Overview
The article examines the critical roles and significance of corporate boards concerning unions, highlighting the essential need for worker representation to bolster corporate governance. It posits that the inclusion of workers or union representatives on boards can significantly enhance decision-making, accountability, and labor relations. This approach advocates for a governance structure that not only prioritizes corporate success but also champions employee welfare.
Furthermore, the integration of worker perspectives on boards is not merely a matter of representation; it is a strategic imperative that can lead to improved organizational outcomes. By fostering an environment where employee voices are heard, companies can cultivate stronger labor relations and build trust with their workforce. This trust is foundational for achieving sustainable corporate success, as it aligns the interests of both the organization and its employees.
In addition, the article encourages union leadership to recognize the profound impact that board composition can have on corporate governance. By advocating for the inclusion of worker representatives, unions can drive a transformation in how companies operate, ensuring that employee welfare is a central consideration in corporate decision-making processes.
Ultimately, this governance model presents a compelling case for action. Union leaders are called to champion these changes, paving the way for a future where corporate boards reflect the diverse voices of their workforce, thereby enhancing both accountability and performance.
Introduction
Understanding the intricate dynamics of corporate governance is essential, particularly as labor unions navigate their role within this framework. The corporate board serves as a critical decision-making body, influencing not only the direction of a company but also the welfare of its employees. As unions strive to advocate for worker rights and representation, a pressing question emerges: how