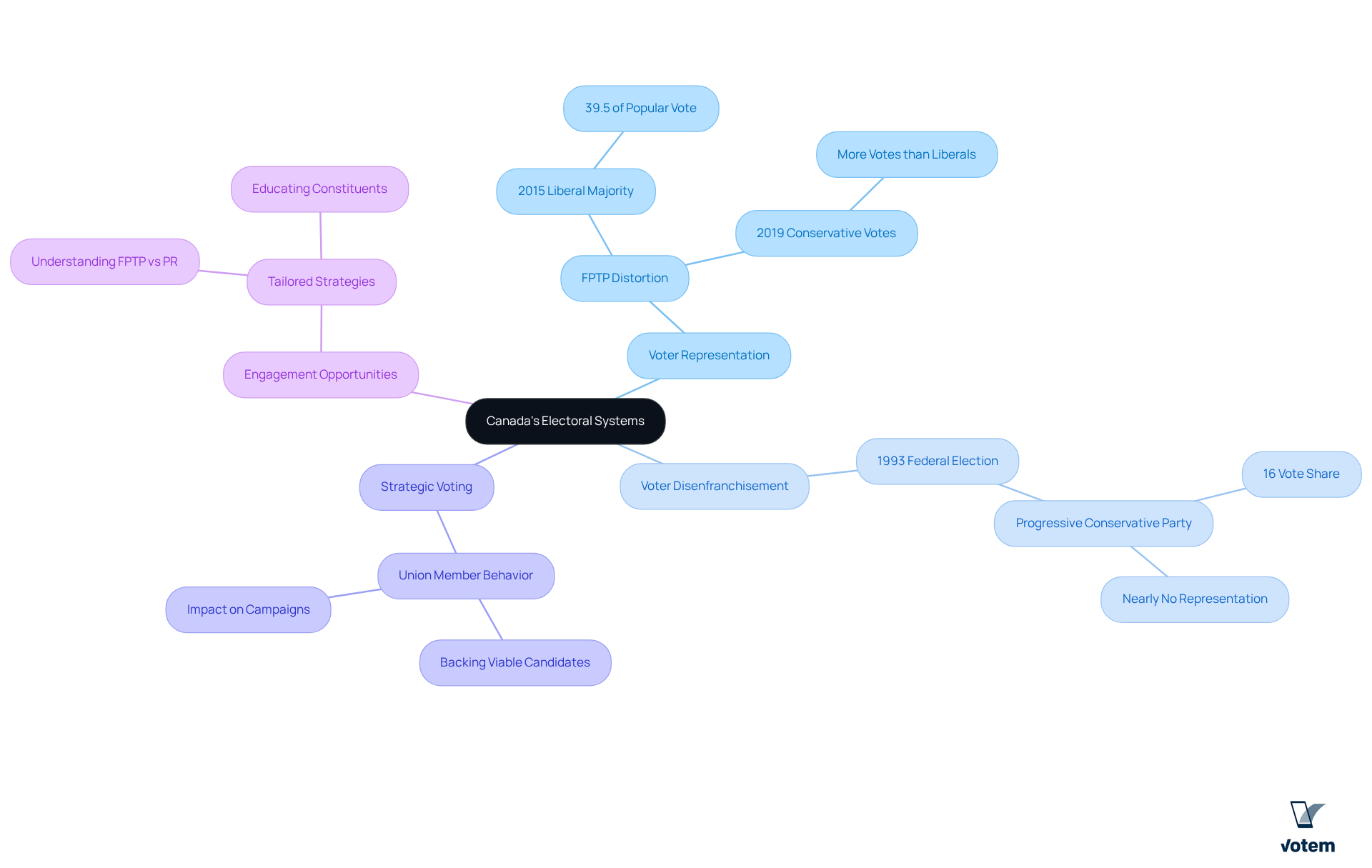
Canada’s electoral environment is characterized by a blend of systems, with First Past The Post (FPTP) dominating federal contests and various forms of proportional representation (PR) utilized at the provincial level. This duality carries several critical implications:
-
Voter Representation: FPTP frequently leads to a considerable disconnect between the percentage of votes received and the number of seats won. For example, in the 2015 federal election, the Liberal Party achieved a majority with only 39.5% of the popular vote, demonstrating how FPTP can distort representation and leave numerous voters feeling disenfranchised. This situation is particularly concerning for organizations, as unrepresented members may withdraw from the electoral process altogether.
