Overview
Voting districts are defined geographic areas created to elect representatives to legislative bodies. They play a crucial role in facilitating representative democracy and ensuring that constituents’ voices are heard. Well-organized districts enhance voter participation and trust in the electoral system. Conversely, poorly structured districts can lead to disenfranchisement and unequal representation. This highlights the importance of understanding their characteristics and historical context, as it is essential for fostering a fair electoral process.
Introduction
Voting districts are fundamental to the democratic process, acting as the backbone of representative governance. By delineating geographic areas for the election of officials, these districts ensure that the diverse voices of constituents are not only heard but also represented.
However, the effectiveness of these districts is often undermined by challenges such as gerrymandering and unequal representation, which raise critical questions about the integrity of electoral outcomes.
Furthermore, how can a deeper understanding of the importance and characteristics of voting districts empower citizens to advocate for a more equitable political landscape?
Define Voting Districts: Purpose and Importance
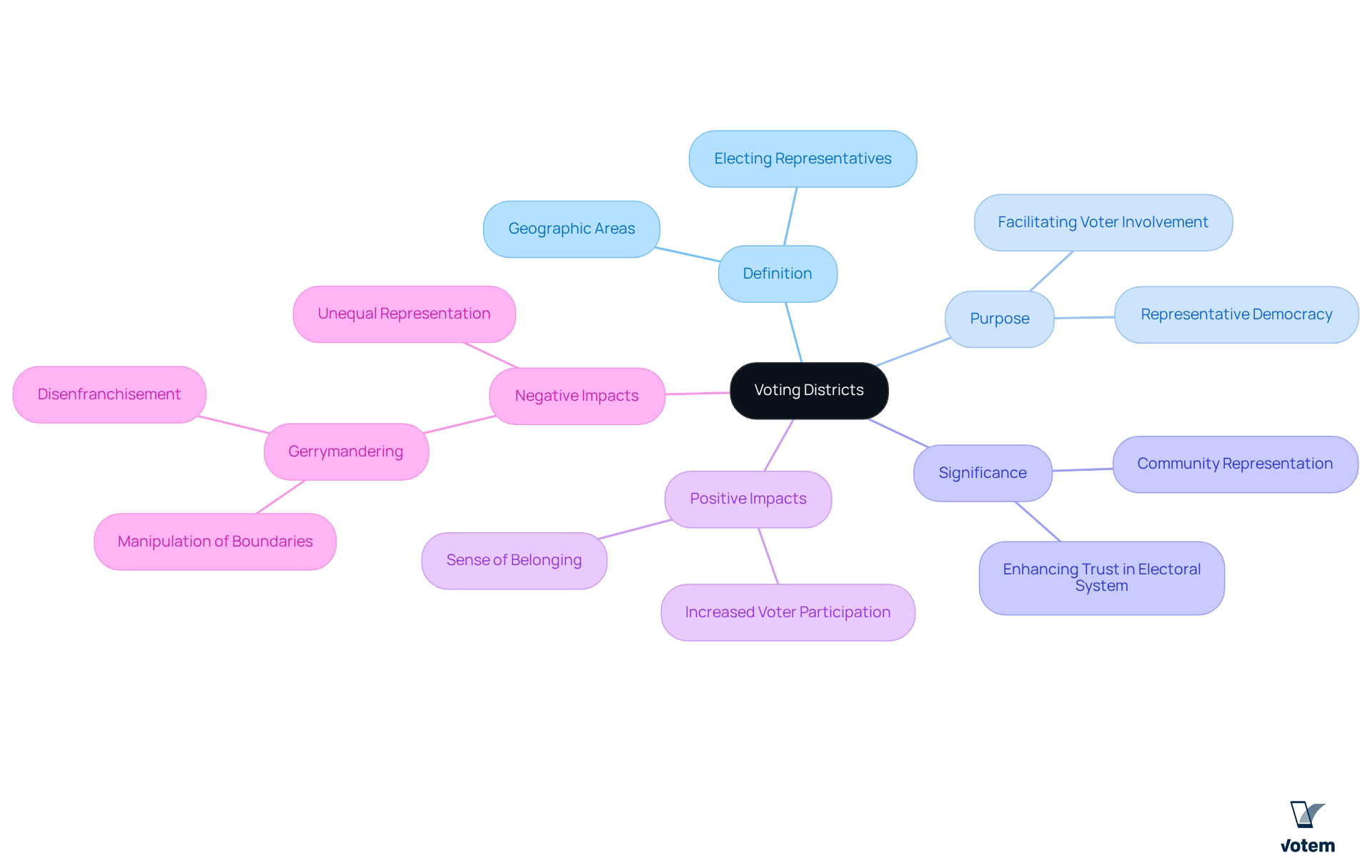
What are voting districts? They are defined geographic areas established for the purpose of electing representatives to legislative bodies, with each area typically selecting one or more officials. Their significance lies in facilitating representative democracy, ensuring that constituents’ voices are effectively heard in government. Well-organized areas can greatly enhance voter involvement and confidence in the electoral system. For instance, when regions are designed to reflect community interests and demographics, they foster a sense of belonging and stimulate participation in elections.
