Overview
The four types of voting—plurality, majority, ranked-choice, and proportional representation—are essential electoral systems that significantly influence election outcomes and public participation. Each type possesses unique characteristics that warrant careful examination.
For instance:
- Plurality voting allows candidates to win by securing the most votes, even without a majority, which can lead to diverse electoral dynamics.
- Majority voting, on the other hand, requires candidates to obtain more than half the votes, ensuring broader support.
- Ranked-choice voting introduces a more nuanced approach, enabling voters to rank candidates in order of preference.
- Proportional representation seeks to align seats in the legislature with the overall vote share of parties.
Understanding these systems is crucial as they shape democratic engagement and representation in various political contexts. Furthermore, practical examples illustrate how these voting methods can enhance or hinder public participation, prompting reflection on their implications for union leadership and broader electoral strategies.
Introduction
Understanding the mechanics of voting is crucial in a democratic society, where the method of casting a ballot can significantly influence electoral outcomes. The four primary types of voting—plurality, majority, ranked-choice, and proportional representation—each offer unique advantages and challenges that shape public participation and representation. Furthermore, with various systems in play, how can voters determine which method best reflects their preferences and values?
Exploring these voting types not only illuminates their historical context but also highlights their profound impact on democracy today. By engaging with these concepts, voters can better navigate the electoral landscape and make informed decisions that resonate with their values.
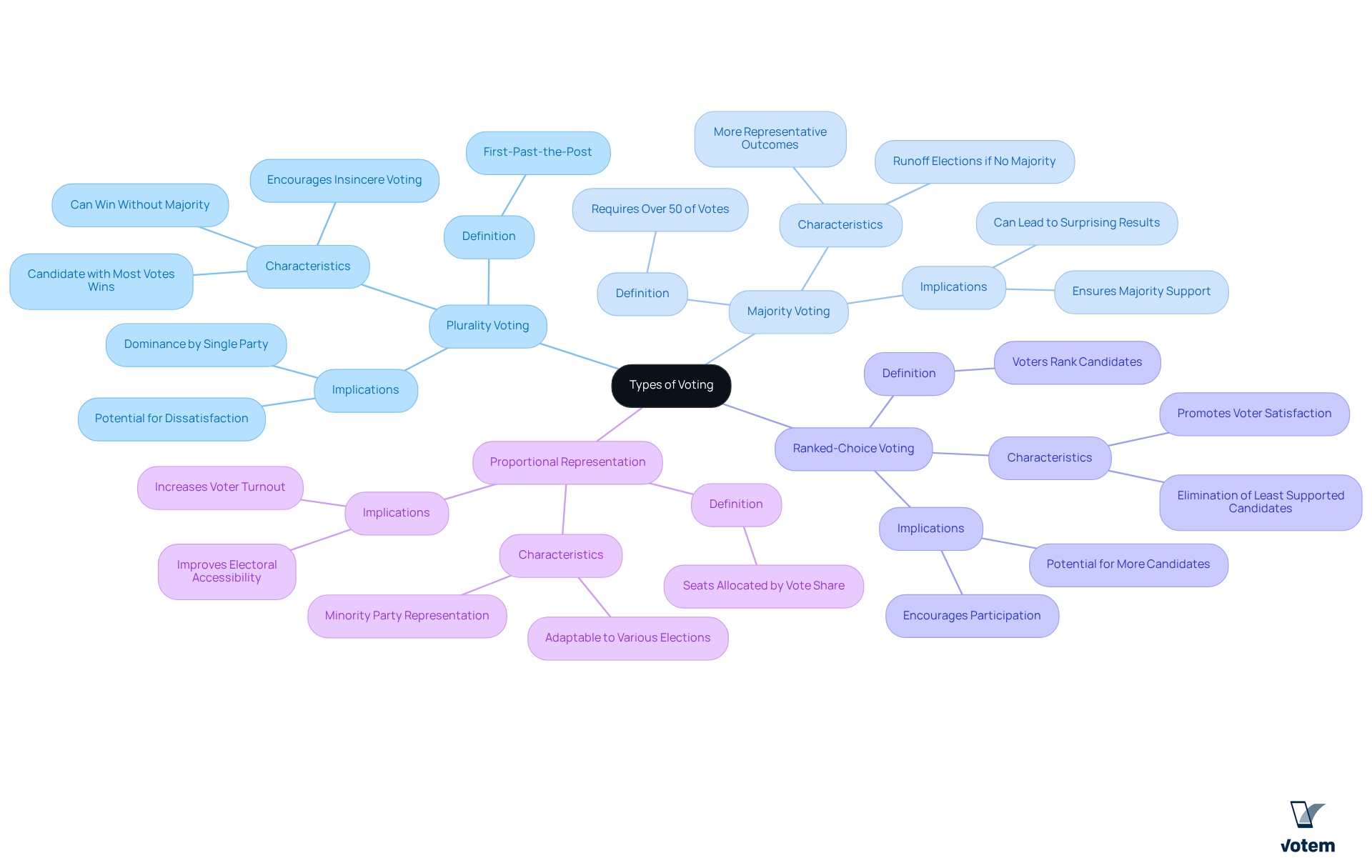
Define the Four Types of Voting
The 4 types of voting—plurality, majority, ranked-choice, and proportional representation—are the four main categories of electoral systems that play a crucial role in shaping electoral outcomes and enhancing public participation.
