Overview
The D’Hondt system represents a pivotal method of proportional representation, meticulously designed to allocate legislative positions in direct relation to the votes garnered by each party. This approach not only enhances electoral fairness but also significantly reduces the incidence of wasted votes.
The article elaborates on the systematic procedure involved in vote counting, division, and seat allocation, detailing its practical applications across various countries.
Furthermore, it highlights the balance the D’Hondt system strikes between larger and smaller parties, ultimately fostering a diverse political environment that is essential for a healthy democracy.
Introduction
The quest for fair electoral representation is a pivotal issue that often leads to complex discussions about the systems governing our democratic processes. Among these, the D’Hondt method emerges as a powerful tool, effectively translating votes into legislative seats and balancing the scales between larger and smaller political parties. As this method continues to influence elections across various countries, one must critically consider: does it truly promote inclusivity, or does it inadvertently favor established powers? This exploration delves into the mechanics of the D’Hondt system, its applications, and the ongoing debate surrounding its advantages and criticisms. Ultimately, it reveals the profound impact this method has on modern electoral representation.
Define the D’Hondt Method and Its Purpose
The d’Hondt system, developed by Belgian mathematician Victor, is a prominent highest averages method used for allocating positions in party-list proportional representation systems. Its primary objective is to align the distribution of legislative positions with the votes garnered by each group using the d’Hondt system, thereby enhancing electoral fairness. By mitigating the gap between the percentage of votes and the corresponding percentage of positions, this method fosters a more equitable political environment.