Conversely, inadequately structured regions can lead to disenfranchisement and unequal representation, ultimately undermining the democratic process. The manipulation of regional boundaries, commonly referred to as gerrymandering, can diminish the electoral influence of specific groups, further eroding trust in the system. Therefore, recognizing what are voting districts is crucial for .
In this context, Votem‘s innovative online voting solutions play a vital role, enhancing accessibility for all qualified participants, including military personnel and individuals with disabilities. As Linda McCulloch noted, implementing Votem’s modern system was a significant accomplishment, allowing for greater access to the electoral process. Furthermore, Votem’s capacity to manage a substantial increase in votes, as evidenced by their handling of 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, underscores their effectiveness in boosting voter participation and trust in the electoral system.
Trace the History of Voting Districts: Evolution and Impact
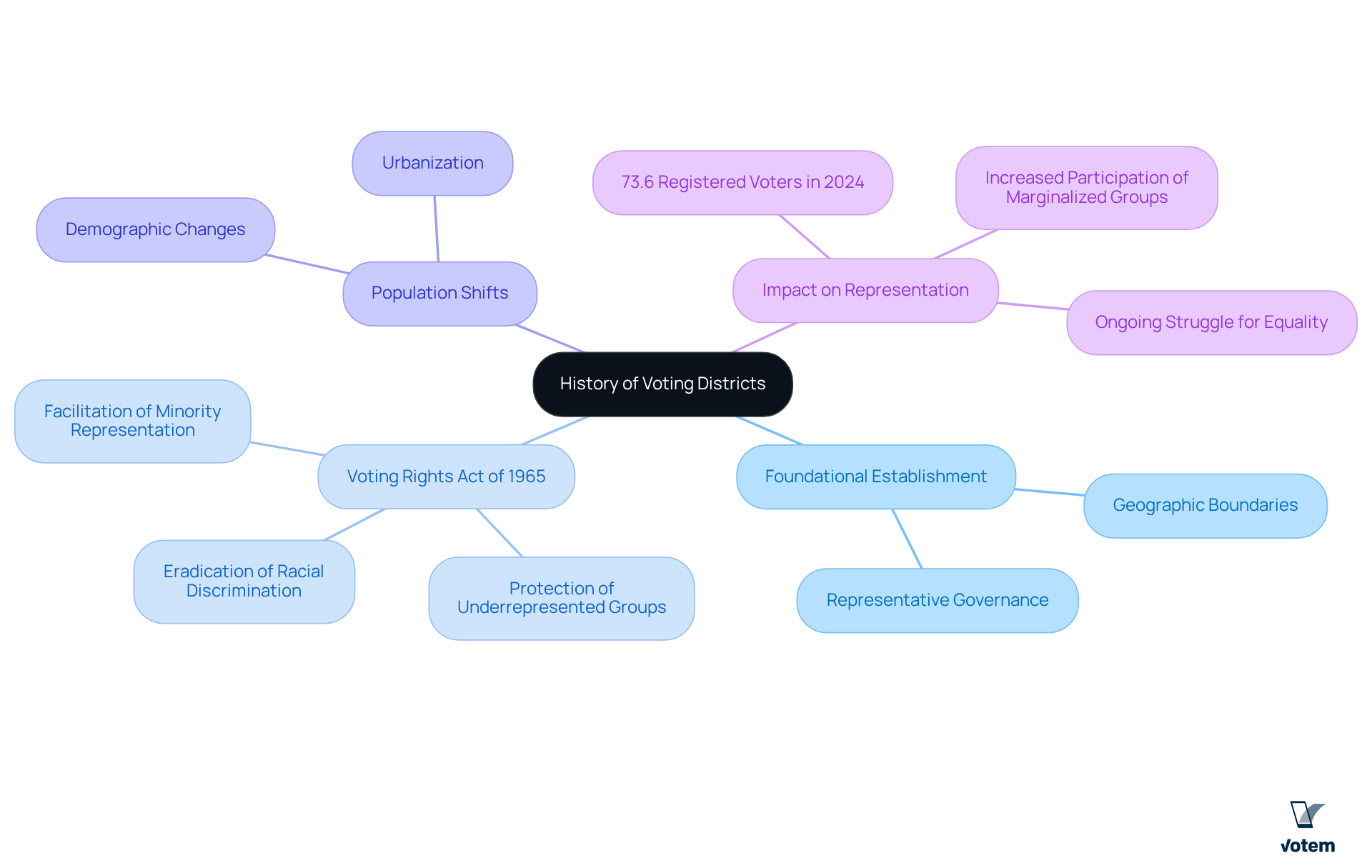
The concept of electoral regions, also known as voting districts, traces back to the foundational establishment of representative governance, where geographic boundaries primarily defined these areas. As society has progressed, however, various factors—including population shifts, urbanization, and demographic changes—have significantly influenced voting districts.
A pivotal moment in this evolution was the enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which sought to eradicate racial discrimination in electoral practices. This landmark legislation not only aimed to protect the but also facilitated the creation of regions that more accurately reflected minority populations.