-
Voter Disenfranchisement: The FPTP system can cause significant portions of the electorate to feel unrepresented, a challenge that organizations must address. The 1993 Canadian federal election serves as a case in point, where the Progressive Conservative Party’s vote share fell to 16%, resulting in nearly no parliamentary representation despite a substantial voter base. Such disenfranchisement can diminish collective influence and participant engagement.
-
Strategic Voting: Unions must acknowledge that members may resort to strategic voting to amplify their impact, often backing candidates they perceive as having a better chance of winning rather than their preferred choice. This behavior complicates collective campaigns and candidate endorsements, necessitating a nuanced understanding of the electoral dynamics at play.
-
Engagement Opportunities: The diversity of electoral systems across Canada allows labor organizations to tailor their engagement strategies effectively. By understanding the specific electoral environment—whether FPTP or PR—unions can better educate and motivate their constituents to participate in voting within different election systems, ensuring that their voices are heard.
Given these considerations, it is imperative for labor leaders to advocate for electoral reforms that promote fairer voting systems, enhancing representation and involvement for all members.
Implement Secure and Compliant Election Processes
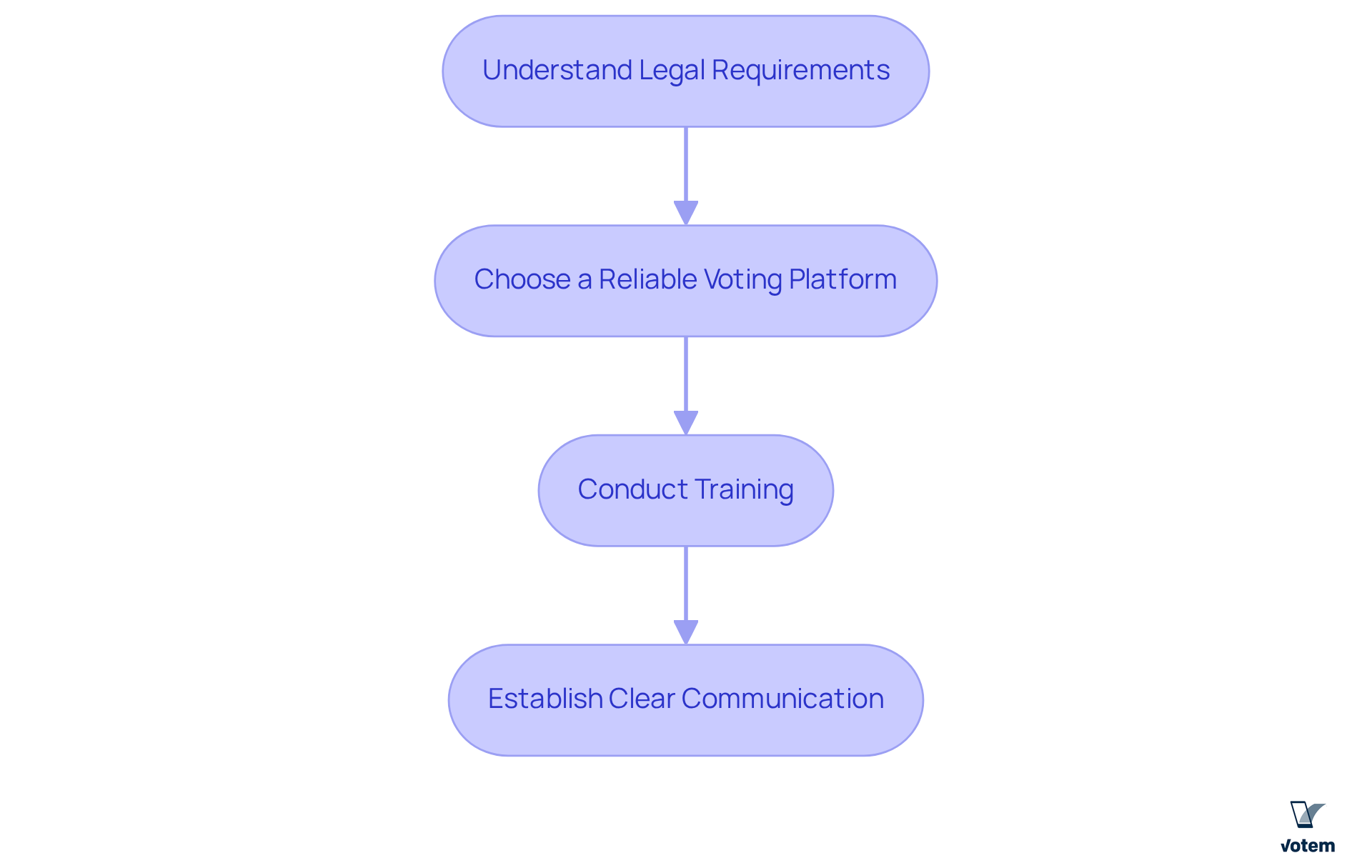
To implement secure and compliant election processes, union leaders must take decisive action:
-
Understand Legal Requirements: It is essential to familiarize yourself with the labor laws and regulations governing union voting, including mandates set forth by the NCUA, DOL, ERISA, and the Labor-Management Reporting and Disclosure Act (LMRDA). These regulations ensure that election systems operate fairly and transparently, safeguarding the rights of all participants. This includes the necessity for confidential ballots and robust protections in election systems to ensure equitable voting.
-
Choose a Reliable Voting Platform: Selecting a dependable platform, such as Votem’s CastIron, is crucial. This platform guarantees encrypted ballots and an immutable audit trail, enhancing security and ensuring compliance with legal standards. Votem’s innovative solutions have effectively managed significant voting events and election systems, including the receipt of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, demonstrating their capacity to handle large-scale voting processes. The platform’s encryption technology and detailed transaction logs are vital for maintaining voting integrity while ensuring accessibility for all qualified voters, including those with disabilities and military personnel.
-
Conduct Training: Providing comprehensive training for officials on compliance and security protocols is imperative. This approach minimizes risks and ensures that all personnel are well-versed in best practices, fostering a culture of accountability and integrity. Furthermore, maintaining documentation of security policies and procedures for election systems is essential for compliance and consistency.
-
Establish Clear Communication: Keeping participants informed about the voting process, regulations, and their rights is paramount. Clear communication builds trust and encourages involvement, which is vital for achieving successful voting outcomes. Informing members about voting security procedures enhances their understanding and confidence in the election systems. This is exemplified by the positive feedback from organizations that have utilized Votem’s services, such as the New Mexico State Republican Party, which expressed satisfaction with the performance of Votem software.