Particularly advantageous in multi-member districts, the d’Hondt system empowers smaller groups to make their voices heard while still providing a slight advantage to larger organizations. This equilibrium cultivates a , ensuring that various perspectives are represented in the legislative process.
Furthermore, empirical research indicates that although the d’Hondt system tends to favor larger groups, it still provides smaller factions a viable opportunity to secure positions, thereby contributing to a more balanced system. For instance, in recent elections employing this method, smaller groups have successfully bolstered their presence in legislatures, underscoring its effectiveness in promoting inclusivity and reducing voter disenfranchisement.
Explain the Procedure of the D’Hondt Method
The d’hondt system employs a systematic procedure designed to ensure proportional representation in electoral systems. This aligns seamlessly with Votem’s mission to enhance accessibility, security, and transparency in elections. Understanding the key steps involved is essential:
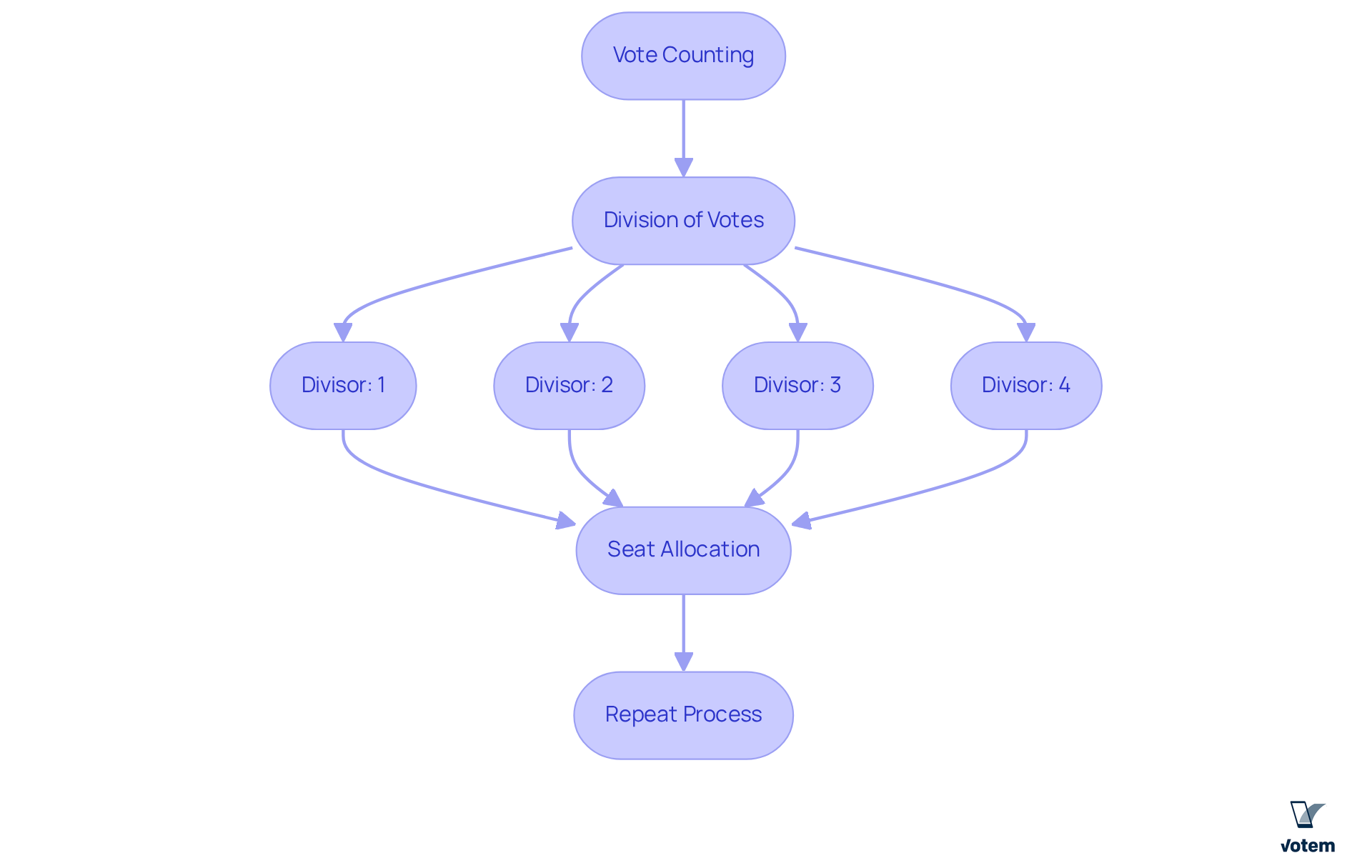
- Vote Counting: The process commences with the tallying of total votes received by each group during the election.
- Division of Votes: Each group’s total votes are divided by a series of divisors: 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. This division generates a list of quotients for each group.
- Seat Allocation: The quotients are ranked from highest to lowest. Groups with the highest quotients are assigned available positions in the legislature, one at a time, until all positions are filled.
- Repeat: If an entity secures a position, its total votes are divided by the next divisor, and the process continues until all positions are allocated.
This approach significantly reduces wasted votes, ensuring that smaller parties receive representation proportional to their support, thereby enhancing democratic participation. For instance, in a recent election with 9,000 voters, the quota was established at 900 votes per seat, showcasing its effectiveness in equitable seat distribution. By utilizing