Overview
Statutory voting often favors majority shareholders, resulting in diminished engagement among union members. In contrast, cumulative voting significantly enhances participation and representation, especially for minority stakeholders. This article illustrates that cumulative voting empowers voters by allowing them to concentrate their ballots, thereby increasing their sense of agency. As a result, participation rates can rise dramatically, showcasing a clear advantage over the limitations inherent in statutory voting methods. Furthermore, the implications of these voting systems underscore the importance of adopting practices that foster inclusivity and active involvement among all stakeholders.
Introduction
The dynamics of voting methods play a pivotal role in influencing the level of engagement among union members, a crucial element for fostering a vibrant democratic process. Statutory and cumulative voting each present distinct advantages and challenges, shaping how voices are heard within labor organizations.
- Statutory voting often favors majority stakeholders, whereas cumulative voting provides a more inclusive approach, empowering minority members to make a meaningful impact.
This raises an essential question: which method truly enhances engagement and representation among union members? By exploring the nuances of these voting systems, we uncover critical insights into their potential to either bolster or hinder participation in the electoral process.
Define Statutory and Cumulative Voting
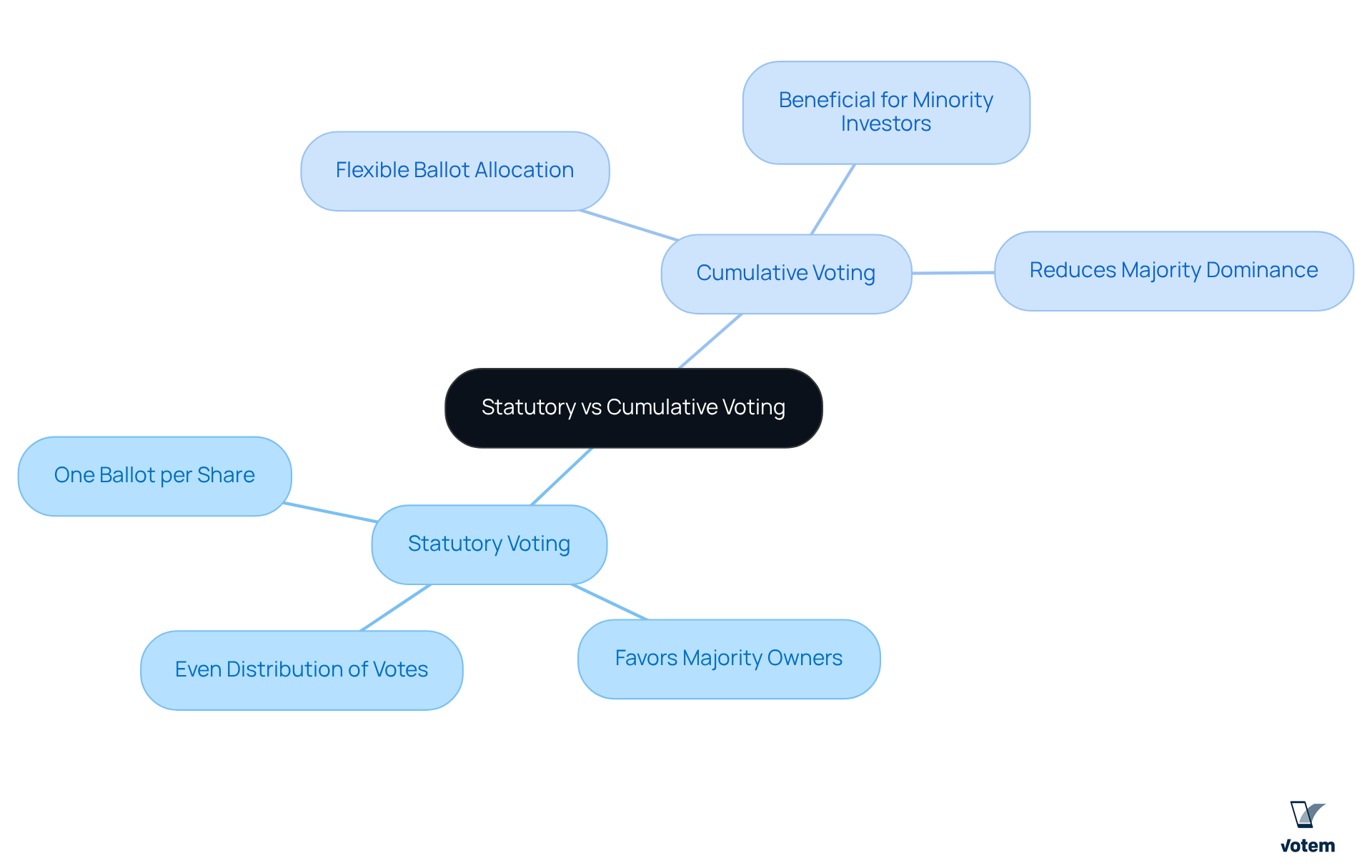
In the context of statutory vs cumulative voting, statutory balloting, commonly known as straight voting, allows each stockholder or member to cast one ballot per share for each candidate or position available. For example, a participant with ten shares can cast ten ballots for every candidate in a contest. This method is prevalent in corporate governance, favoring majority owners and ensuring they retain significant influence over election results. Statutory balloting generally results in a straightforward allocation of shares, where shareholders can only distribute their support evenly among candidates.
