Overview
Undervotes represent a significant concern in electoral processes, occurring when voters select fewer candidates on a ballot than permitted. This phenomenon often arises from various factors, including ballot design, voter indifference, and confusion, particularly in elections with numerous choices. Addressing these issues is imperative, as undervotes can profoundly influence election outcomes, representation, and public trust in the electoral process. Recognizing the impact of undervotes is essential for ensuring a fair and transparent electoral system.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of voting is essential for a healthy democracy. However, many voters remain unaware of a critical phenomenon known as undervotes. These occur when individuals cast fewer votes than allowed, often due to confusion, disinterest, or even intentional abstention.
As elections grow increasingly competitive, the implications of undervotes become more pronounced, potentially skewing results and undermining representation.
What drives voters to undervote? How can this trend be addressed to ensure that every voice is heard in the electoral process?
Define Undervotes: Understanding the Concept
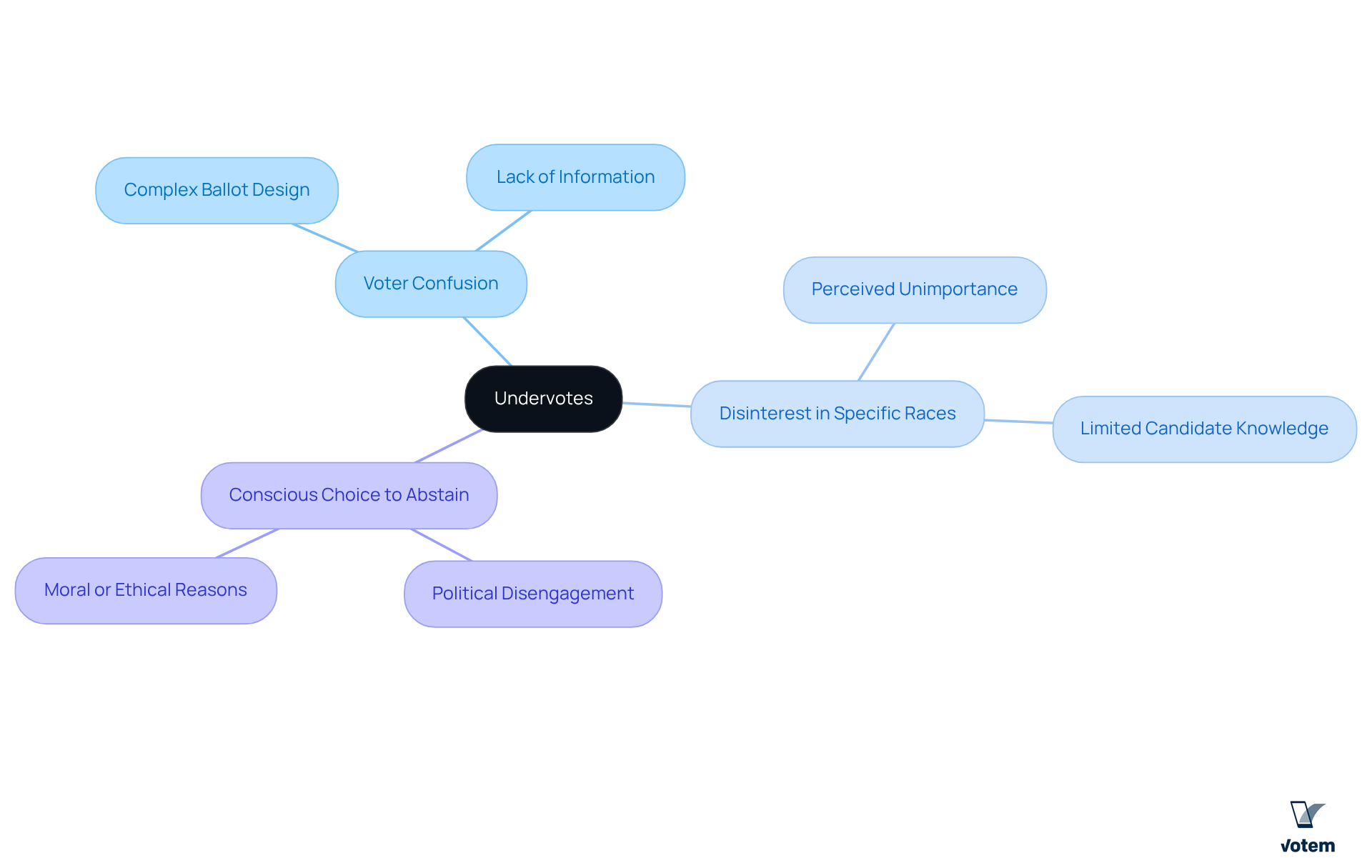
An undervote occurs when an individual selects fewer options on a ballot than the maximum number permitted for that election. For example, if a voter is allowed to choose three candidates but only selects two, this results in an undervote. Various factors can lead to undervotes, including:
