Overview
Ranked-choice voting (RCV) stands to significantly enhance union elections and member engagement. By allowing voters to express their preferences more fully, RCV fosters a more inclusive and representative electoral process. This article underscores the importance of RCV by presenting compelling evidence: it not only boosts voter turnout—alleviating the fear of ‘wasting’ a vote—but also encourages a diverse array of candidates. The result is more democratic outcomes and increased member satisfaction within unions.
Furthermore, the implementation of RCV can transform the electoral landscape for unions. Imagine a system where every vote counts, and the fear of splitting the vote is eliminated. This shift not only empowers voters but also enriches the democratic process, leading to a broader representation of voices within unions. In addition, by attracting a wider range of candidates, RCV can invigorate union leadership, making it more reflective of its membership.
In conclusion, adopting ranked-choice voting is not merely a procedural change; it is a strategic move towards revitalizing union elections. Union leadership should consider this approach seriously, as it promises to enhance engagement, satisfaction, and ultimately, the democratic integrity of union representation. The time to act is now—embrace RCV for a stronger, more inclusive future.
Introduction
Ranked-choice voting (RCV) is not merely a reform; it stands as a powerful tool capable of reshaping the landscape of union elections. By allowing voters to rank candidates based on their preferences, RCV mitigates the risks of vote-splitting and encourages a diverse array of candidates to participate. Ultimately, this leads to elections that genuinely reflect the collective will of the membership. However, a critical question arises: how can unions effectively implement this transformative voting system to maximize participation and ensure that every voice is heard?
Define Ranked-Choice Voting and Its Importance
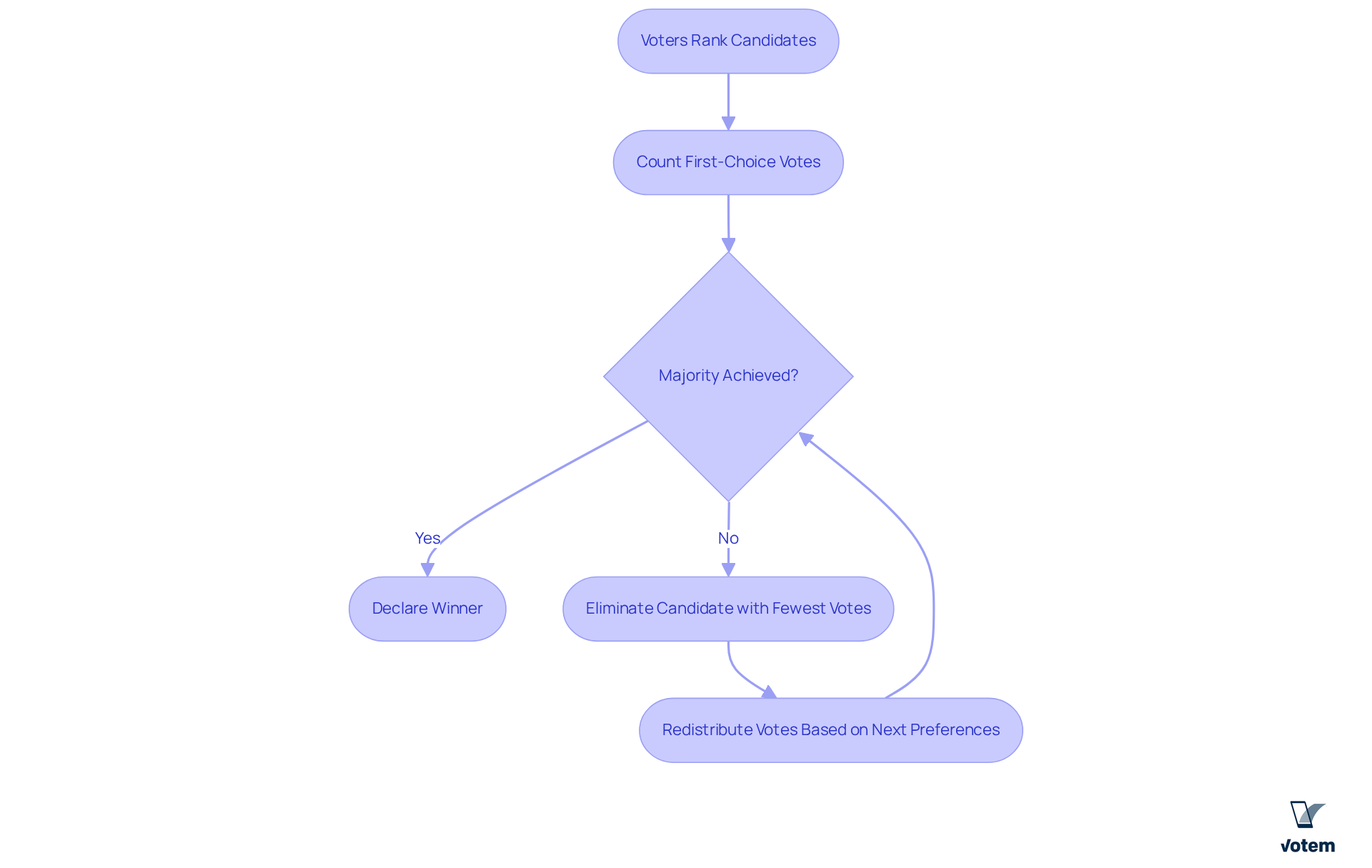