Plurality Voting, which is one of the 4 types of voting, is commonly referred to as ‘first-past-the-post’ and allows individuals to select one candidate. The candidate with the highest number of votes wins, regardless of securing a majority. Votem’s innovative online voting solutions ensure that this process is accessible to everyone, including individuals with disabilities and military personnel, thereby enhancing participation. As Linda McCulloch noted, implementing Votem’s system represented a significant achievement in expanding access for all qualified voters.
In the context of the 4 types of voting, Majority Voting is a system where a candidate must receive more than 50% of the votes to win. If no candidate achieves this threshold, a runoff election may occur between the leading candidates. Votem’s bolsters this method by providing transparent and auditable election processes, fostering trust among voters. A testament to its effectiveness, the National Radio Hall of Fame successfully conducted an election with Votem, garnering 299,000 ballots—a notable increase from the previous year.
Ranked-Choice Voting is one of the 4 types of voting that enables voters to rank their options in order of preference. If no candidate garners a majority of top-choice selections, the candidate with the least support is eliminated, and their ballots are reallocated until one candidate secures a majority. This method promotes voter participation and satisfaction, aligning with Votem’s mission to simplify the electoral process and enhance accessibility. The New Mexico State Republican Party expressed their satisfaction with Votem’s software, indicating a desire to utilize it for future elections.
Proportional Representation is one of the 4 types of voting, which allocates seats based on the share of ballots each party receives, ensuring that minority parties are represented in the legislature. Votem’s adaptable online ballot platform accommodates various election types and governance needs, making it an ideal choice for organizations aiming to improve electoral accessibility and safety, especially in light of challenges posed by Covid-19. Votem facilitated the delivery of 123,000 ballots, more than double the turnout of the previous election, demonstrating its effectiveness in boosting voter participation.
