Overview
Ranked voting, or ranked-choice voting (RCV), is an electoral system that empowers voters to rank candidates according to their preferences. This innovative approach not only promotes a more representative outcome but also mitigates the risk of vote splitting among similar candidates. Furthermore, RCV significantly enhances democratic participation within unions. By ensuring that leadership mirrors the collective preferences of members, RCV fosters a more inclusive electoral process. This system is essential for union leadership seeking to engage members effectively and reflect their diverse voices.
Introduction
Ranked voting, or ranked-choice voting (RCV), signifies a transformative shift in electoral systems. This innovative method empowers voters to express their preferences more fully by ranking candidates rather than selecting just one. By enhancing democratic participation within unions, ranked voting ensures that leadership authentically reflects the collective will of the workforce. However, as organizations contemplate the adoption of this approach, complexities and potential challenges to voter engagement emerge.
How can unions effectively navigate these intricacies to harness the full benefits of ranked voting?
Define Ranked Voting and Its Significance
What is ranked voting? It is an electoral system known as ranked-choice voting (RCV) that empowers participants to prioritize candidates based on their preferences rather than limiting them to a single option. This approach is essential as it facilitates a more nuanced expression of voter preferences, resulting in outcomes that more accurately reflect the electorate’s will. For unions, implementing a ranked system can significantly boost democratic participation among members, ensuring that leadership aligns with the collective preferences of the workforce. Furthermore, RCV reduces the risk of vote splitting, where similar candidates may divide the vote, thus enabling candidates with broader appeal to secure victory.
Votem has demonstrated proven success in managing large-scale online balloting, as evidenced by their handling of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame—a remarkable increase from the previous year. This achievement illustrates how Votem’s innovative online ballot solutions enhance accessibility and security, facilitating participation for all members, including those with disabilities and military personnel. In addition, endorsements from organizations such as the New Mexico State Republican Party highlight Votem’s transformative impact on electoral participation, with one election seeing more than double the engagement compared to prior years. By minimizing the chances of vote splitting and enabling candidates with wider appeal to thrive, ranked-choice voting can significantly enhance the democratic process within unions.
In summary, what is ranked voting emerges as a transformative electoral method for unions, fostering democratic participation, increasing voter turnout, and promoting a more representative leadership structure. Its capacity to reflect the diverse preferences of union members positions it as an indispensable tool for modern electoral processes.
Trace the History and Adoption of Ranked Voting
What is ranked voting? It traces its origins to the early 20th century, emerging as a response to the shortcomings of traditional plurality election systems. The first notable implementation occurred in the 1910s in Australia, where it was adopted for federal elections. This early adoption set the stage for a significant evolution in electoral processes.
Throughout the years, various regions, including urban centers in the United States and countries like Ireland and New Zealand, have embraced tiered election systems. This evolution reflects a growing recognition of the need for more equitable electoral processes. Furthermore, in recent years, the movement has gained substantial support, particularly among labor organizations. Alternative balloting is increasingly viewed as a method to empower members and ensure equitable representation.
Cities such as San Francisco and New York have successfully implemented ranked-choice procedures for local elections, which exemplify what is ranked voting, demonstrating its effectiveness and adaptability in contemporary electoral frameworks. The schedule of prioritized ballot implementation in union elections emphasizes its contribution to promoting democratic involvement and inclusiveness among members. This indicates a crucial change in how organizations handle decision-making, fostering a more engaged and representative leadership.