Rank based voting represents a transformative electoral system that allows voters to rank candidates based on their preferences rather than selecting just one. This method ensures that if no candidate secures a majority of first-choice votes, the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated, and their votes are redistributed according to the subsequent preferences expressed. This process continues until a candidate achieves a majority, leading to a more representative outcome. RCV effectively reduces the risk of vote-splitting and encourages a diverse range of candidates to enter the race, broadening their appeal to voters.
For unions, embracing rank based voting can significantly enhance member engagement and strengthen the democratic process in leadership elections. By creating a more inclusive atmosphere, RCV empowers members to articulate their preferences more completely, resulting in elections that genuinely reflect the collective will of the membership. Case studies, such as the successful implementation of RCV in New York City, reveal that 96% of participants found the system straightforward and accessible, with 76% expressing a desire to maintain or expand its use. This high level of satisfaction indicates that RCV not only simplifies the voting process but also increases participation and trust in the electoral system.
Moreover, RCV has been shown to elevate voter turnout in elections, as evidenced by its application in various regions across the United States, where 13 million individuals currently utilize this system. The bipartisan backing for rank based voting, underscored by an increasing number of bills advocating for its adoption, highlights its potential to revolutionize union elections into more democratic and engaging processes. By adopting RCV and utilizing Votem’s innovative CastIron platform—featuring secure, user-friendly tools like real-time vote tracking and robust encryption—unions can ensure that their leadership accurately reflects the true preferences of their members, ultimately fostering stronger representation and a more vibrant organizational culture.