Explore the Historical Context of Voting Types
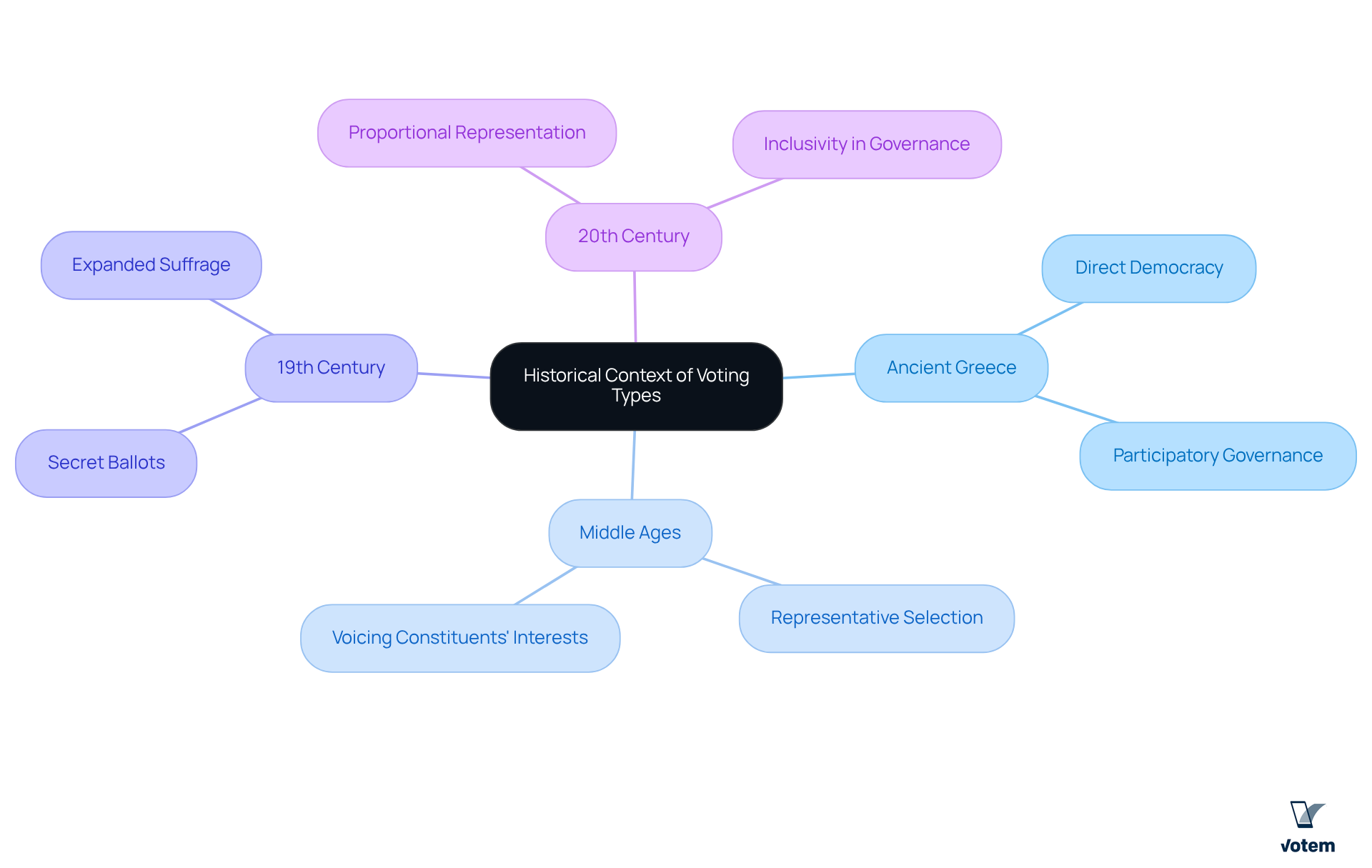
The development of electoral systems can be traced back to ancient democracies, particularly in Greece and Rome, where early forms of balloting were established. These foundational practices have significantly influenced modern electoral processes over the centuries, shaped by various political, social, and economic changes.
- Ancient Greece: This era introduced the concept of direct democracy, empowering citizens to vote directly on legislation. This practice laid the groundwork for participatory governance, setting the stage for future electoral systems.
- Middle Ages: During this period, balloting became more structured, marked by the selection of representatives who voiced the interests of their constituents. This shift towards was crucial in evolving the electoral landscape.
- 19th Century: The introduction of secret ballots and the expansion of suffrage were pivotal milestones that enhanced voter privacy and broadened access to the electoral process. These changes promoted democratic ideals and increased public participation in governance.
