Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of voting machines, focusing on their features, security measures, and costs. It highlights the distinctions between Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) units and optical scan systems. While DRE machines are known for their user-friendly interfaces, optical scan systems stand out for their enhanced security and auditability, primarily due to the inclusion of a paper trail. This crucial aspect ultimately reinforces the integrity of the electoral process. Organizations seeking reliable voting solutions must consider these factors when selecting voting machines, ensuring that their choice supports both efficiency and security in elections.
Introduction
The evolution of voting technology has fundamentally transformed the electoral landscape, offering a diverse array of machines that promise to enhance the voting experience. As organizations increasingly seek secure and reliable methods for conducting elections, it becomes paramount to understand the intricacies of different voting systems—ranging from Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) units to optical scan systems. However, with rising concerns over security vulnerabilities and compliance standards, decision-makers must consider how to select the most effective voting machines for their unique needs. This article explores the features, benefits, and costs associated with various voting machines, equipping readers with the insights necessary to navigate this critical choice.
Overview of Voting Machines: Types and Functions
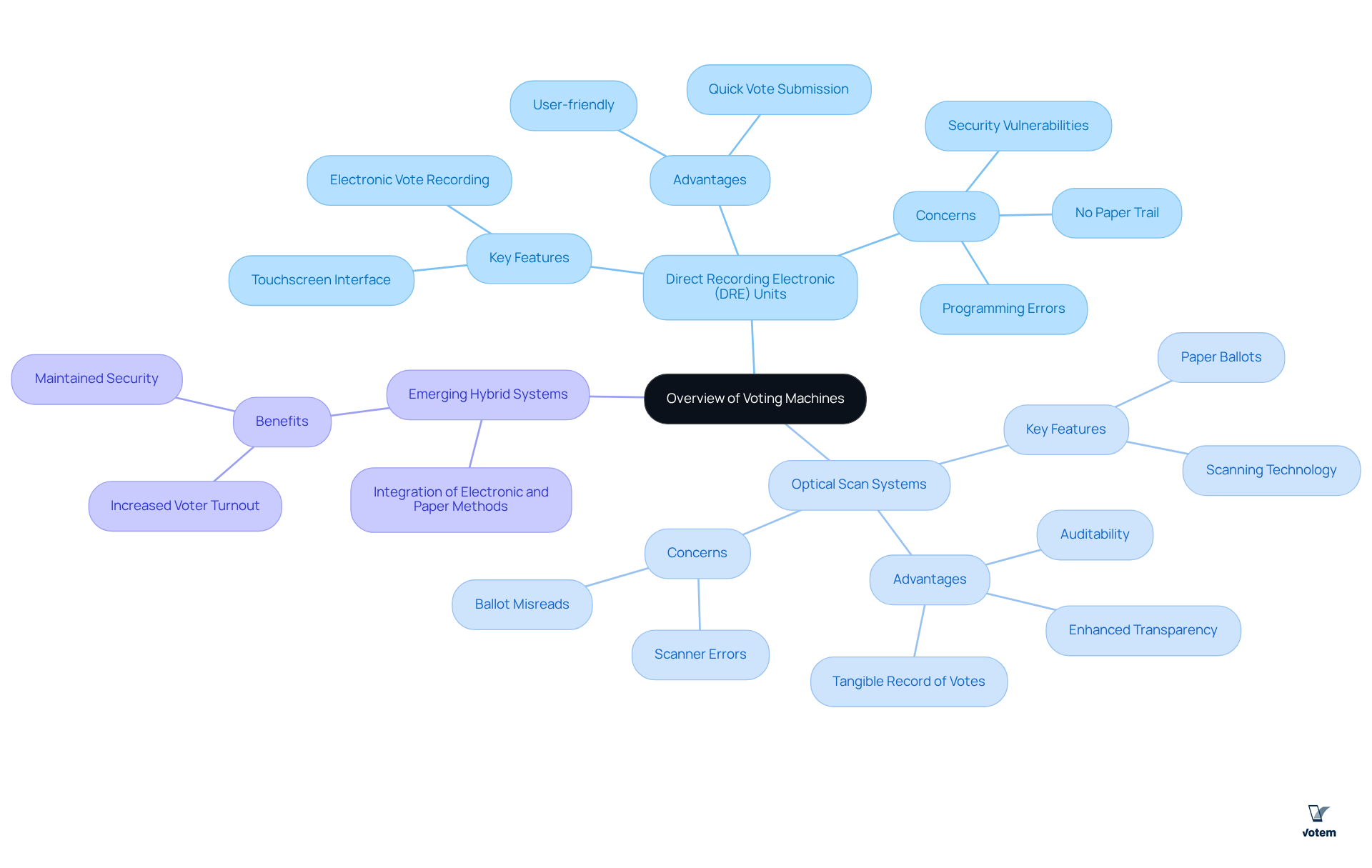
Voting machines can be broadly categorized into two main types: Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) units and optical scan systems. Voting machines, like DRE devices, allow individuals to submit their selections directly on a touchscreen or via buttons, documenting the choices electronically without a paper trail. While this method is user-friendly, it raises significant concerns about security and reliability; have resulted in lost votes and discrepancies in vote counts. Conversely, optical scan systems require individuals to mark paper ballots, which are subsequently scanned and tallied by voting machines. This method not only provides a tangible record of votes but also enhances transparency and auditability, making it a preferred option in many collective voting scenarios where compliance is essential. As of 2025, approximately 70% of labor elections are utilizing voting machines, specifically optical scan systems, reflecting a growing preference for methods that bolster public confidence and election integrity.