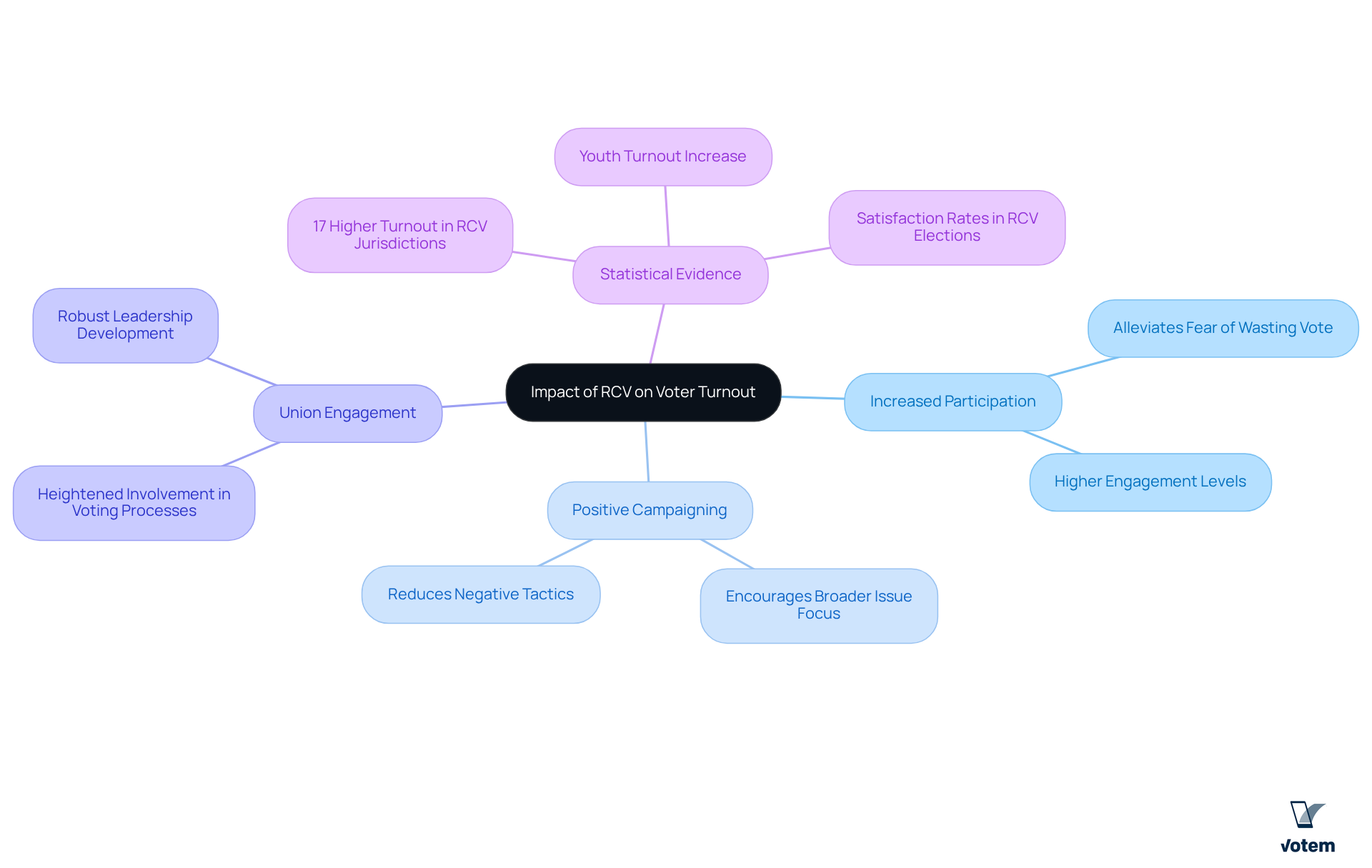
Explore the Impact of RCV on Voter Turnout and Engagement
Research indicates that rank based voting can significantly enhance voter participation by allowing individuals to express their preferences more freely. This system alleviates the fear of wasting a vote, as voters can participate in rank based voting by ranking multiple candidates without the pressure of selecting only one. Such inclusivity fosters higher engagement levels, making members feel their voices are heard and valued.
Furthermore, RCV encourages campaigns to prioritize broader issues over negative tactics, cultivating a more positive electoral atmosphere. Unions that adopt RCV may witness heightened involvement in voting processes, leading to more robust leadership and greater representative decision-making.
In fact, studies indicate that individuals in RCV jurisdictions are 17% more likely to turn out for municipal elections compared to those in non-RCV areas. This underscores the potential of RCV to invigorate union elections and enhance member involvement.