this organized method, the d’hondt system promotes a balanced framework, facilitating a diverse political environment. In contrast to single-member plurality systems, it markedly decreases wasted votes, reinforcing its role as a fair electoral tool. Votem’s commitment to further strengthens the proportional representation method, positioning it as a reliable ally for efficient electoral processes.
Discuss Applications of the D’Hondt Method in Electoral Systems
The d’hondt system serves as a fundamental aspect of , effectively employed in numerous nations to ensure just electoral outcomes. Its key applications illustrate its significance:
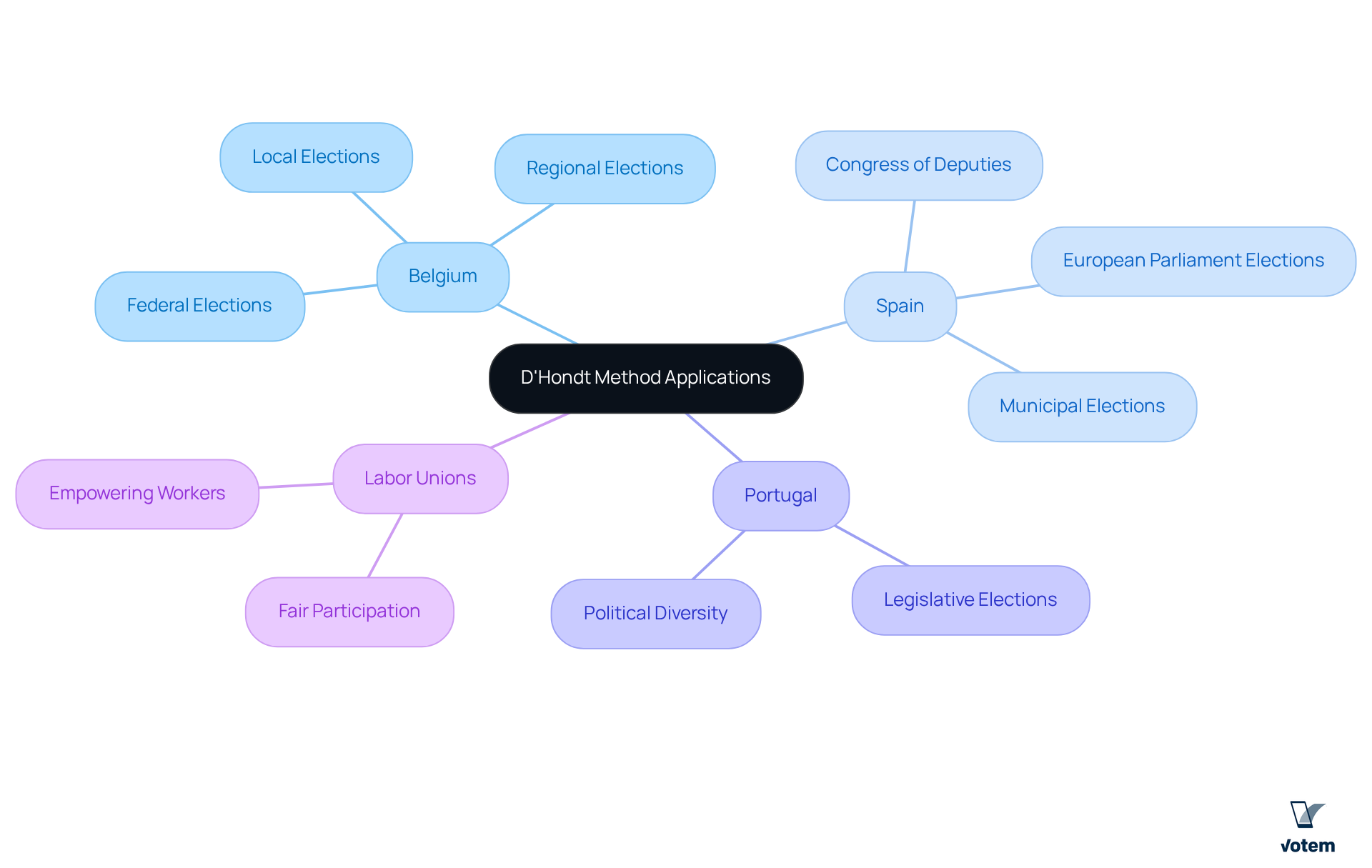
- Belgium: This method is integral to federal, regional, and local elections, accurately reflecting the country’s diverse political landscape and facilitating representation for various parties.
- Spain: Utilized in the Congress of Deputies, the d’hondt system is a proportional representation method that fosters a multi-political system, enabling smaller groups to secure seats while ensuring a stable government.
- Portugal: The d’hondt system is crucial in legislative elections, as it allows smaller parties to gain a voice, contributing to a balanced political environment.
- Labor Unions: In union elections, the method guarantees fair participation of various groups, empowering workers and enhancing the democratic process within the organization. By applying this method, unions can better reflect the diverse voices of their members, promoting inclusivity and fairness in decision-making.
Furthermore, adopting this method not only strengthens representation but also addresses the challenges faced by union leadership in fostering a democratic environment. It is imperative for union leaders to consider these applications as they strive for equitable representation within their organizations.
Evaluate the Advantages and Criticisms of the D’Hondt Method
The method presents a blend of advantages and criticisms that are essential for understanding its impact on electoral representation.