The impact of the Voting Rights Act is evident in the statistical landscape of electoral regions; for instance, the 2024 presidential election saw 73.6% of the eligible population registered to vote, highlighting increased participation among historically marginalized groups.
The ongoing evolution of electoral regions underscores the persistent struggle for equality and representation, making their historical trajectory essential for understanding the dynamics of contemporary electoral processes.
Examine Key Characteristics of Voting Districts: Structure and Criteria
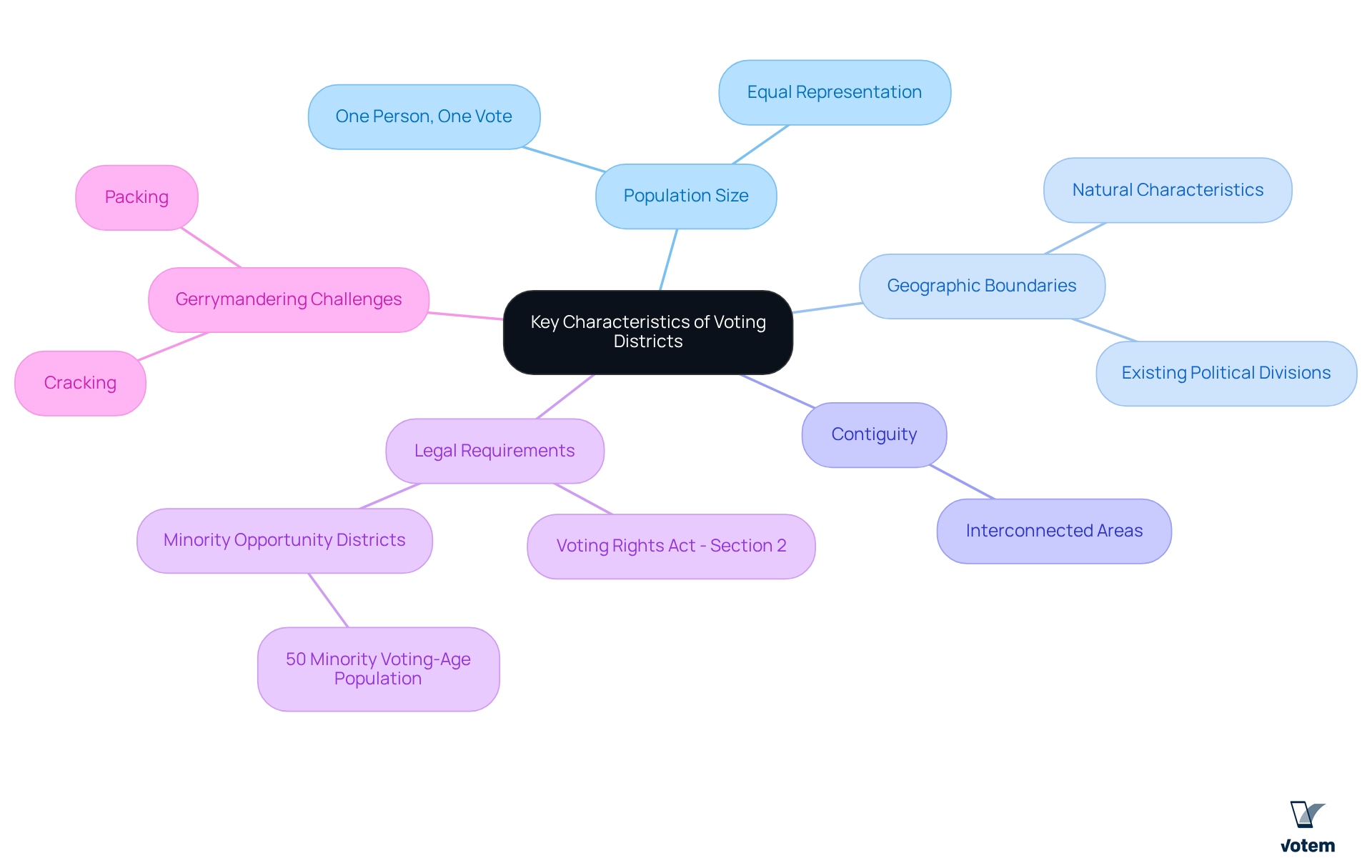
Key features of electoral areas are critical to understanding the electoral process. These features encompass population size, geographic boundaries, and the principle of contiguity. Ideally, regions should maintain approximately equal populations to ensure fair representation—a fundamental concept known as ‘one person, one vote.’ As established by the Supreme Court, minorities must constitute at least 50% of a minority opportunity area’s voting-age population. This requirement is essential for comprehending the surrounding voting areas.
Geographic boundaries are often delineated to reflect natural characteristics or existing political divisions. In addition, contiguity ensures that all sections of an area remain interconnected. Furthermore, regions must comply with legal mandates, including Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act, which requires that the same number of minority opportunity areas from a prior redistricting plan be replicated in any new plan. This legal context is vital for grasping the implications of districting practices.