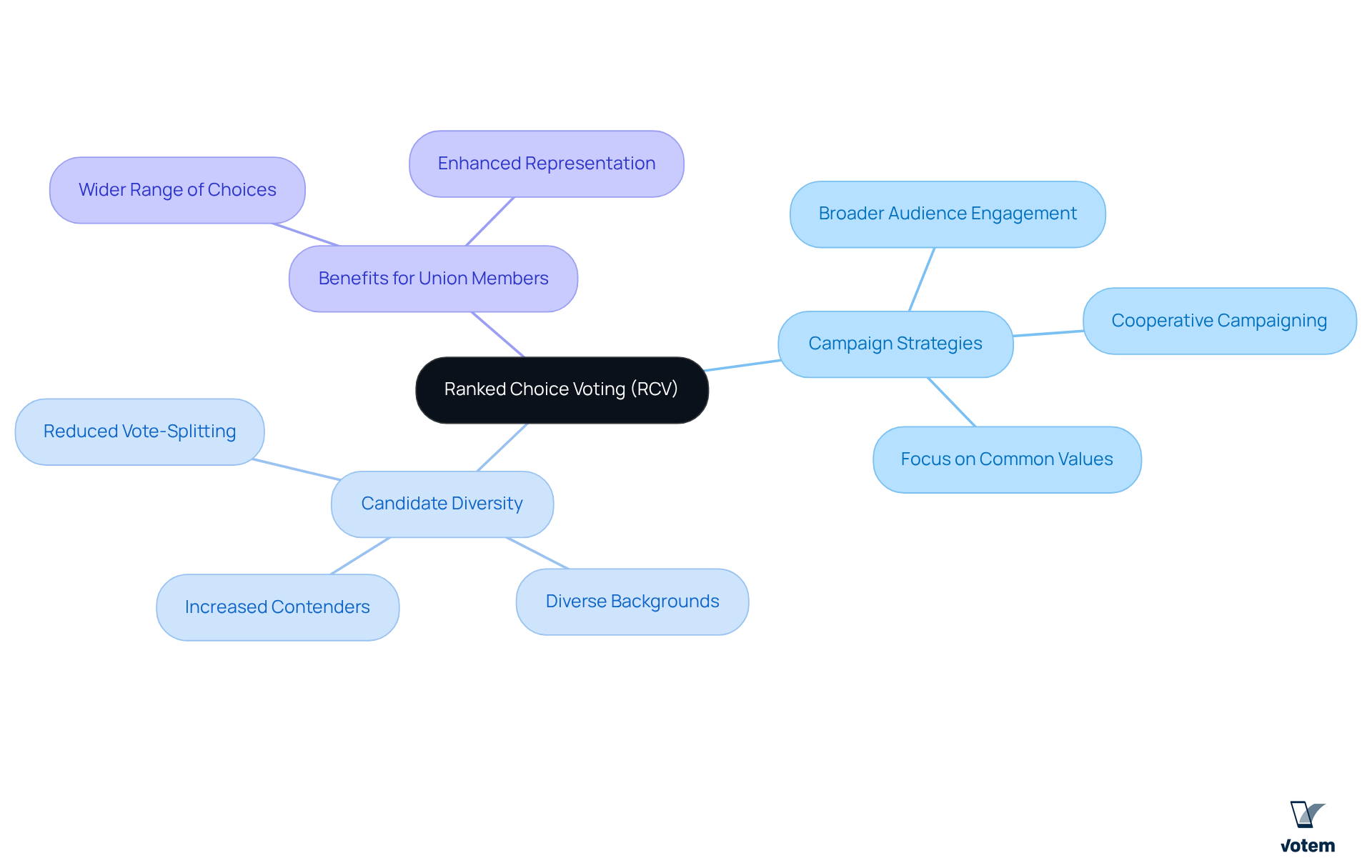
Analyze How RCV Influences Campaign Strategies and Candidate Diversity
Rank based voting fundamentally reshapes campaign strategies by compelling contenders to engage a broader audience. Candidates must attract not only their core supporters but also those who may prefer other contenders, fostering a more cooperative campaigning environment. This shift encourages applicants to concentrate on common values and concerns, aligning with the principles of rank based voting, rather than resorting to divisive tactics.