- 20th Century: The emergence of proportional representation systems aimed to ensure fairer representation for diverse political parties, reflecting the complexities of modern societies and the need for inclusivity in governance.
These historical developments underscore the ongoing evolution of ballot practices, illustrating how ancient systems continue to inform and shape contemporary electoral frameworks. As we reflect on these transformations, it is essential to recognize their relevance in addressing current challenges in electoral participation and representation.
Identify Key Characteristics of Each Voting Type
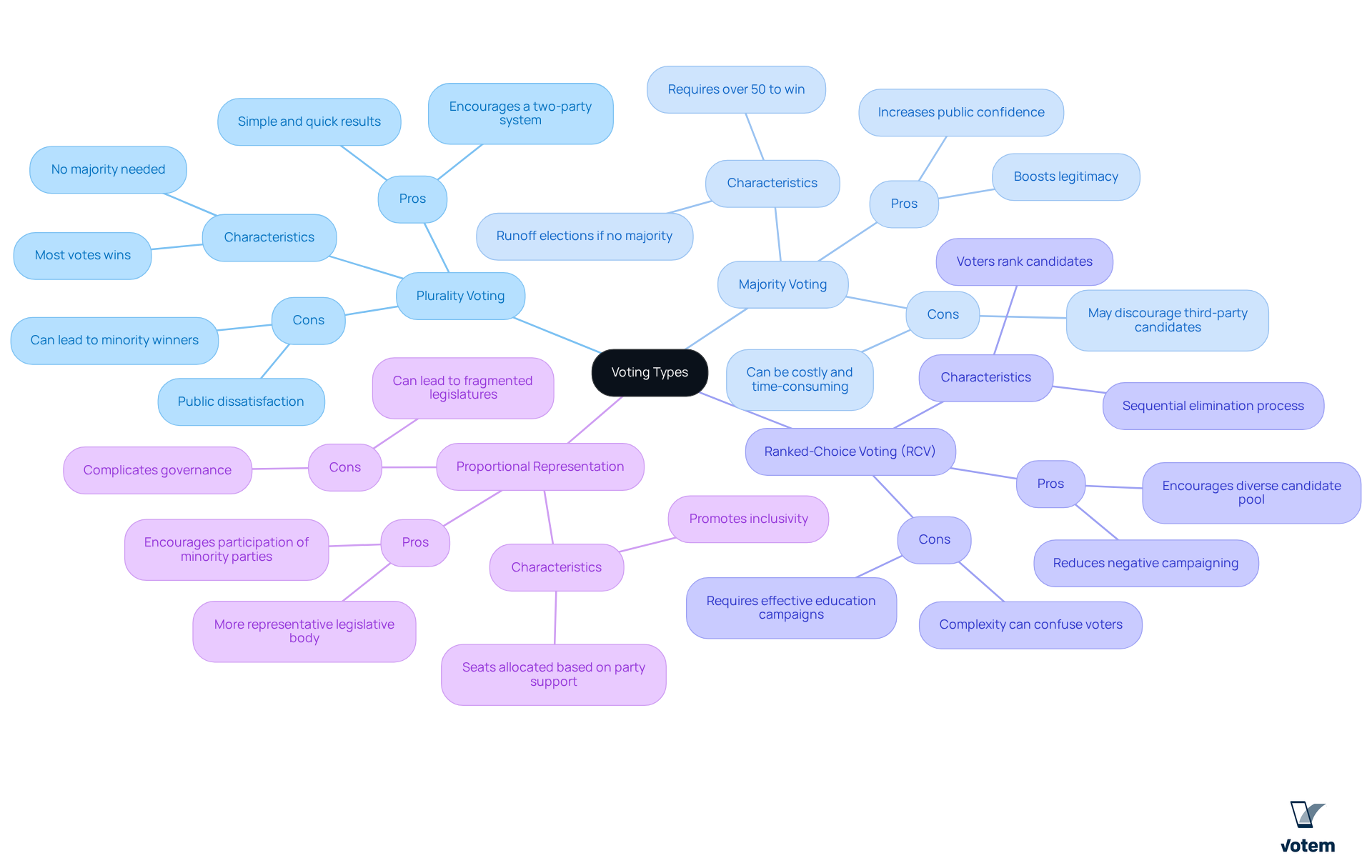
Each voting type possesses unique characteristics that significantly influence electoral outcomes:
- Plurality Voting: This method is straightforward and efficient, allowing a candidate to win with the most votes, even if they do not achieve a majority. However, this can lead to situations where the chosen individual does not represent the majority’s preference, often resulting in public dissatisfaction.