Enhance Voter Engagement and Turnout Strategies
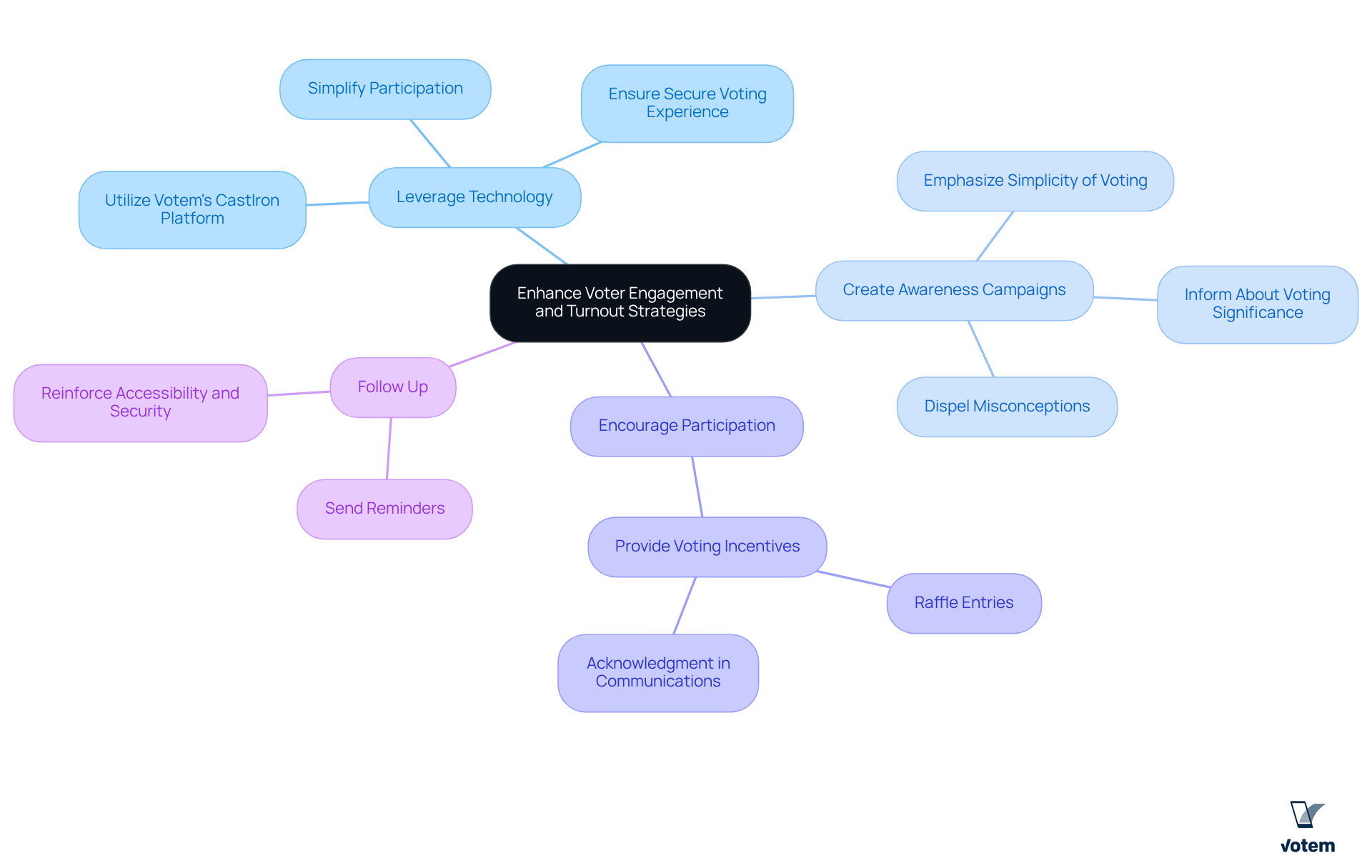
To enhance voter engagement and turnout, union leadership must consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize Votem’s CastIron platform, a mobile-first voting solution that simplifies participation and ensures a secure and trustworthy voting experience. This patented technology allows voters to engage easily and securely, meeting them where they are. By embracing modern solutions, unions can significantly improve participation rates.
-
Create Awareness Campaigns: Develop campaigns that inform individuals about the significance of their vote and how it influences their rights and working conditions. Emphasizing the simplicity of voting through Votem’s innovative solutions can help dispel misconceptions and motivate individuals to take action.
-
Encourage Participation: Consider providing rewards for voting, such as entry into a raffle or acknowledgment in organizational communications. These incentives can effectively motivate individuals to engage with the voting process, fostering a culture of participation within the union.
-
Follow Up: Use reminders and follow-up communications to encourage members to vote as election day approaches. Reinforcing the accessibility and security of the voting process with Votem’s platform can alleviate any concerns and prompt action.
By integrating these strategies, unions can enhance voter participation and strengthen democratic engagement within their organizations.