Furthermore, rank based voting enhances participant diversity by allowing more individuals to enter the race without the fear of vote-splitting, which creates a more inclusive electoral landscape. For instance, in Minneapolis, the implementation of RCV led to a notable increase in the number of contenders, particularly from diverse backgrounds, reflecting a richer array of perspectives.
This inclusivity ultimately benefits union members by providing them with a wider range of choices that align with their values and needs. Research shows that individuals from racial and ethnic minority groups have a greater chance of participating in rank based voting contests, leading to a more representative political atmosphere.
As a result, RCV not only promotes a more civil discourse among candidates but also enhances the overall democratic process within unions, ensuring that diverse voices are heard and represented.
Implement RCV in Union Elections: A Step-by-Step Guide
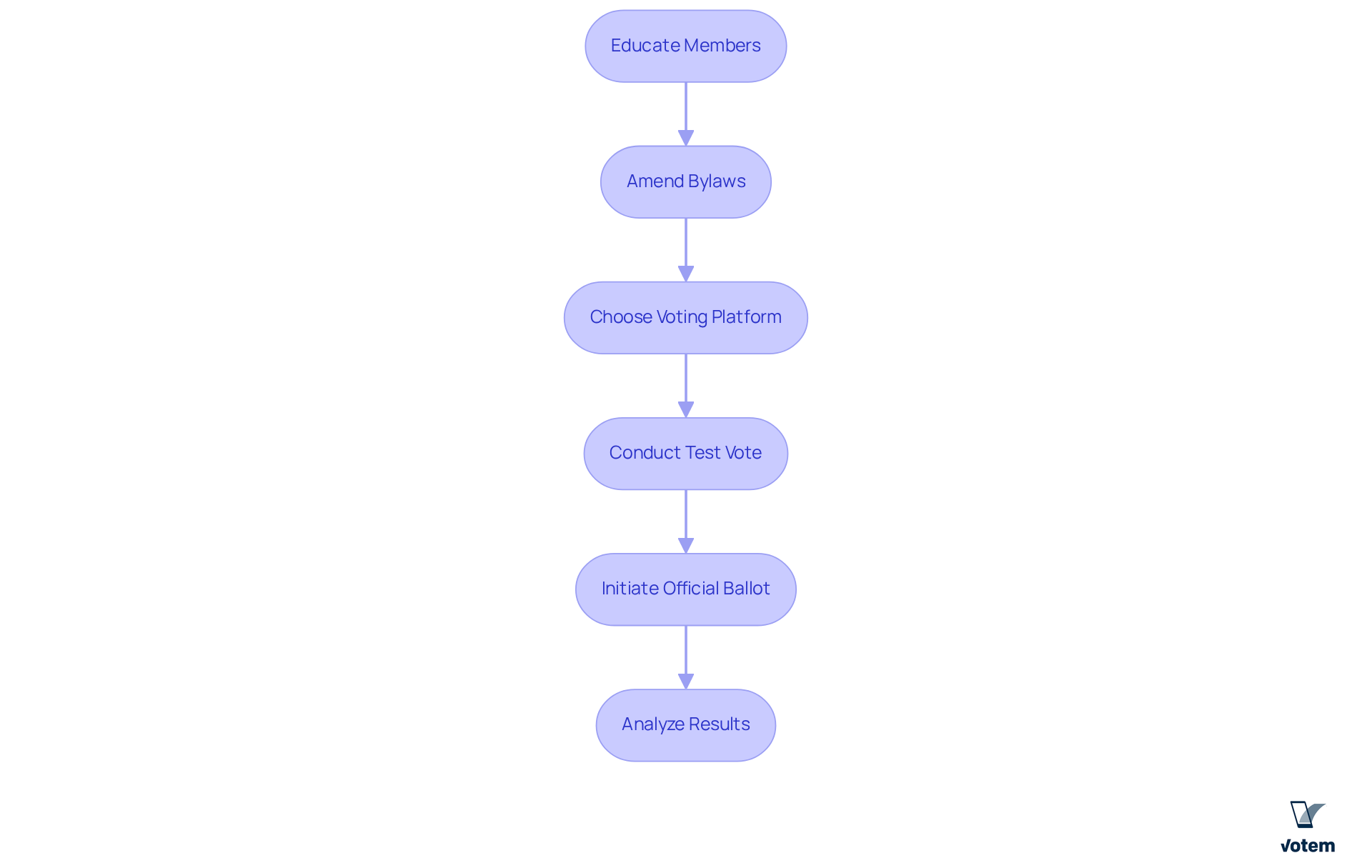
Implementing rank based voting in union elections requires a strategic approach that encompasses several essential steps.