- Majority Voting: Among the 4 types of voting, Majority Voting requires that an individual attains over 50% of the votes to win, ensuring broader support. While it boosts legitimacy and public confidence, it may incur additional costs and time due to runoff elections. For instance, in the French Presidential elections, a second round occurs if no participant achieves a majority in the first round.
- Ranked-Choice Voting (RCV): RCV is one of the 4 types of voting that enables individuals to rank candidates according to their preferences, fostering a more varied candidate pool and minimizing negative campaigning. Research suggests that RCV can result in heightened satisfaction and involvement, especially within minority groups. However, its complexity can pose challenges for some individuals, necessitating effective education campaigns to enhance understanding.
- Proportional Representation: Proportional Representation, one of the 4 types of voting, assigns seats in accordance with the support obtained by parties, promoting inclusivity and representation of minority parties. While it can lead to a more representative legislative body, it may also result in fragmented legislatures and coalition governments, complicating governance.
Understanding the 4 types of voting is essential for assessing their effect on election results and the representation of public preferences in different political situations.
Provide Examples of Each Voting Type in Practice
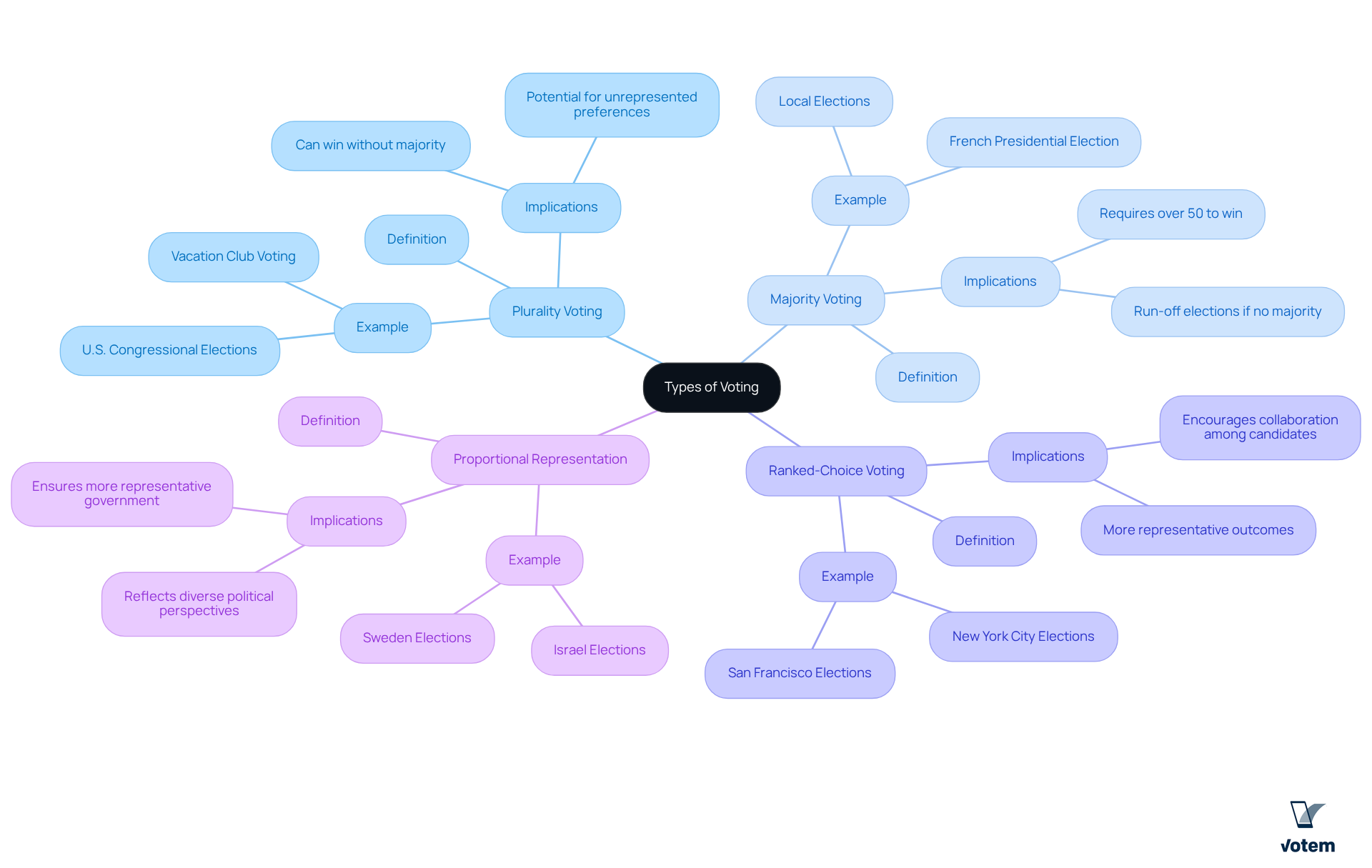
Understanding the 4 types of voting is essential, as voting systems play a crucial role in shaping electoral outcomes. Consider the following examples of each voting type in practice:
- Plurality Voting: This method is prevalent in U.S. congressional elections, where the candidate with the most votes wins, even without achieving a majority. For instance, in a recent election, an individual could succeed with only 30% of the support, highlighting the possibility of unrepresented preferences among the electorate. Votem’s innovative ensure that all qualified voters, including military personnel and those with disabilities, can participate in these elections, thereby enhancing accessibility.