can they effectively engage with corporate boards to ensure that labor interests are prioritized amidst the often competing demands of shareholders? This exploration delves into the roles and responsibilities of corporate boards, highlighting the significant impact they have on union relations and the opportunities for collaboration that lie ahead.
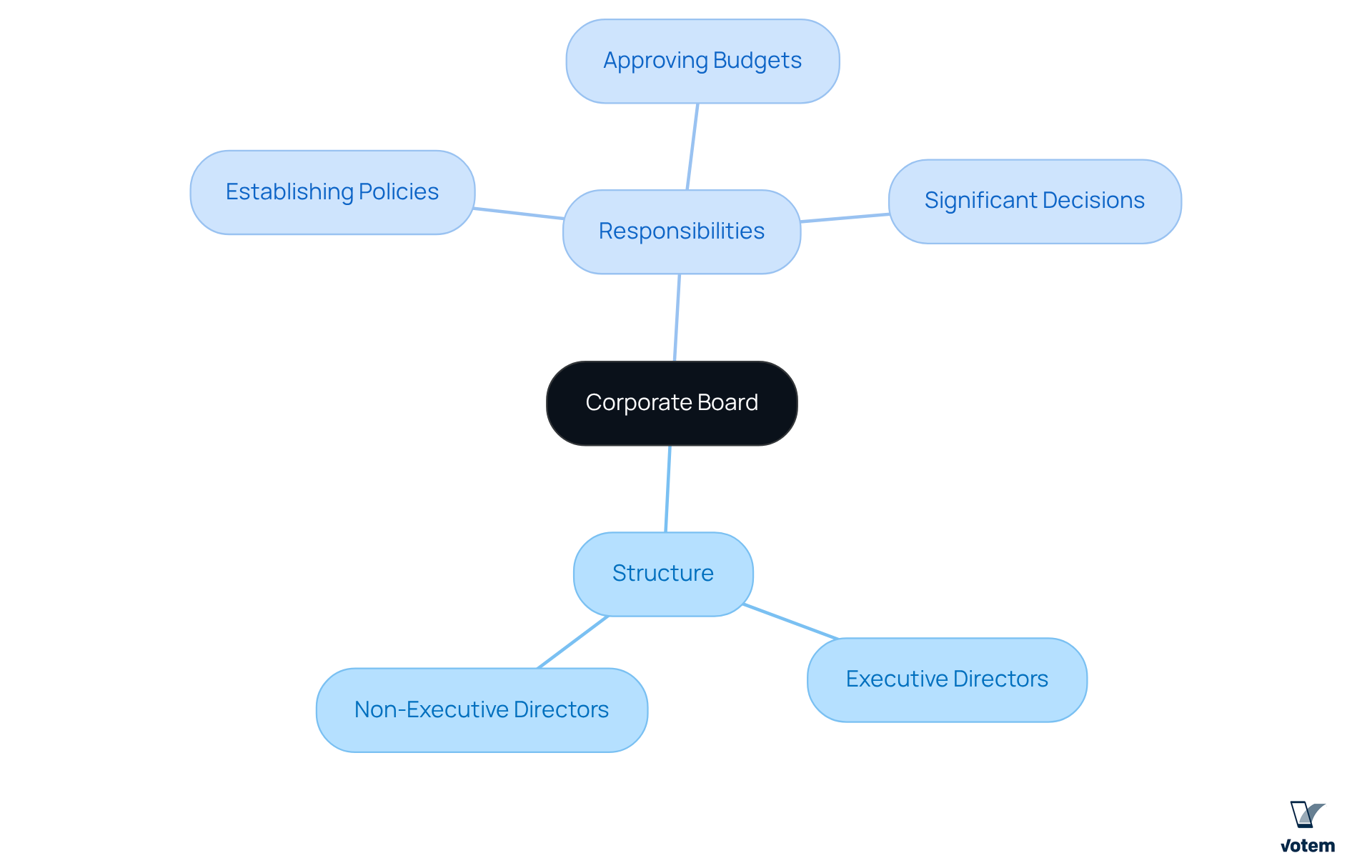
Define Corporate Board: Structure and Purpose
A corporate board, often referred to as the directors’ assembly, is a pivotal group of individuals selected to represent shareholders and oversee the operations of a corporation. The primary aim of this assembly is to ensure that the organization operates in alignment with the interests of its stakeholders, which include shareholders, employees, and the broader community. Typically, a corporate board comprises a blend of executive directors—who are integral to the firm’s management—and non-executive directors, who maintain independence from the organization. This dual structure facilitates a crucial balance of oversight and operational insight, empowering the governing body to effectively guide the organization while holding management accountable.
The corporate board has extensive and critical responsibilities. They include:
- Establishing organizational policies
- Approving budgets
- Making significant decisions that shape the entity’s trajectory, such as mergers and acquisitions
Furthermore, this governance framework not only enhances accountability but also fosters a culture of transparency and trust among stakeholders. By understanding the dynamics and responsibilities of a company council, union leaders can better navigate the complexities of corporate governance and advocate for the interests of their constituents.
Explore Roles and Responsibilities of Board Members
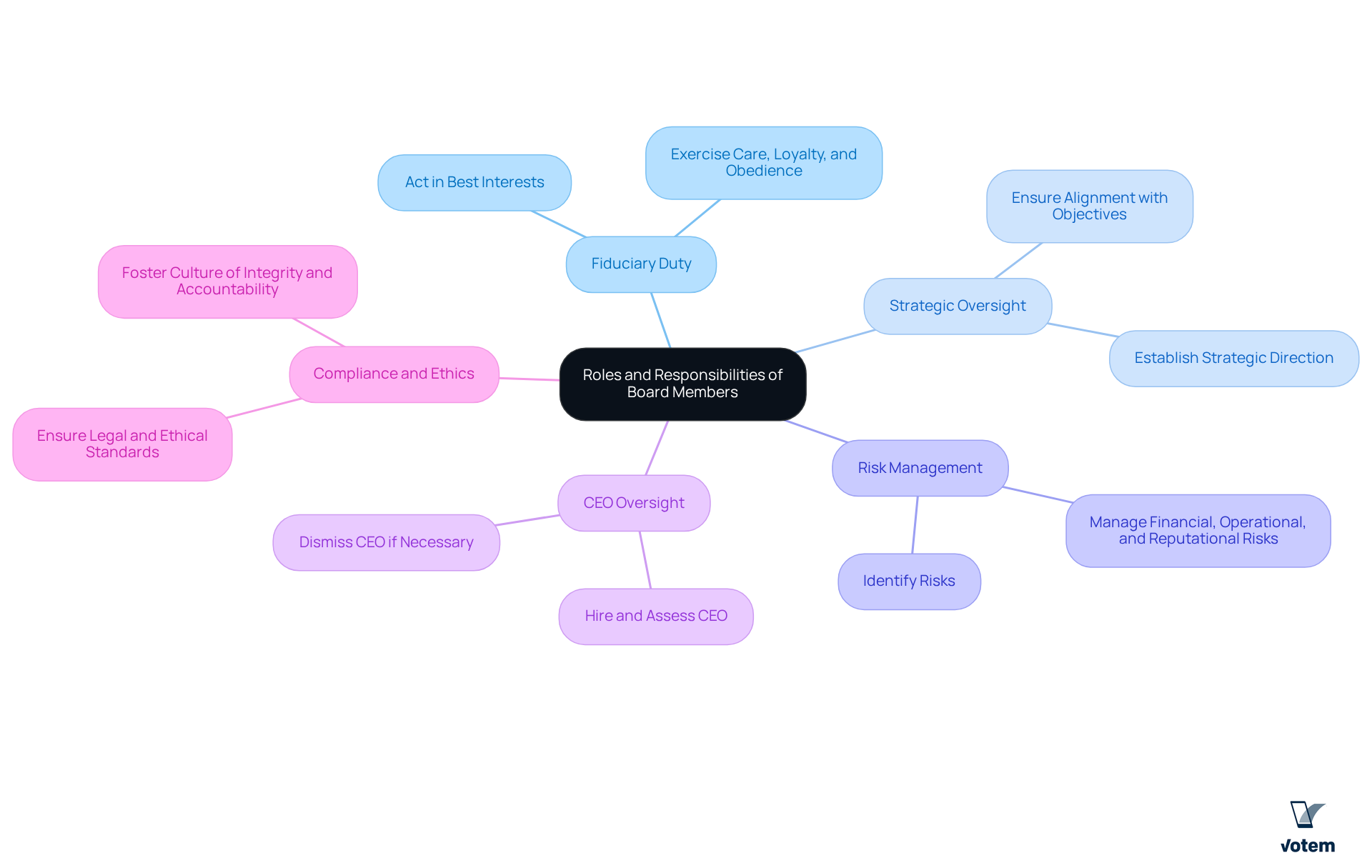
Members of the corporate board hold several key responsibilities that are essential for the effective governance of a corporation.