-
It is crucial to educate members about rank based voting, highlighting its advantages and operational mechanics. Organizing workshops or informational sessions can effectively address questions and alleviate concerns. Research indicates that providing election education materials significantly enhances comprehension and utilization of rank based voting ballots, which is vital for maximizing the effectiveness of rank based voting.
-
Next, review and amend union bylaws to integrate RCV, ensuring compliance with relevant labor laws and regulations. This step is imperative to align the new voting method with existing governance structures, thereby reinforcing the union’s commitment to democratic practices.
-
Choosing a secure voting platform is another critical step. Opt for an online voting solution, such as Votem’s CastIron, which supports RCV and adheres to compliance requirements. Votem’s innovative system enhances accessibility for all eligible participants, including military personnel and individuals with disabilities, ensuring that every voice is heard. A testimonial underscores this achievement: “Implementing Votem’s new, modern system which allowed greater access for all qualified voters from military voters to voters with disabilities was my greatest accomplishment in office.”
-
Before the official vote, conducting a test vote using RCV is advisable. This practice familiarizes members with the process and identifies potential issues, helping to build confidence in the new voting method.
-
Once members are comfortable with RCV, initiate the official ballot. Ensure all members have access to the voting platform and understand how to rank their choices. Notably, rank based voting (RCV) has been linked to a 10-point increase in participation compared to conventional polls, making it an appealing option for unions. Votem has demonstrated its capability in managing large-scale voting events, such as the National Radio Hall of Fame, where they oversaw 299,000 votes, showcasing their ability to boost voter participation. A testimonial reflects this success: “Votem successfully handled the receipt of 299,000 votes on behalf of the National Radio Hall of Fame, an increase over last years’ 126,000 votes received. Thank you for your efforts in every way!”
-
After the vote, it is essential to analyze the results to assess RCV’s effectiveness in enhancing engagement and turnout. Collect feedback from members to refine future elections. For instance, in New York City, 95% of voters found RCV simple, indicating a positive reception that can encourage further adoption.
By adhering to these steps, unions can effectively implement rank based voting, which fosters a more democratic and engaging electoral process.
Conclusion
Ranked-choice voting (RCV) stands as a pivotal advancement in electoral systems, particularly for unions striving to elevate member engagement and democratize their leadership elections. By empowering voters to rank candidates based on their preferences, RCV ensures that elected representatives genuinely reflect the collective will of the membership, thereby fostering a more inclusive and participatory electoral process.
Key insights throughout this discussion underscore the significance of RCV in:
- Mitigating vote-splitting
- Boosting voter turnout
- Cultivating a more diverse candidate pool
The positive ramifications of RCV are evidenced by various case studies, which illustrate its capacity to streamline the voting process and enhance member satisfaction. Furthermore, the implementation of RCV can invigorate campaigns, prompting candidates to concentrate on shared values and engage a broader audience, ultimately contributing to a more civil and representative electoral environment.