Moreover, the potential challenges posed by gerrymandering, such as cracking and packing, represent significant obstacles within the realm of electoral regions. These characteristics are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the electoral process. It is imperative for union leadership to recognize these elements and their impact on fair representation, thereby ensuring that electoral areas are structured to uphold democratic principles.
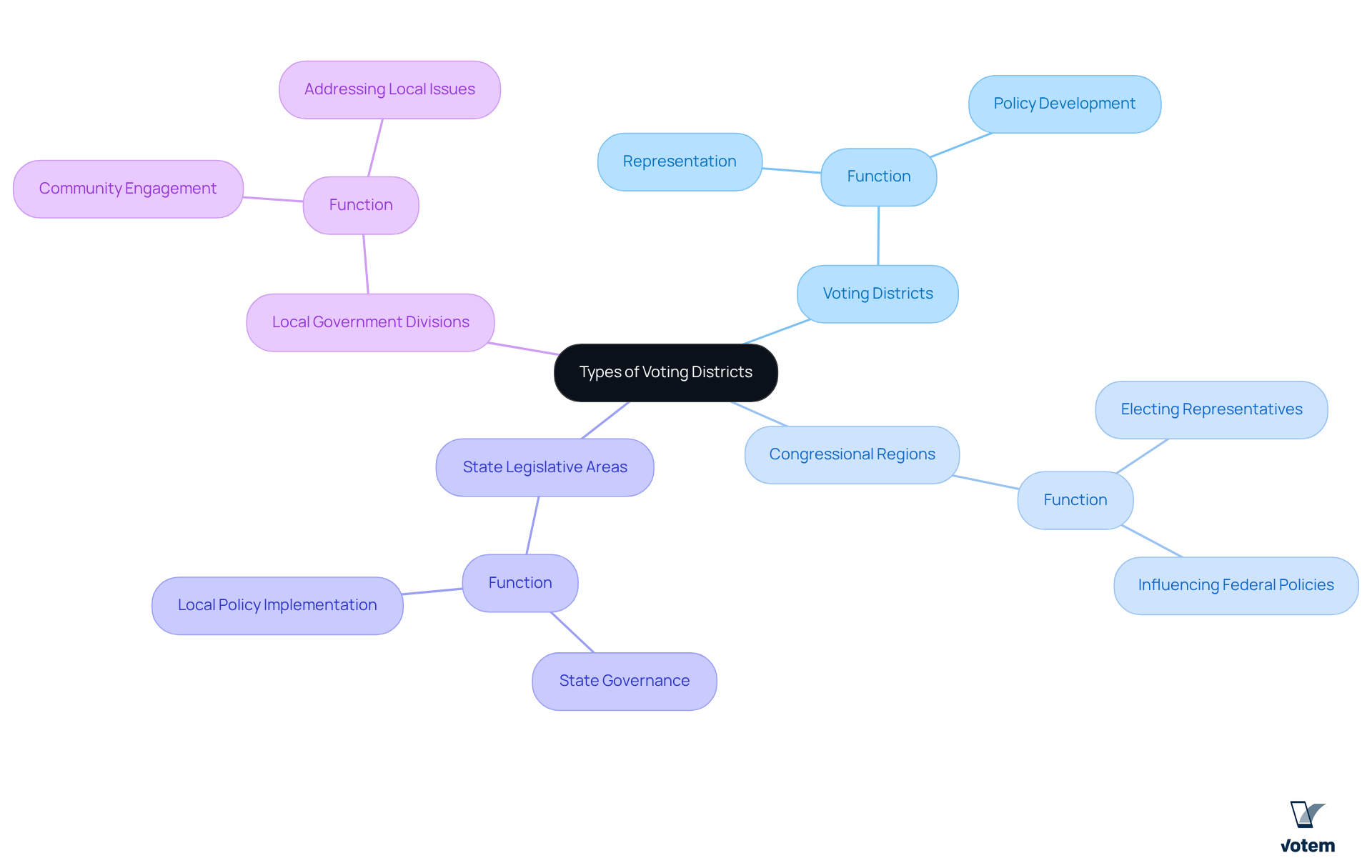
Explore Types of Voting Districts: Examples and Functions
Voting areas can be classified into various types, including what are voting districts, congressional regions, state legislative zones, and local government divisions. Congressional regions are essential for electing representatives to the U.S. House of Representatives, while state legislative areas serve comparable functions at the state level. Local government areas, such as school board or city council regions, focus on community-level governance. Each category of region serves a unique function, influencing how policies are developed and implemented. Well-structured local districts, for instance, can significantly enhance and ensure that local issues are adequately addressed in governance.
As of August 1, 2025, Virginia boasts 6,292,585 registered individuals, a statistic that underscores the significance of participation in shaping policy development. The active participation of these voters is crucial, as each vote carries substantial weight in the democratic process. Rev. Theodore Hesburgh aptly stated, “Voting is a civic sacrament,” emphasizing the moral obligation of citizens to engage in elections. This perspective enriches the conversation about electoral districts, linking their importance to broader civic values.