- Majority Voting: Commonly employed in local elections, such as mayoral races, this system mandates that an individual must receive over 50% of the votes to win. If no nominee reaches this threshold, a runoff election is conducted. A notable example is the French presidential election, where a runoff occurs between the top two contenders if no one secures a majority in the first round, ensuring that the elected president has broad support. Votem’s commitment to accessibility has been acknowledged, as evidenced by the New Mexico State Republican Party’s satisfaction with Votem’s software, which they intend to utilize again for their upcoming elections.
- Ranked-Choice Voting: Implemented in cities like San Francisco and New York City, this system allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference. In a recent election in New York City, for example, no contender achieved a majority in the first round, prompting officials to tally second-choice selections. This method fosters collaboration among candidates and can lead to more representative outcomes. Votem’s platform has been instrumental in enhancing participation, as demonstrated by their management of 299,000 ballots for the National Radio Hall of Fame, a significant increase from the previous year.
- Proportional Representation: Utilized in countries such as Sweden and Israel, this system allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives. This approach ensures a more representative government, allowing diverse political perspectives to be reflected in the legislature. Votem’s dedication to election integrity and accessibility has contributed to record voter participation, as shown by their effective implementation of solutions that address diverse voter needs.
These examples illustrate the varying implications of different voting systems, underscoring the importance of grasping their mechanics and outcomes in fostering democratic engagement.
Conclusion
Understanding the four types of voting—plurality, majority, ranked-choice, and proportional representation—reveals their fundamental role in shaping electoral outcomes and enhancing democratic participation. Each system offers distinct mechanisms that influence how representatives are chosen and how effectively the electorate’s preferences are reflected in governance.
Throughout this article, we explored the key characteristics of each voting type, highlighting their advantages and potential drawbacks.
- Plurality voting, while straightforward, can lead to unrepresented preferences.
- Majority voting ensures broader support but may require costly runoff elections.