- Fiduciary Duty stands at the forefront; board members are legally obligated to act in the best interests of the organization and its shareholders, which necessitates exercising care, loyalty, and obedience in their decision-making processes.
- Furthermore, they engage in Strategic Oversight, establishing the strategic direction of the organization to ensure alignment with long-term objectives and values.
- Risk Management is another critical area; board members must identify and manage risks that could impact the organization’s performance, encompassing financial, operational, and reputational risks.
- In addition, they are tasked with CEO Oversight, responsible for hiring, assessing, and, if necessary, dismissing the CEO to ensure effective leadership that aligns with the organization’s goals.
- Lastly, Compliance and Ethics is paramount; board members must guarantee that the company adheres to legal and ethical standards, fostering a culture of integrity and accountability.
By fulfilling these roles, members of the corporate board can significantly influence organizational policies and practices, including those related to labor relations and staff welfare.
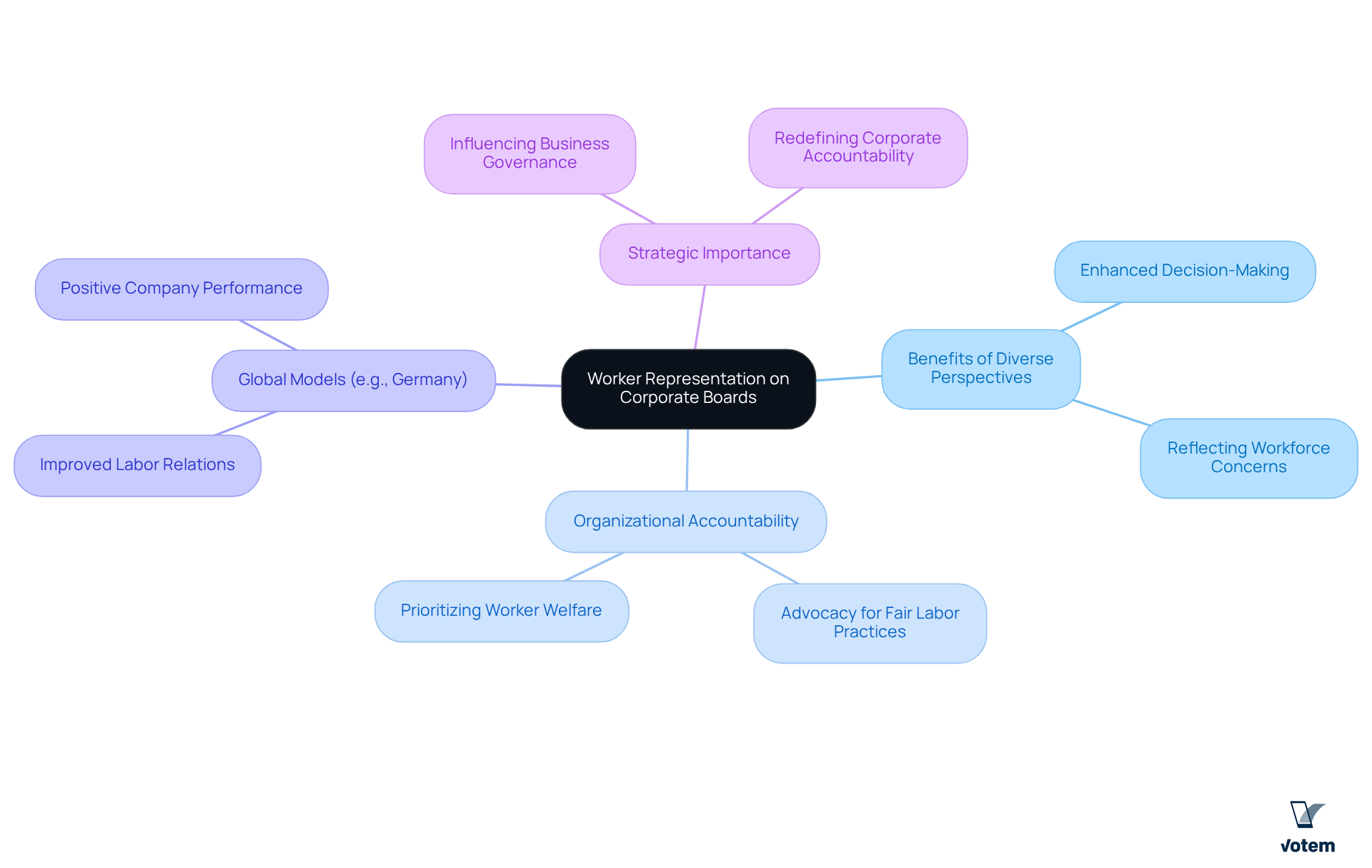
The Importance of Worker Representation on Corporate Boards
The corporate board increasingly recognizes worker participation as a vital component of effective corporate governance. By incorporating laborers or union delegates into governance structures, companies can benefit from diverse perspectives that reflect the concerns of the workforce. This representation not only enhances decision-making but also ensures that committee members with firsthand knowledge of workforce issues can provide insights that might otherwise be overlooked. Furthermore, having workers on boards fosters organizational accountability; these representatives can advocate for fair labor practices and ensure that worker welfare is prioritized in business strategies.