Historically, elections have served as a cornerstone of democracy, evolving over centuries to reflect the values of freedom, equality, and justice. Votem’s innovative online voting solutions have played a pivotal role in enhancing accessibility for all eligible participants, including military personnel and individuals with disabilities. Testimonials from various stakeholders highlight the effectiveness of Votem’s systems in increasing voter turnout and ensuring secure, efficient elections. Ignoring elections can lead to self-inflicted consequences, diminishing the voice of the electorate and undermining the democratic process. Thus, the function of what are voting districts extends beyond mere representation; they are instrumental in fostering democratic participation and ensuring that governance is responsive to the community’s needs.
Conclusion
Voting districts are pivotal in ensuring the effective functioning of democracy by delineating geographic areas for electing representatives. These districts amplify the voices of constituents and foster community engagement in the electoral process. When designed thoughtfully, voting districts enhance representation and build trust in governance; conversely, poorly structured areas can lead to disenfranchisement and undermine the democratic fabric.
The historical evolution of voting districts is significant, particularly the impact of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 in promoting equitable representation. Key characteristics such as population equality, geographic boundaries, and legal requirements underscore the necessity of maintaining the integrity of electoral processes. Furthermore, exploring various types of voting districts illustrates their unique functions in shaping policy and governance at local, state, and federal levels.