- Voter confusion
- Disinterest in specific races
- A conscious choice to abstain from certain issues
It is essential to understand what are undervotes, as they can significantly influence the overall outcome of elections, especially in close races where every vote is critical. Therefore, it is imperative for union leadership to recognize the implications of undervotes and address the underlying causes to ensure every voice is heard in the electoral process.
Identify Causes of Undervotes: Factors Influencing Voter Behavior
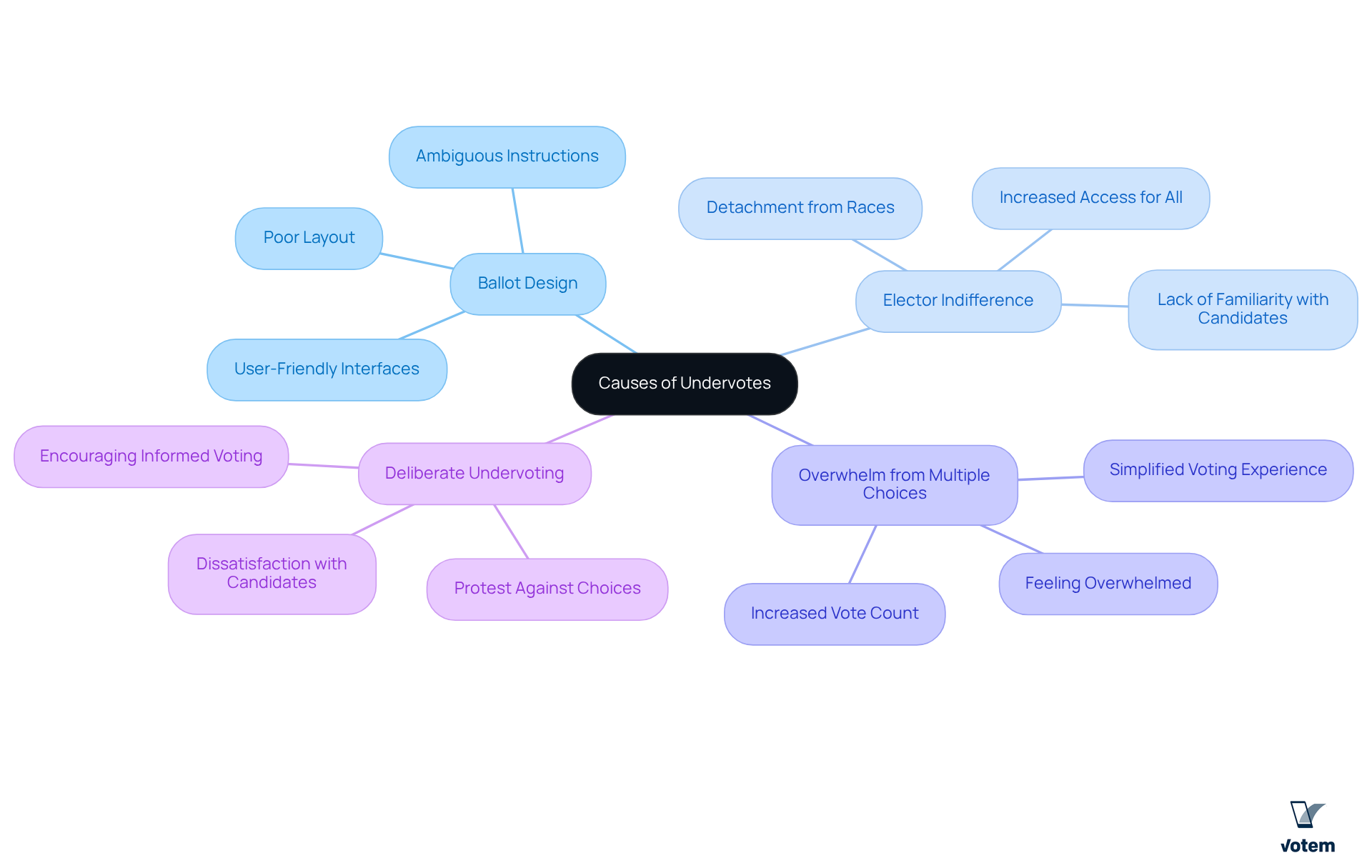
Several factors can lead to undervotes, including:
-
Ballot Design: Poorly designed ballots can perplex participants, causing them to overlook certain races or issues. If the layout is disorganized or if instructions are ambiguous, individuals may unintentionally undervote, raising the question of what are undervotes. Votem’s contemporary ballot system addresses this challenge by offering clear, user-friendly interfaces that enhance participant understanding and involvement.
-
Elector Indifference: Some individuals may feel detached from certain races or candidates, which leads to their decision not to participate in those contests, prompting the question of what are undervotes. This phenomenon is frequently observed in community contests where the public may not be acquainted with the candidates. As highlighted by a client, “Implementing the new, modern system which allowed greater access for all qualified participants from military personnel to individuals with disabilities was my greatest accomplishment in office.”
-
In elections featuring numerous candidates or propositions, participants may feel overwhelmed and may choose not to make selections in every category, leading to questions about what are undervotes. The company’s innovative online voting solutions simplify the voting experience, helping to reduce feelings of confusion and ensuring that participants can easily navigate their choices. A testimonial emphasizes this, stating, “The organization successfully managed the receipt of 299,000 votes on behalf of the National Radio Hall of Fame, an increase over last year’s 126,000 votes received.”
-
What are undervotes: Some individuals may deliberately opt to undervote as a means of protest or to convey dissatisfaction with the available choices. This behavior can reflect broader sentiments about the electoral process or specific candidates. By enhancing voter participation through secure and accessible mobile voting solutions, the organization aims to address these concerns and encourage more informed voting decisions. As stated by another pleased client, “Votem assisted in delivering 123,000 votes, more than double the participation of the previous vote in 2015 and the highest count of votes since the voting process commenced 30 years ago!