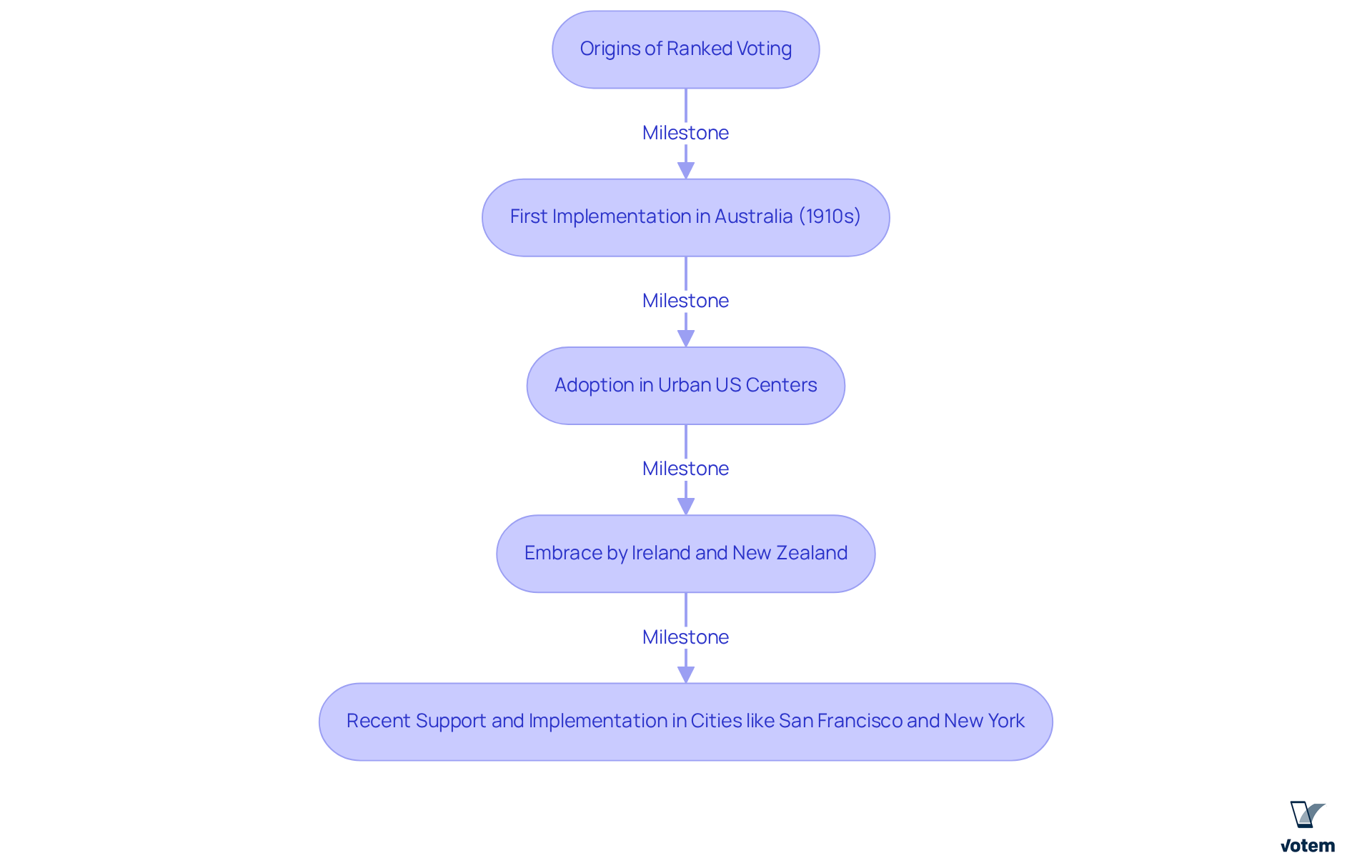
Explain How Ranked Voting Works
In a ranked voting system, ranked voting allows voters to use a ballot that enables them to rank nominees according to their preferences. Should an individual garner a majority of first-choice votes, they win outright. However, if no participant achieves this majority, the individual with the fewest votes is eliminated. Their votes are subsequently redistributed to the remaining contenders based on the next preferences indicated on those ballots. This elimination and redistribution process continues until an individual secures a majority.
This approach not only enables individuals to express their preferences more comprehensively but also encourages participants to appeal to a broader audience. Candidates strive to be the second or third choice of constituents who may initially favor other options, fostering a more inclusive electoral atmosphere. Studies indicate that individuals of color frequently evaluate more options than their white counterparts, thereby enhancing representation in elections. Additionally, experts suggest that preferential selection can lead to more civil campaigns, as candidates seek to gain support from a wider electorate, thereby reducing negative campaigning and promoting cooperation among candidates.
As of April 2025, preferential selection has been adopted in 52 American jurisdictions, encompassing nearly 14 million participants, underscoring its growing acceptance. Nonetheless, some critics, such as Jason Snead from the Honest Elections Project, argue that preferential selection methods can be confusing, potentially discouraging citizen engagement. Furthermore, a study conducted by the MIT election lab found that while transitioning to a preference-based system did not yield financial savings for municipalities, it also did not incur additional costs, indicating a neutral financial impact. Overall, understanding what ranked voting is can enhance participation and satisfaction by allowing individuals to support their preferred candidates without the fear of wasting their ballots.
Evaluate the Benefits and Challenges of Ranked Voting
Ranked balloting offers significant advantages, particularly in enhancing citizen involvement by ensuring that members’ preferences are accurately represented. This system has the potential to boost voter turnout, as individuals are less likely to perceive their votes as wasted. Furthermore, preferential elections encourage participants to engage constructively with a broader audience, thereby reducing negative campaigning. For instance, in Las Cruces, NM, where choice selection has been implemented since 2019, the electoral process has become more inclusive, allowing a diverse range of candidates to compete and succeed more effectively. RCV has fostered a more representative election process and increased citizen participation in the city, demonstrating its positive impact.