- Ranked-choice voting promotes satisfaction and inclusivity but demands a higher level of voter understanding.
- Proportional representation fosters diversity in legislative bodies, although it can complicate governance through coalition-building.
In a world where democratic engagement is crucial, recognizing the significance of these voting systems is paramount. Each type of voting not only impacts individual elections but also shapes the broader landscape of governance and representation. Embracing this understanding can empower citizens to advocate for electoral reforms that enhance participation and ensure that all voices are heard in the democratic process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four types of voting?
The four types of voting are plurality, majority, ranked-choice, and proportional representation.
How does Plurality Voting work?
Plurality Voting, also known as ‘first-past-the-post,’ allows individuals to select one candidate, and the candidate with the highest number of votes wins, regardless of securing a majority.
What is Majority Voting?
Majority Voting requires a candidate to receive more than 50% of the votes to win. If no candidate achieves this, a runoff election may occur between the leading candidates.
What is Ranked-Choice Voting?
Ranked-Choice Voting enables voters to rank their options in order of preference. If no candidate receives a majority of top-choice selections, the candidate with the least support is eliminated, and their ballots are reallocated until one candidate secures a majority.
What is Proportional Representation?
Proportional Representation allocates seats based on the share of ballots each party receives, ensuring that minority parties are represented in the legislature.
How does Votem enhance participation in voting?
Votem’s online voting solutions ensure accessibility for everyone, including individuals with disabilities and military personnel, thereby enhancing public participation in elections.
What are some benefits of using Votem’s voting platform?
Votem’s platform provides secure, transparent, and auditable election processes, which foster trust among voters and improve electoral accessibility and safety.
Can you provide an example of Votem’s effectiveness in an election?
The National Radio Hall of Fame successfully conducted an election using Votem, receiving 299,000 ballots, which was a notable increase from the previous year.
List of Sources
- Define the Four Types of Voting
- Plurality voting | Research Starters | EBSCO Research (https://ebsco.com/research-starters/political-science/plurality-voting)
- Ranked-Choice Voting – Center for Effective Government (https://effectivegov.uchicago.edu/primers/ranked-choice-voting)
- Plurality vs. Majority Voting | Differences & Examples – Lesson | Study.com (https://study.com/learn/lesson/plurality-voting-vs-majority-voting-summaries-differences-uses.html)
- Explore the Historical Context of Voting Types
- Voter turnout, 2018-2022 (https://pewresearch.org/politics/2023/07/12/voter-turnout-2018-2022)
- census.gov (https://census.gov/topics/public-sector/voting.html)
- Identify Key Characteristics of Each Voting Type
- Plurality vs. Majority Voting | Differences & Examples – Lesson | Study.com (https://study.com/learn/lesson/plurality-voting-vs-majority-voting-summaries-differences-uses.html)
- What We Know About Ranked Choice Voting, Updated for 2025 (https://americanbar.org/groups/public_interest/election_law/american-democracy/our-work/what-we-know-about-ranked-choice-voting-2025)
- Ranked-Choice Voting – Center for Effective Government (https://effectivegov.uchicago.edu/primers/ranked-choice-voting)
- britannica.com (https://britannica.com/topic/election-political-science/Plurality-and-majority-systems)
- Provide Examples of Each Voting Type in Practice
- New York City’s mayoral primary casts bright light on ranked choice voting — and its future nationally (https://nbcnews.com/politics/elections/new-york-city-mayoral-primary-casts-bright-light-ranked-choice-voting-rcna213812)
- Plurality vs. Majority Voting | Differences & Examples – Lesson | Study.com (https://study.com/learn/lesson/plurality-voting-vs-majority-voting-summaries-differences-uses.html)
- courses.lumenlearning.com (https://courses.lumenlearning.com/coloradomesa-mathforliberalartscorequisite/chapter/plurality-method)
- Exploring Plural Voting as a Method for Citizen Engagement (https://newamerica.org/political-reform/briefs/exploring-plural-voting-as-a-method-for-citizen-engagement)