Examine Implications of Undervotes: Impact on Elections and Representation
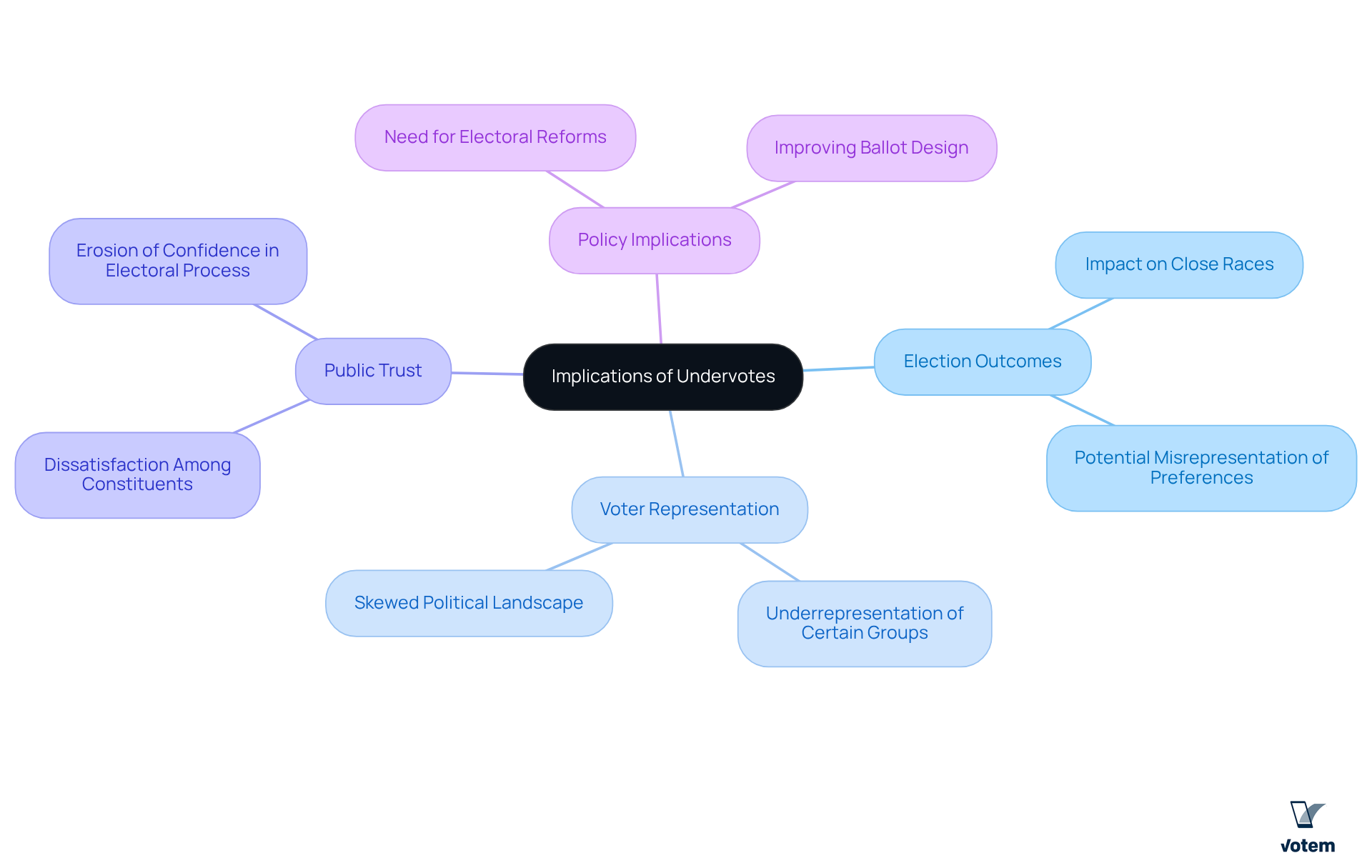
Understanding what are undervotes is essential, as they can have significant implications for elections and representation.
Election Outcomes: In close races, undervotes can dramatically alter results, potentially leading to outcomes that do not accurately reflect the true preferences of the electorate. For instance, if a substantial number of individuals opt not to cast their full ballot in a tightly contested election, the winning candidate may not possess the majority backing of the constituents.
Voter Representation: Furthermore, undervotes can result in the underrepresentation of certain groups or issues, particularly if specific demographics are more inclined to undervote. This phenomenon can skew the political landscape and subsequently influence policy decisions.
Public Trust: In addition, elevated rates of undervoting may indicate dissatisfaction or confusion among constituents, which can erode public confidence in the electoral process. If individuals perceive that their selections are not adequately represented, they may be less motivated to engage in future elections.