Emerging hybrid systems that integrate both electronic and paper methods are gaining traction, offering a compromise between speed and security. These systems can enhance voter turnout while maintaining the necessary safeguards against potential vulnerabilities. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations, particularly unions, that prioritize secure and compliant voting machines in their processes. This ensures that their electoral practices meet the highest standards of transparency and accountability.
Key Features and Benefits of Popular Voting Machines
Voting machines widely employed today come equipped with a range of features designed to and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. For example, Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) devices often include accessibility options tailored for individuals with disabilities, while optical scan systems provide a verifiable paper trail that facilitates post-election audits.
Key benefits of these voting systems are profound:
- Accessibility: Machines that comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) ensure that every voter can engage fully in the electoral process.
- Security: Contemporary voting machines utilize encryption and secure ballot storage to mitigate risks of tampering and fraud, thereby safeguarding the integrity of the voting process. Votem’s platform aligns with NCUA, DOL, ERISA, and SOC 2 requirements, underscoring its commitment to secure online voting.
- User Experience: Intuitive interfaces and mobile-friendly designs can significantly boost voter participation, particularly in collective voting scenarios where member engagement is vital. Notably, Votem’s mobile-first user experience has demonstrated an increase in turnout by up to three times on launch day.
- Auditability: Voting machines that utilize optical scan systems foster transparency by permitting post-election audits, which in turn bolster trust in the electoral process. States like Colorado have adopted risk-limiting audits to confirm voting results, offering robust statistical evidence of integrity.
These features are indispensable for organizations that demand reliable and secure voting machines, ensuring that every member’s voice is both heard and counted.