As of April 2025, RCV is utilized in 52 American jurisdictions, illustrating its growing acceptance and applicability. However, the adoption of ordered balloting presents challenges, particularly within unions. The complexity of the voting procedure can confuse some individuals, potentially leading to lower participation rates among those unfamiliar with the system. Additionally, the counting process for ranked votes is often more intricate and time-consuming than traditional methods, which can delay results and create uncertainty. For example, during the implementation of RCV in St. Paul, the transition necessitated extensive education and outreach to ensure voters comprehended the new system. RCV advocates argue that this system prompts candidates to adopt more moderate positions and engage in less negative campaigning, further underscoring the advantages of positive campaigning.
Despite these obstacles, many unions are actively investigating what is ranked voting as a method to enhance democratic practices and increase member participation in leadership elections. The potential for improved representation and engagement renders it a compelling option, even as unions navigate the complexities of its implementation.
Conclusion
Ranked voting, particularly in the form of ranked-choice voting (RCV), stands as a pivotal electoral system that empowers voters to express their preferences more fully. By allowing individuals to rank candidates rather than select just one, RCV enhances the democratic process, especially within unions, by more accurately reflecting the collective will of the members. This system not only promotes greater participation but also mitigates the risks associated with vote splitting, paving the way for candidates who resonate with a broader base.
The article highlights several key arguments surrounding ranked voting, including:
- Its historical context
- Implementation in various regions
- The mechanics of how it operates
The benefits of RCV are evident:
- Increased voter turnout
- Reduced negative campaigning
- The promotion of more inclusive electoral environments
Despite some challenges, such as potential confusion over the voting process and the complexity of counting ranked votes, the growing acceptance of this system in over 50 jurisdictions underscores its relevance and adaptability in modern electoral frameworks.
Ultimately, the significance of ranked voting lies in its ability to foster a more engaged and representative leadership within unions. As organizations continue to explore methods to enhance democratic practices, embracing ranked voting can serve as a catalyst for positive change. This innovative approach to elections not only empowers members but also ensures that their diverse preferences are acknowledged and valued, reinforcing the importance of inclusive decision-making in shaping the future of union leadership.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ranked voting?
Ranked voting, also known as ranked-choice voting (RCV), is an electoral system that allows participants to prioritize candidates based on their preferences instead of selecting just one option.
Why is ranked voting significant?
Ranked voting is significant because it enables a more nuanced expression of voter preferences, leading to outcomes that better reflect the electorate’s will. It also enhances democratic participation among union members and reduces the risk of vote splitting among similar candidates.
How does ranked voting benefit unions?
Implementing ranked voting in unions can significantly boost democratic participation among members, ensuring that leadership aligns with the collective preferences of the workforce. It promotes broader candidate appeal and enhances voter turnout.
What evidence supports the effectiveness of ranked voting?
Votem has successfully managed large-scale online balloting, such as handling 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, which demonstrated increased accessibility and security in the voting process. Endorsements from organizations like the New Mexico State Republican Party also highlight the transformative impact of ranked voting on electoral participation.
How does ranked voting reduce vote splitting?
Ranked voting minimizes the chances of vote splitting by allowing voters to rank candidates in order of preference, which helps candidates with broader appeal to secure victory rather than splitting the vote among similar candidates.
What impact does ranked voting have on voter turnout?
Ranked voting can significantly enhance voter turnout by fostering a more representative leadership structure and encouraging greater participation in the electoral process.
List of Sources
- Define Ranked Voting and Its Significance
- Ranked Choice Voting – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/our-reforms/ranked-choice-voting)
- Case Studies (https://starvoting.org/case_studies)
- Research and data on RCV in practice – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/resources/data-on-rcv)
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- Trace the History and Adoption of Ranked Voting
- Ranked Choice Voting (https://ncsl.org/elections-and-campaigns/ranked-choice-voting)
- Case Studies (https://starvoting.org/case_studies)
- Ranked-choice voting (RCV) (https://ballotpedia.org/Ranked-choice_voting_(RCV))
- Explain How Ranked Voting Works
- New York City’s mayoral primary casts bright light on ranked choice voting — and its future nationally (https://nbcnews.com/politics/elections/new-york-city-mayoral-primary-casts-bright-light-ranked-choice-voting-rcna213812)
- Ranked choice voting – SciLine (https://sciline.org/elections/ranked-choice-voting-quotes)
- Ranked choice is ‘the hot reform’ in democracy. Here’s what you should know about it (https://npr.org/2023/12/13/1214199019/ranked-choice-voting-explainer)
- Ranked Choice Voting – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/our-reforms/ranked-choice-voting)
- Dr. Rachael Cobb: Ranked choice voting – SciLine (https://sciline.org/elections/rank-choice-voting)
- Evaluate the Benefits and Challenges of Ranked Voting
- Case Studies (https://starvoting.org/case_studies)
- Ranked Choice Voting – FairVote (https://fairvote.org/our-reforms/ranked-choice-voting)
- Ranked-Choice Voting – Center for Effective Government (https://effectivegov.uchicago.edu/primers/ranked-choice-voting)