Policy implications: Understanding what are undervotes and their implications is crucial. This knowledge can inform electoral reforms aimed at enhancing participant engagement and improving ballot design, ultimately leading to more representative outcomes.
Strategies to Mitigate Undervotes: Enhancing Voter Engagement
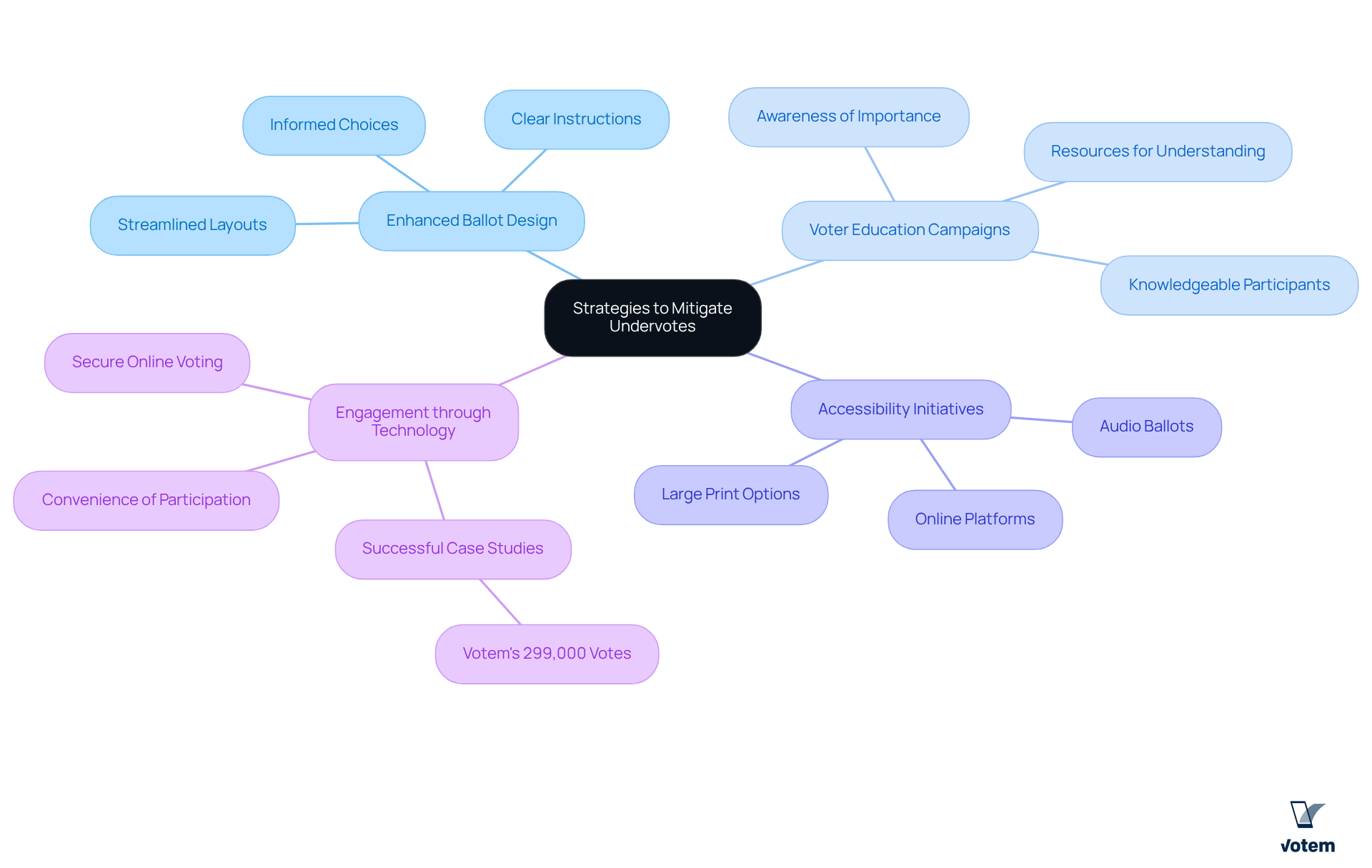
To effectively mitigate what are undervotes and enhance voter engagement, several strategies can be implemented.