Advantages:
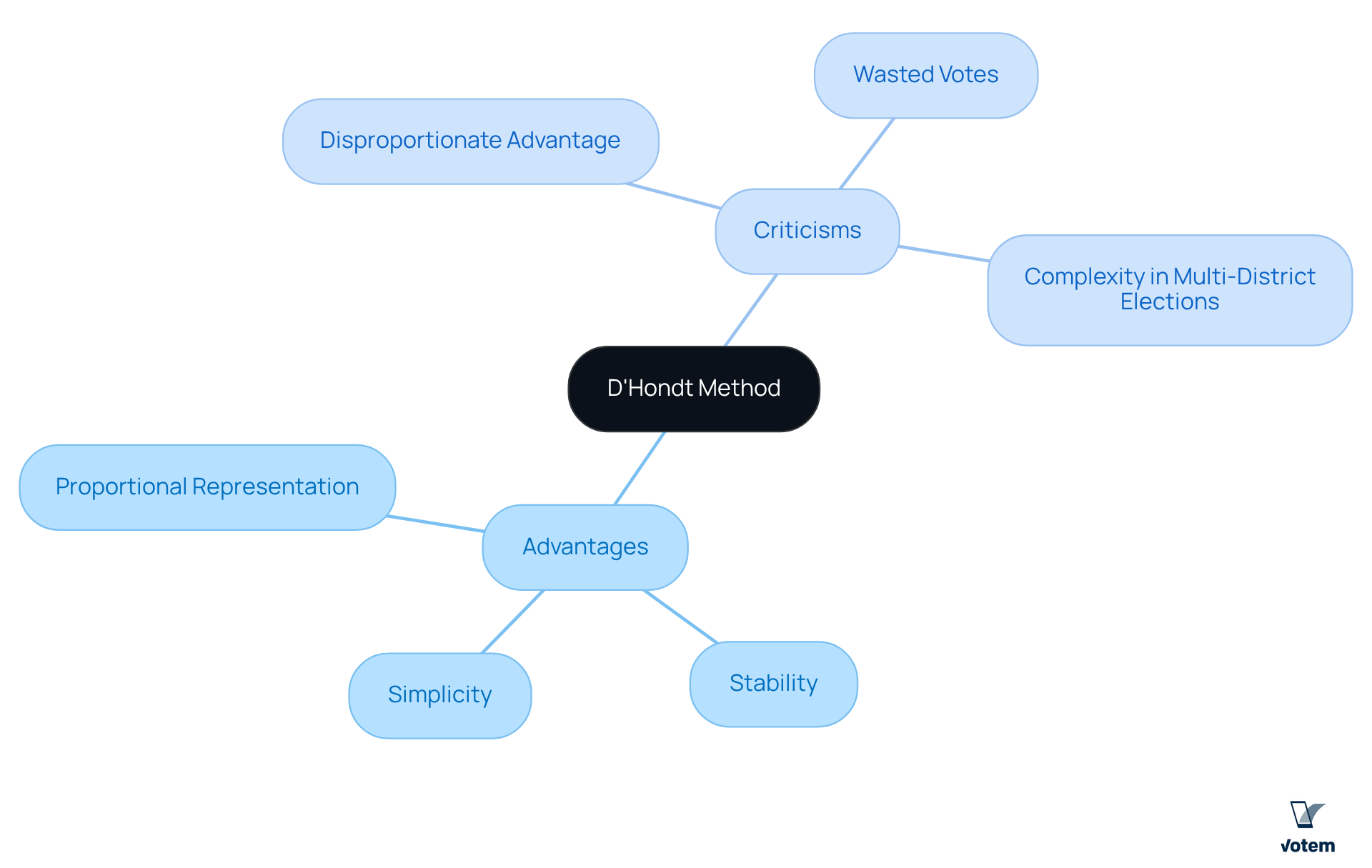
- Proportional Representation: This method effectively translates votes into seats, ensuring that the distribution of seats reflects the electorate’s preferences. Such a system is particularly beneficial in promoting fairness across diverse political landscapes.
- Stability: By supporting larger groups, the method can lead to more stable governments, decreasing the chances of coalition instability. This stability is crucial in maintaining effective governance, especially in multi-party systems.
- Simplicity: The d’hondt system is relatively straightforward to understand and implement, which makes it accessible for various electoral bodies. Its clarity aids in public comprehension, fostering trust in the electoral process.
Criticisms:
- Disproportionate Advantage: One of the primary criticisms is that smaller parties may struggle to gain representation, as the method tends to favor larger parties. This can lead to a lack of diversity in governance, undermining the representation of minority voices.
- Wasted Votes: Votes cast for groups that do not meet the threshold for allocation may be regarded as wasted. This phenomenon can discourage voter participation, as individuals may feel their votes do not contribute to the electoral outcome.
- Complexity in Multi-District Elections: In elections involving multiple districts, the use of the proportional representation method can become complicated. This complexity may lead to confusion among voters, potentially impacting their engagement and understanding of the electoral process.
The formula is computed as V / (1 + S), where V signifies the count of votes obtained by a group and S indicates the number of positions occupied by that group. This mathematical method guarantees that larger groups obtain a proportional portion of influence while still permitting smaller groups an opportunity to gain seats.
Understanding these advantages and criticisms is crucial for organizations, particularly labor unions, that are for their electoral processes. The method’s ability to balance representation while ensuring stability makes it a significant consideration in modern electoral systems.