Ultimately, understanding the intricacies of voting districts is crucial for fostering a representative democracy that reflects the diverse voices within a community. As citizens, engaging in the electoral process is not merely a right but a responsibility that shapes the future of governance. Embracing this civic duty ensures that the democratic system remains robust and responsive to the needs of all constituents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are voting districts?
Voting districts are defined geographic areas established for the purpose of electing representatives to legislative bodies, with each area typically selecting one or more officials.
Why are voting districts important?
Voting districts are important because they facilitate representative democracy, ensuring that constituents’ voices are effectively heard in government. Well-organized areas enhance voter involvement and confidence in the electoral system.
How do well-structured voting districts affect voter participation?
Well-structured voting districts can foster a sense of belonging and stimulate participation in elections by reflecting community interests and demographics.
What are the consequences of inadequately structured voting districts?
Inadequately structured voting districts can lead to disenfranchisement and unequal representation, undermining the democratic process.
What is gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering is the manipulation of regional boundaries to diminish the electoral influence of specific groups, which can erode trust in the electoral system.
How does Votem enhance the voting process?
Votem enhances the voting process by providing innovative online voting solutions that improve accessibility for all qualified participants, including military personnel and individuals with disabilities.
What did Linda McCulloch say about Votem’s system?
Linda McCulloch noted that implementing Votem’s modern system was a significant accomplishment, allowing for greater access to the electoral process.
How effective is Votem in managing votes?
Votem has demonstrated its effectiveness in managing a substantial increase in votes, as evidenced by handling 299,000 votes for the National Radio Hall of Fame, which boosts voter participation and trust in the electoral system.
List of Sources
- Define Voting Districts: Purpose and Importance
- Understanding Redistricting: How It Shapes Our Democracy (https://headcount.org/voter-education/understanding-redistricting-how-it-shapes-our-democracy)
- Trump prompted a battle over voting maps. Here’s how redistricting affects voters (https://npr.org/2025/08/18/nx-s1-5495427/trump-redistricting-texas-congress-california)
- Legal Fights Over Voting Districts Could Play Role in Control of Congress for 2024 (https://news.wttw.com/2023/09/06/legal-fights-over-voting-districts-could-play-role-control-congress-2024)
- Redistricting and Gerrymandering: What to Know | Bipartisan Policy Center (https://bipartisanpolicy.org/explainer/redistricting-and-gerrymandering-what-to-know)
- Where are the lines drawn? – All About Redistricting (https://redistricting.lls.edu/redistricting-101/where-are-the-lines-drawn)
- Trace the History of Voting Districts: Evolution and Impact
- Voting Rights Act of 1965: History and Timeline (https://naacpldf.org/voting-rights-act-history-timeline)
- census.gov (https://census.gov/topics/public-sector/voting.html)
- History Of Federal Voting Rights Laws (https://justice.gov/crt/history-federal-voting-rights-laws)
- 45 Inspiring Quotes About Voting and Elections (https://shutterfly.com/ideas/inspiring-quotes-about-voting-and-elections)
- Redistricting | US House of Representatives: History, Art & Archives (https://history.house.gov/Exhibitions-and-Publications/BAIC/Historical-Essays/Power-Diversity/Redistricting)
- Examine Key Characteristics of Voting Districts: Structure and Criteria
- Congressional District Voting Rates and Population Characteristics (https://census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/congressional-district-voting-rates-and-population-characteristics.html)
- Public Mapping Project – Redistricting Criteria: The Voting Rights Act (https://publicmapping.org/what-is-redistricting/redistricting-criteria-the-voting-rights-act)
- What is Redistricting and How Does it Work? (https://naacpldf.org/how-redistricting-works)
- Where are the lines drawn? – All About Redistricting (https://redistricting.lls.edu/redistricting-101/where-are-the-lines-drawn)
- Redistricting and Gerrymandering: What to Know | Bipartisan Policy Center (https://bipartisanpolicy.org/explainer/redistricting-and-gerrymandering-what-to-know)
- Explore Types of Voting Districts: Examples and Functions
- 45 Inspiring Quotes About Voting and Elections (https://shutterfly.com/ideas/inspiring-quotes-about-voting-and-elections)
- Home (https://elections.virginia.gov/resultsreports/registration-statistics)
- Jesuit Resource – Election Day Quotes (https://xavier.edu/jesuitresource/online-resources/quote-archive1/election-dayvoting)