Conversely, when considering statutory vs cumulative voting, participants are provided with the flexibility to allocate their total ballots in a more adaptable manner. If a voter has ten ballots and three positions are open, they can choose to cast all ten for one candidate or distribute them among various candidates. This approach is particularly beneficial for minority investors, as it allows them to concentrate their votes on preferred candidates, thereby enhancing their representation in the voting process. The concept of cumulative voting, especially when compared to statutory vs cumulative voting, is designed to reduce the dominance of majority shareholders, creating a more equitable platform for all members involved.
With Votem’s versatile online ballot system, unions can effectively implement both statutory and cumulative voting methods, catering to diverse processes and governance needs. Votem’s platform facilitates various methods for casting ballots, including online, phone, and hybrid options, alongside customizable ballot layouts. This empowers organizations to engage their members more effectively, ensuring that every voice is heard in the decision-making process.
Examine Applications and Implications of Each Voting Method
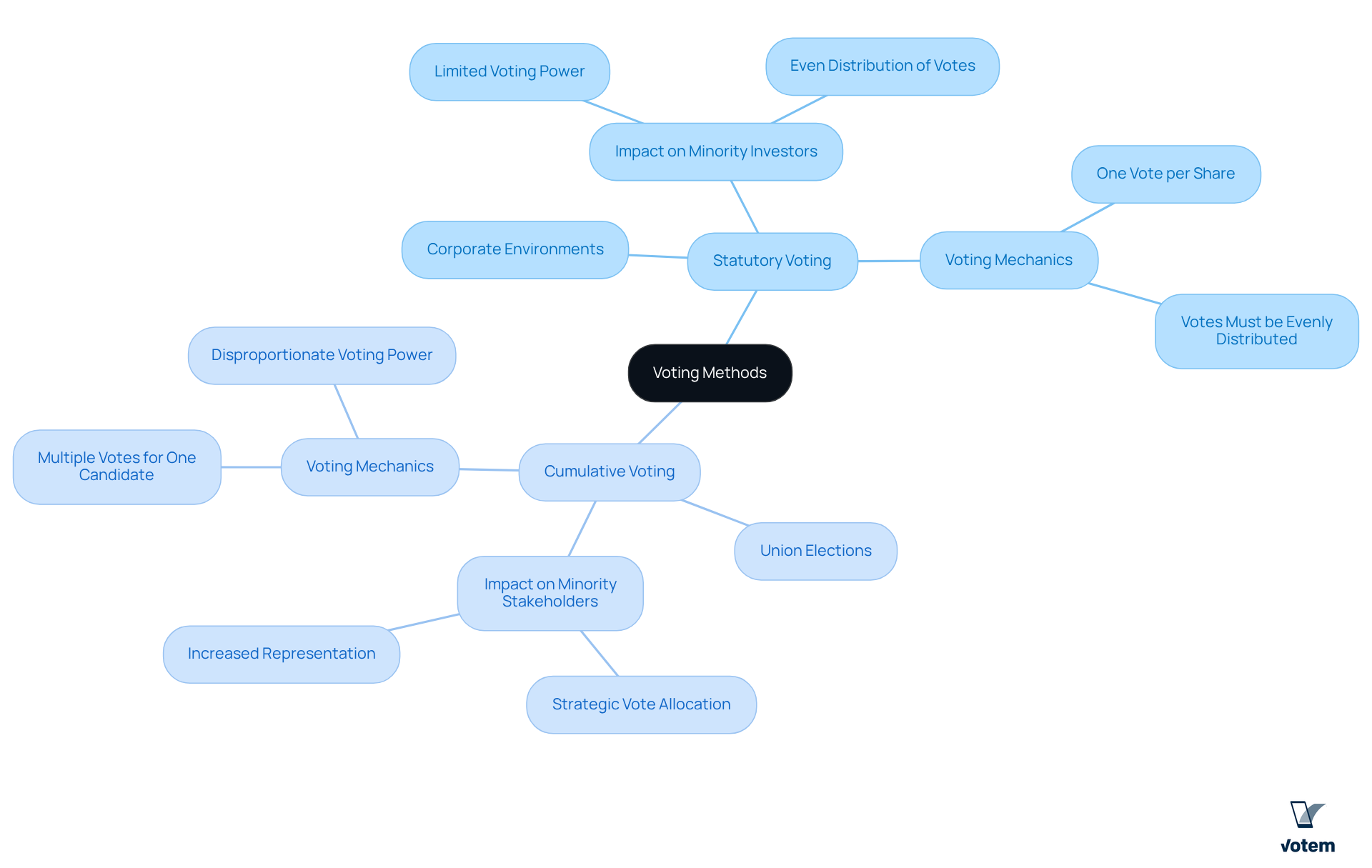
In corporate environments, statutory vs cumulative voting is prevalent, designed to ensure a transparent decision-making process. This method is often preferred by larger organizations, where majority stakeholders wield significant influence over board elections. Consequently, minority investors may find their impact diminished, as their decision-making power is curtailed in a system that inherently favors those with greater ownership stakes. For instance, under the concept of statutory vs cumulative voting, an owner of 100 shares can cast only 100 votes, which must be distributed evenly among candidates, thus limiting their ability to concentrate votes on a preferred candidate.
Conversely, when considering statutory vs cumulative voting, cumulative voting is particularly advantageous in union elections, where minority representation is crucial. This approach highlights the differences between statutory vs cumulative voting, allowing participants to allocate their votes strategically and empowering smaller groups or minority stakeholders to exert considerable influence in the decision-making process. For example, a shareholder with 50 shares can cast up to 300 votes for a single director, significantly increasing the chances of electing representatives who align with their interests. This method not only promotes more equitable outcomes but also enhances member satisfaction, as individuals feel their preferences can meaningfully shape election results when considering statutory vs cumulative voting.
Statistics reveal that cumulative balloting can elevate engagement levels among union members, encouraging participation from those who might otherwise feel marginalized. A 2021 survey found that 86 percent of voters supported the recall process, reflecting a desire for more inclusive electoral methods. Experts assert that this voting system can enhance the democratic process within unions, ensuring that diverse voices are effectively heard and represented. Mark Baldassare noted that the referendum process can be particularly confusing, underscoring the importance of transparent ballot methods like cumulative systems that empower citizens.