Countries with established worker representation models, such as Germany, exemplify how this approach can lead to improved labor relations and overall company performance. As unions strive to influence business governance, promoting worker representation on the corporate board emerges as an essential strategy for ensuring that staff interests are adequately represented in the highest levels of decision-making. Are we prepared to embrace this critical shift in governance? The time to act is now, as the inclusion of worker voices can redefine corporate accountability and enhance organizational success.
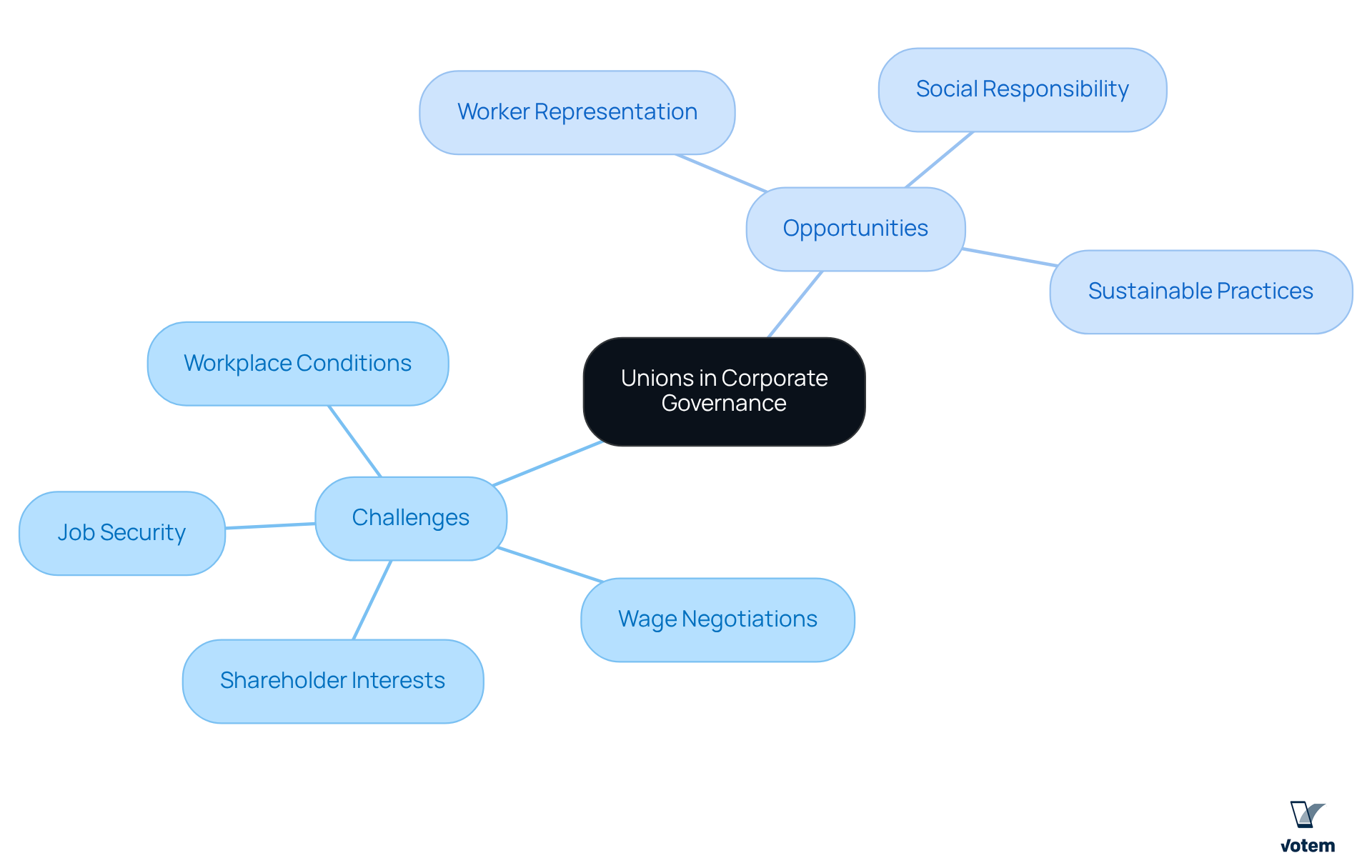
Challenges and Opportunities for Unions in Corporate Governance
Unions face significant challenges and promising opportunities within the realm of business governance. A primary challenge lies in the traditional perception of company panels, which often prioritize shareholder interests to the detriment of employee welfare. This dynamic frequently results in tension between unions and company leadership, particularly concerning vital issues such as wage negotiations, job security, and workplace conditions.
However, there are considerable opportunities for unions to engage constructively with the corporate board. By advocating for policies that promote worker representation and participation in decision-making, unions can shift the narrative toward a more inclusive governance approach. Furthermore, as stakeholders increasingly demand social responsibility and ethical practices, unions can position themselves as essential allies in advancing sustainable business practices that benefit both employees and the organization.
By navigating these challenges and seizing opportunities, unions can significantly enhance their influence on the corporate board and in corporate governance. This proactive approach not only advocates effectively for workers’ rights but also contributes to a more equitable and sustainable business environment. Union leadership must recognize these dynamics and act decisively to foster collaboration and drive meaningful change.
Conclusion
The significance of corporate boards extends far beyond mere governance; they serve as crucial entities that shape the intersection between corporate interests and the workforce. Understanding the structure, roles, and responsibilities of these boards empowers unions to navigate the complexities of corporate governance effectively, advocating for the rights and welfare of their members.