The adoption of ranked-choice voting transcends mere procedural change; it represents a transformative stride toward a more engaged and representative union culture. As unions contemplate the implementation of RCV, they are encouraged to embrace this innovative voting method, ensuring that every member’s voice is heard and valued. By taking decisive action now, unions can pave the way for a more vibrant democratic process, fostering stronger leadership and a deeper connection among members.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ranked-choice voting (RCV)?
Ranked-choice voting is an electoral system that allows voters to rank candidates based on their preferences instead of selecting just one. If no candidate receives a majority of first-choice votes, the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated, and their votes are redistributed according to the voters’ subsequent preferences until a candidate achieves a majority.
Why is ranked-choice voting important?
RCV is important because it reduces the risk of vote-splitting, encourages a diverse range of candidates to enter the race, and leads to more representative outcomes. It also enhances member engagement in union elections and reflects the collective will of the membership.
How does ranked-choice voting benefit unions?
RCV enhances member engagement and strengthens the democratic process in union leadership elections by allowing members to express their preferences more completely, resulting in elections that better reflect the membership’s desires.
What evidence supports the effectiveness of ranked-choice voting?
Case studies, such as the implementation of RCV in New York City, show that 96% of participants found the system straightforward and accessible, and 76% wanted to maintain or expand its use. Furthermore, RCV has been linked to elevated voter turnout in various regions across the United States.
How many people currently use ranked-choice voting in the United States?
Currently, 13 million individuals in the United States utilize ranked-choice voting.
What technological platform can unions use to implement ranked-choice voting?
Unions can use Votem’s innovative CastIron platform, which features secure, user-friendly tools such as real-time vote tracking and robust encryption to ensure accurate representation of member preferences.
List of Sources
- Define Ranked-Choice Voting and Its Importance
- New York voters love ranked choice voting: 78% ranked more than 1 candidate in 2025 mayoral primary – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/press/nyc-2025-cast-vote-record)
- As ranked choice voting gains momentum, parties in power push back • Missouri Independent (https://missouriindependent.com/2023/08/21/as-ranked-choice-voting-gains-momentum-parties-in-power-push-back)
- Update on Ranked Choice Voting Legislation at Federal and State Levels (https://amacad.org/news/federal-state-legistlation-ranked-choice-voting)
- Bipartisan American Bar Association task force endorses ranked choice voting – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/bipartisan-american-bar-association-task-force-endorses-ranked-choice-voting)
- Explore the Impact of RCV on Voter Turnout and Engagement
- Ranked Choice Voting and Voter Turnout – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/ranked-choice-voting-and-voter-turnout)
- Does ranked choice Voting Increase voter turnout and mobilization? (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S026137942400074X)
- Research and data on RCV in practice – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/resources/data-on-rcv)
- Analyze How RCV Influences Campaign Strategies and Candidate Diversity
- What We Know About Ranked-Choice Voting (https://newamerica.org/political-reform/reports/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting/candidates-and-campaigns)
- Does ranked choice Voting Increase voter turnout and mobilization? (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S026137942400074X)
- Research and data on RCV in practice – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/resources/data-on-rcv)
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- American Journal of Political Science | MPSA Journal | Wiley Online Library (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ajps.12908)
- Implement RCV in Union Elections: A Step-by-Step Guide
- As ranked choice voting gains momentum, parties in power push back • Oregon Capital Chronicle (https://oregoncapitalchronicle.com/2023/08/23/as-ranked-choice-voting-gains-momentum-parties-in-power-push-back)
- It’s the biggest month for ranked choice voting in primary elections – FairVote Action (https://fairvoteaction.org/its-the-biggest-month-for-ranked-choice-voting-in-primary-elections)
- Research and data on RCV in practice – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/resources/data-on-rcv)
- Electing Union Officers Using Remote Electronic Voting Systems (https://dol.gov/agencies/olms/compliance-assistance/tips/remote-electronic-voting-systems)