Compare Effectiveness in Voter Engagement and Representation
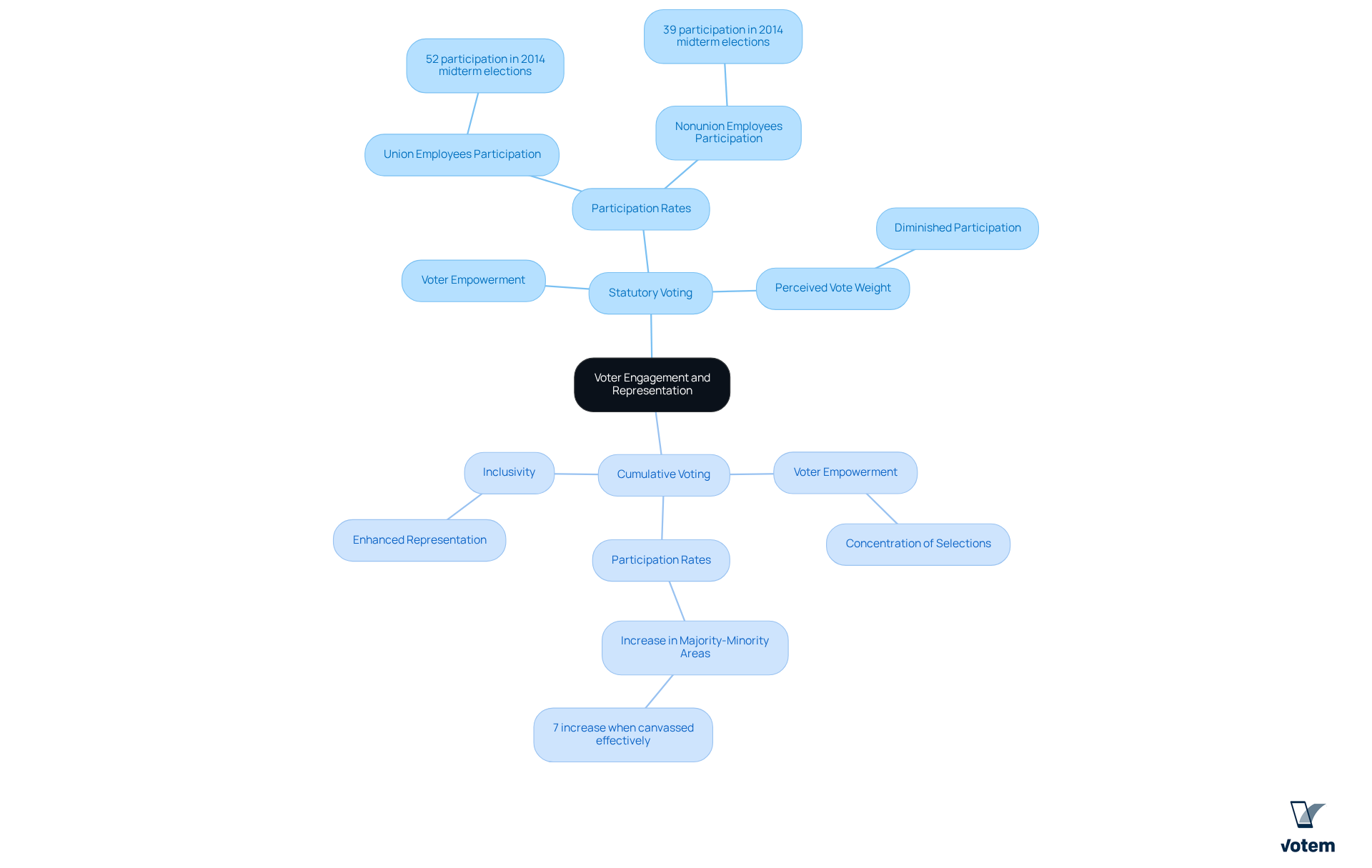
Cumulative voting, when compared to statutory vs cumulative voting, significantly enhances voter engagement, particularly among minority shareholders and union members. This method allows voters to concentrate their selections, fostering a sense of empowerment and investment in the electoral process. Research indicates that when members perceive their choices as impactful, participation rates rise considerably. In contests utilizing cumulative balloting, for instance, participation can increase by as much as 7 percent in majority-minority areas when canvassed effectively.
Conversely, in the context of statutory vs cumulative voting, there is often diminished participation among minority members, who may feel their votes carry less weight in a system dominated by majority shareholders. This perspective can lead to indifference and lower participation levels, as members may believe their preferences are unlikely to sway the outcome. The 2014 midterm elections exemplify this, with only 52 percent of union employees participating compared to 39 percent of nonunion employees, highlighting the influence of election methods on engagement.
While the process of statutory vs cumulative voting provides a straightforward approach, cumulative balloting offers a more inclusive framework that enhances representation and engagement among all members. This inclusivity is especially vital in union contexts, where diverse voices are crucial for effective decision-making and governance. Votem’s innovative online voting solutions not only boost voter participation but also prioritize accessibility and security, as demonstrated by testimonials from satisfied clients. For example, Votem successfully managed the receipt of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, showcasing a substantial increase in voter participation compared to previous years. Furthermore, the New Mexico State Republican Party expressed satisfaction with Votem’s software performance, affirming their commitment to utilizing these services for future elections.