This article has explored the multifaceted roles of corporate boards, from establishing organizational policies and overseeing management to ensuring compliance and ethical governance. The inclusion of worker representation on these boards not only enriches decision-making but also strengthens accountability, highlighting the importance of diverse perspectives in corporate governance. Furthermore, unions face both challenges and opportunities in influencing board dynamics, emphasizing the need for proactive engagement in advocating for employee interests.
In light of these insights, it is imperative for unions to recognize their potential to shape corporate governance through strategic advocacy and collaboration. By pushing for worker representation and prioritizing employee welfare, unions can redefine the corporate landscape, fostering a more equitable and sustainable business environment. The time to act is now; embracing this shift can lead to enhanced organizational success and a more balanced approach to corporate governance that benefits all stakeholders involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a corporate board?
A corporate board, also known as the directors’ assembly, is a group of individuals selected to represent shareholders and oversee the operations of a corporation.
What is the primary purpose of a corporate board?
The primary aim of a corporate board is to ensure that the organization operates in alignment with the interests of its stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, and the broader community.
What is the typical composition of a corporate board?
A corporate board typically comprises a mix of executive directors, who are involved in the firm’s management, and non-executive directors, who maintain independence from the organization.
What are the key responsibilities of a corporate board?
Key responsibilities of a corporate board include establishing organizational policies, approving budgets, and making significant decisions that shape the entity’s trajectory, such as mergers and acquisitions.
How does a corporate board enhance accountability and transparency?
The governance framework established by a corporate board enhances accountability and fosters a culture of transparency and trust among stakeholders.