Conclusion
Understanding electoral systems is crucial for union leaders who aim to advocate effectively for their members and ensure fair representation. By mastering the intricacies of various electoral frameworks—such as First-Past-The-Post, Proportional Representation, and Ranked Choice Voting—leaders can navigate the complexities of political engagement and representation within their organizations with greater efficacy.
Throughout this article, key insights into the implications of Canada’s electoral systems have been provided, highlighting issues such as voter disenfranchisement and the importance of strategic voting. The necessity of secure and compliant election processes has been underscored, with actionable steps outlined to ensure transparency and integrity in voting. Furthermore, innovative strategies to enhance voter engagement and turnout have been emphasized, particularly through the use of technology and awareness campaigns.
Ultimately, the significance of adopting best practices in electoral systems cannot be overstated. Union leaders are called to champion reforms that promote equitable representation and foster active participation among members. By embracing these practices, unions can empower their constituents, enhance democratic engagement, and create a more inclusive political landscape that truly reflects the voices of all members.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of electoral systems?
Electoral systems serve as frameworks that dictate how votes are translated into seats within legislatures or leadership positions, ensuring fair representation and aligning with the interests of members.
What are the primary types of electoral systems?
The primary types of electoral systems include First-Past-The-Post (FPTP), Proportional Representation (PR), and Ranked Choice Voting (RCV).
How does the First-Past-The-Post (FPTP) system work?
In the FPTP system, the candidate with the most votes wins, which can lead to a lack of proportional representation and situations where a candidate wins without securing a majority of the votes.
What are the advantages of Proportional Representation (PR)?
PR allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, promoting equitable representation and leading to higher electoral participation and civic engagement.
What is Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) and its benefits?
RCV allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference, which can reduce vote-splitting and increase participation by supporting minor candidates, fostering a more diverse candidate pool.
What challenges have been associated with Ranked Choice Voting?
Challenges with RCV include confusion among voters during implementation, as seen in Santa Fe, NM, where a brief educational period led to misunderstandings.
How do electoral systems impact union representation and participation?
The choice of electoral systems significantly influences union representation and participation, making it essential to consider the implications of each system carefully.
What advancements are being made to enhance the electoral process?
Votem’s online voting solutions aim to improve accessibility, security, and transparency in polling processes, which can increase electoral participation and confidence.
List of Sources
- Explore the Fundamentals of Electoral Systems
- Proportional Representation: Boosting Voter Turnout and Strengthening Democracy – Protect Democracy (https://protectdemocracy.org/work/proportional-representation-voter-turnout)
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- 4.6 Chapter Summary – Elections: Process & Performance (https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/electionsprocessandperformance/chapter/4-6-chapter-summary)
- Examine Canada’s Electoral Systems and Their Implications
- First Past the Post has played havoc with Canadian federal elections (https://electoral-reform.org.uk/first-past-the-post-has-played-havoc-with-canadian-federal-elections)
- Implement Secure and Compliant Election Processes
- 16 million workers were unionized in 2024: Millions more want to join unions but couldn’t (https://epi.org/publication/millions-of-workers-millions-of-workers-want-to-join-unions-but-couldnt)
- Checklist for Conducting Local Union Officer Elections (https://dol.gov/agencies/olms/compliance-assistance/elections/checklist)
- Electing Union Officers Using Remote Electronic Voting Systems (https://dol.gov/agencies/olms/compliance-assistance/tips/remote-electronic-voting-systems)
- Enhance Voter Engagement and Turnout Strategies
- West Virginia was the first state to use mobile voting. Should others follow? (https://news.uchicago.edu/story/voting-mobile-devices-increases-election-turnout)
- Voter Turnout Database | International IDEA (https://idea.int/data-tools/data/voter-turnout-database)
- The Varied Voice of Labor: Unpacking the Political Engagement of Labor in the 2024 Election – Center for Labor and a Just Economy (https://clje.law.harvard.edu/the-varied-voice-of-labor-unpacking-the-political-engagement-of-labor-in-the-2024-election)
- Service Employees International Union (SEIU) (https://seiu.org/2024/03/workers-ready-to-make-decisive-impact-in-2024-elections)