Conclusion
The d’Hondt system serves as a pivotal mechanism in electoral representation, meticulously designed to ensure that legislative positions align closely with the votes garnered by various political groups. By fostering a more equitable political landscape, this method amplifies the voices of smaller parties while preserving a degree of stability within larger organizations, ultimately contributing to a more inclusive democratic process.
Key aspects of the d’Hondt method have been thoroughly explored, including its systematic procedures for vote counting, division, and seat allocation. The advantages of this method—such as its capacity to reduce wasted votes and promote proportional representation—are significant. However, criticisms pointing to potential imbalances favoring larger parties cannot be overlooked. The practical applications of the d’Hondt system across various countries and contexts further underscore its importance in promoting fair representation within electoral systems.
Recognizing the impact of the d’Hondt method on electoral outcomes is crucial for electoral bodies, political organizations, and voters alike. By understanding its strengths and weaknesses, stakeholders can make informed decisions that enhance democratic participation and representation. Embracing such systems empowers diverse voices and strengthens the foundation of democratic governance, paving the way for a more balanced and fair political landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the d’Hondt method?
The d’Hondt method is a highest averages system used for allocating positions in party-list proportional representation systems, developed by Belgian mathematician Victor d’Hondt.
What is the primary purpose of the d’Hondt method?
The primary purpose of the d’Hondt method is to align the distribution of legislative positions with the votes received by each group, thereby enhancing electoral fairness and reducing the gap between the percentage of votes and corresponding positions.
In what type of electoral districts is the d’Hondt method particularly advantageous?
The d’Hondt method is particularly advantageous in multi-member districts, as it allows smaller groups to be represented while still giving a slight advantage to larger organizations.
How does the d’Hondt method contribute to a diverse political landscape?
By enabling various perspectives to be represented in the legislative process, the d’Hondt method fosters a diverse political landscape and ensures that multiple voices are heard.
Does the d’Hondt method favor larger groups over smaller ones?
Yes, while the d’Hondt method tends to favor larger groups, it still provides smaller factions with a viable opportunity to secure positions, contributing to a more balanced electoral system.
What evidence supports the effectiveness of the d’Hondt method?
Empirical research shows that smaller groups have successfully increased their presence in legislatures during recent elections that employed the d’Hondt method, highlighting its effectiveness in promoting inclusivity and reducing voter disenfranchisement.
List of Sources
- Define the D’Hondt Method and Its Purpose
- Senedd election 2026: What is the D’Hondt formula and how does it work? (https://senedd.wales/senedd-now/senedd-blog/senedd-election-2026-what-is-the-d-hondt-formula-and-how-does-it-work)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- D’Hondt Method Ensuring Fair Selection in Elections – HAMKO (https://hamko.fi/en/dhondt-method-ensuring-fair-selection-in-elections)
- D’Hondt method – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D’Hondt_method)
- Explain the Procedure of the D’Hondt Method
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method: Its Use in the Northern Ireland Assembly (https://niassembly.gov.uk/news-and-media/assembly-explained/understanding-the-dhondt-method-its-use-in-the-northern-ireland-assembly)
- Everything you wanted to know about D’Hondt voting system before Holyrood election (https://thenational.scot/news/19209143.everything-wanted-know-dhondt-voting-system-holyrood-election)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- Election 2015: What difference would proportional representation have made? (https://bbc.co.uk/news/election-2015-32601281)
- D’Hondt system for picking NI ministers in Stormont (https://bbc.com/news/uk-northern-ireland-politics-13359731)
- Discuss Applications of the D’Hondt Method in Electoral Systems
- 5 Global Elections To Watch In 2025 (https://ndtv.com/world-news/5-global-elections-to-watch-in-2025-7391148)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- General Elections 2025 Portugal (https://robert-schuman.eu/en/monitor/6520-the-social-democratic-party-of-outgoing-prime-minister-luis-montenegro-favourite-in-the-general-election-in-portugal-on-18-may)
- The D’Hondt Method and the scapegoat theory | Ideas for democracy (https://minsait.com/ideasfordemocracy/en/dhondt-method-and-scapegoat-theory)
- D’Hondt method – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D’Hondt_method)
- Evaluate the Advantages and Criticisms of the D’Hondt Method
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method in modern elections (https://eligovoting.com/understanding-the-dhondt-method)
- Rethinking the D’Hondt method (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/2474736X.2019.1625712)
- Understanding the D’Hondt Method: Its Use in the Northern Ireland Assembly (https://niassembly.gov.uk/news-and-media/assembly-explained/understanding-the-dhondt-method-its-use-in-the-northern-ireland-assembly)