Conclusion
Cumulative voting stands out as a powerful mechanism for enhancing engagement and representation among union members, sharply contrasting with the limitations of statutory voting. By enabling voters to allocate their votes more strategically, cumulative voting empowers minority shareholders and ensures that diverse perspectives are integrated into decision-making processes. This flexibility not only fosters a sense of ownership among members but also cultivates a more democratic atmosphere within unions.
Key insights throughout the article illustrate how cumulative voting can significantly elevate participation rates, especially among those who may feel marginalized within a statutory voting framework. The ability to concentrate votes on preferred candidates increases the likelihood of electing representatives who genuinely reflect the interests of all members. Furthermore, the statistics presented underscore the positive correlation between cumulative voting and member satisfaction, highlighting the critical role of inclusive electoral methods in nurturing a vibrant union culture.
Ultimately, the decision between statutory and cumulative voting should be guided by the objective of maximizing member engagement and representation. As unions navigate the evolving landscape of labor relations, embracing cumulative voting emerges as a vital strategy to ensure that every voice is heard. By prioritizing inclusivity and transparency in the electoral process, unions can foster a more active and engaged membership, paving the way for a stronger, more representative governance structure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is statutory voting?
Statutory voting, also known as straight voting, allows each stockholder or member to cast one ballot per share for each candidate or position available. For example, a participant with ten shares can cast ten ballots for every candidate in a contest.
How does statutory voting impact corporate governance?
Statutory voting tends to favor majority owners, ensuring they retain significant influence over election results, as it results in a straightforward allocation of shares where shareholders can only distribute their support evenly among candidates.
What is cumulative voting?
Cumulative voting allows participants to allocate their total ballots in a more flexible manner. For instance, if a voter has ten ballots and three positions are open, they can cast all ten for one candidate or distribute them among various candidates.
Who benefits from cumulative voting?
Cumulative voting is particularly beneficial for minority investors, as it enables them to concentrate their votes on preferred candidates, thereby enhancing their representation in the voting process.
How does cumulative voting compare to statutory voting?
Cumulative voting is designed to reduce the dominance of majority shareholders, creating a more equitable platform for all members involved, in contrast to statutory voting which typically reinforces majority control.
What features does Votem’s online ballot system offer?
Votem’s online ballot system allows unions to implement both statutory and cumulative voting methods, facilitating various methods for casting ballots, including online, phone, and hybrid options, alongside customizable ballot layouts. This empowers organizations to engage their members effectively.
List of Sources
- Define Statutory and Cumulative Voting
- Statutory Voting: What It Is, How It Works (https://investopedia.com/terms/s/statutoryvoting.asp)
- Straight Voting (https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/equities/straight-voting)
- Cumulative Voting | Investor.gov (https://investor.gov/introduction-investing/investing-basics/glossary/cumulative-voting)
- Statutory Voting and Cumulative Voting in Corporate Governance | FinTrak.in posted on the topic | LinkedIn (https://linkedin.com/posts/fintrak-in_understanding-statutory-voting-and-cumulative-activity-7197250076467982336-k-A7)
- Examine Applications and Implications of Each Voting Method
- 2: Power to the People- Recalls and Referendums (https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Courses/California_State_University_Fullerton/Cases_in_California_Politics_and_Administration:_Centering_Equity_and_Social_Justice_Issues/01:_Case_Studies/1.02:_Power_to_the_People-_Recalls_and_Referendums)
- Statutory Voting: What It Is, How It Works (https://investopedia.com/terms/s/statutoryvoting.asp)
- Compare Effectiveness in Voter Engagement and Representation
- Mobilize Voters: How Unions Can Influence the 2020 Elections (https://uniontrack.com/blog/unions-mobilize-voters)
- Jesuit Resource – Election Day Quotes (https://xavier.edu/jesuitresource/online-resources/quote-archive1/election-dayvoting)
- Increasing Voter Participation in America (https://americanprogress.org/article/increasing-voter-participation-america)
- 45 Inspiring Quotes About Voting and Elections (https://shutterfly.com/ideas/inspiring-quotes-about-voting-and-elections)