-
Enhanced Ballot Design: Streamlining ballot layouts and providing clear, concise instructions can significantly reduce confusion among participants, encouraging involvement in all contests. A well-designed ballot enhances clarity and enables individuals to make informed choices.
-
Voter Education Campaigns: Raising awareness about the importance of participating in every race is crucial. Campaigns that offer resources to assist citizens in understanding candidates and issues can result in heightened participation. Research indicates that knowledgeable participants are more inclined to cast their selections across all positions, which helps to decrease what are undervotes.
-
Accessibility Initiatives: Ensuring that election methods are accessible to all, including individuals with disabilities, is essential for increasing participation. Implementing features such as audio ballots, large print options, and online platforms can help create an inclusive electoral environment, demonstrating a commitment to improving access for all eligible participants.
-
Engagement through Technology: Utilizing platforms such as CastIron can enable secure and compliant online voting, allowing participants to engage from anywhere. This convenience can result in increased turnout rates and a decrease in what are undervotes, since individuals are more likely to participate when the process is simplified and accessible. For example, Votem successfully handled the receipt of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, showcasing the effectiveness of their solutions in increasing voter participation.
By focusing on these strategies, organizations can foster a more engaged electorate, ensuring that every voice is heard and every vote counts.
Conclusion
Undervotes represent a critical aspect of the electoral process, underscoring the phenomenon where voters, either intentionally or unintentionally, select fewer candidates than permitted on their ballots. Understanding this concept is essential; undervotes can profoundly impact election outcomes and voter representation, particularly in closely contested races. Recognizing the underlying causes and implications of undervotes is vital for ensuring that every voice is heard and accurately reflected in the democratic process.
The article delves into various factors contributing to undervotes, including:
- Ballot design
- Voter indifference
- The overwhelming nature of numerous candidates
Poor ballot design can lead to confusion, while a lack of familiarity with candidates may cause voters to abstain from certain races. Furthermore, it discusses the implications of undervotes, such as:
- The potential distortion of election results
- Underrepresentation of specific demographics
- The erosion of public trust in the electoral system
Addressing undervotes requires a multifaceted approach. This includes:
- Improving ballot design
- Implementing voter education campaigns
- Ensuring accessibility for all participants
- Leveraging technology to enhance engagement
By prioritizing these strategies, it is possible to foster a more informed and active electorate, ultimately leading to elections that better reflect the will of the people. Every vote matters; by mitigating undervotes, we can strengthen the integrity of the electoral process, ensuring that democracy truly serves its purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an undervote?
An undervote occurs when a voter selects fewer options on a ballot than the maximum number allowed for that election. For instance, if a voter can choose three candidates but only selects two, it results in an undervote.
What factors can lead to undervotes?
Factors that can lead to undervotes include voter confusion, disinterest in specific races, and a conscious choice to abstain from certain issues.
Why is it important to understand undervotes?
Understanding undervotes is important because they can significantly influence the overall outcome of elections, particularly in close races where every vote counts.
What should union leadership do regarding undervotes?
Union leadership should recognize the implications of undervotes and address the underlying causes to ensure that every voice is heard in the electoral process.
List of Sources
- Strategies to Mitigate Undervotes: Enhancing Voter Engagement
- These Inspiring Quotes Will Get You Excited to Vote (https://countryliving.com/life/g24446791/voting-quotes)
- 45 Inspiring Quotes About Voting and Elections (https://shutterfly.com/ideas/inspiring-quotes-about-voting-and-elections)
- Jesuit Resource – Election Day Quotes (https://xavier.edu/jesuitresource/online-resources/quote-archive1/election-dayvoting)