Security and Compliance Considerations for Union Elections
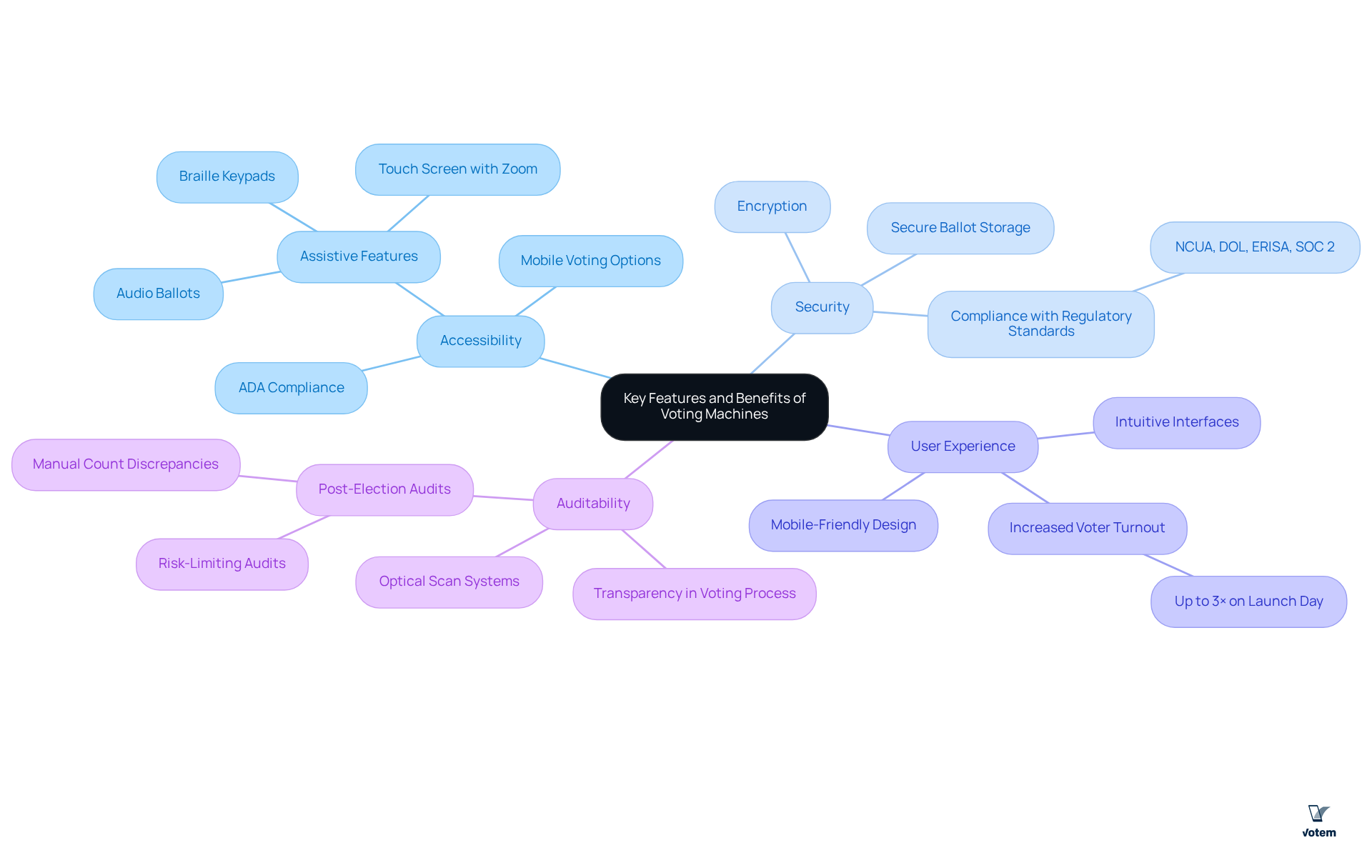
In the realm of collective voting, the safety and adherence of ballot devices are paramount to safeguarding the integrity of the electoral process. Key considerations include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Voting machines must meet the standards set by the U.S. Election Assistance Commission (EAC) and other regulatory bodies, ensuring their suitability for union elections. This compliance is essential for preserving the legitimacy of the voting process.
- Data Security: Robust encryption techniques are vital for protecting electoral data, ensuring that ballots are transmitted and stored securely. The implementation of advanced security protocols is crucial, particularly given that the Department of Homeland Security classified voting infrastructure as critical in January 2017.
- Voter Verification: Systems that facilitate voter verification are instrumental in preventing fraud, ensuring that only eligible individuals participate in the voting process. This feature significantly enhances the overall security of the electoral process.
- Audit Trails: Voting machines equipped with an immutable audit trail are essential for verifying the results after an election. This capability fosters trust among collective members, enabling transparency and accountability in election results. For instance, Votem’s CastIron platform effectively handled over 13 million votes, demonstrating how these features enhance security and trust in the voting process.
By prioritizing these factors, labor organizations can select ballot devices that not only comply with legal standards but also significantly increase public trust, ultimately leading to a more secure and reliable electoral process. As CISA emphasizes, “An electoral process that is both secure and resilient is a vital national interest and one of CISA’s highest priorities.” Moreover, Votem’s platform can by up to three times on launch day, illustrating the effectiveness of secure voting systems in enhancing participation.
Cost-Effectiveness and User Experience: Making the Right Choice
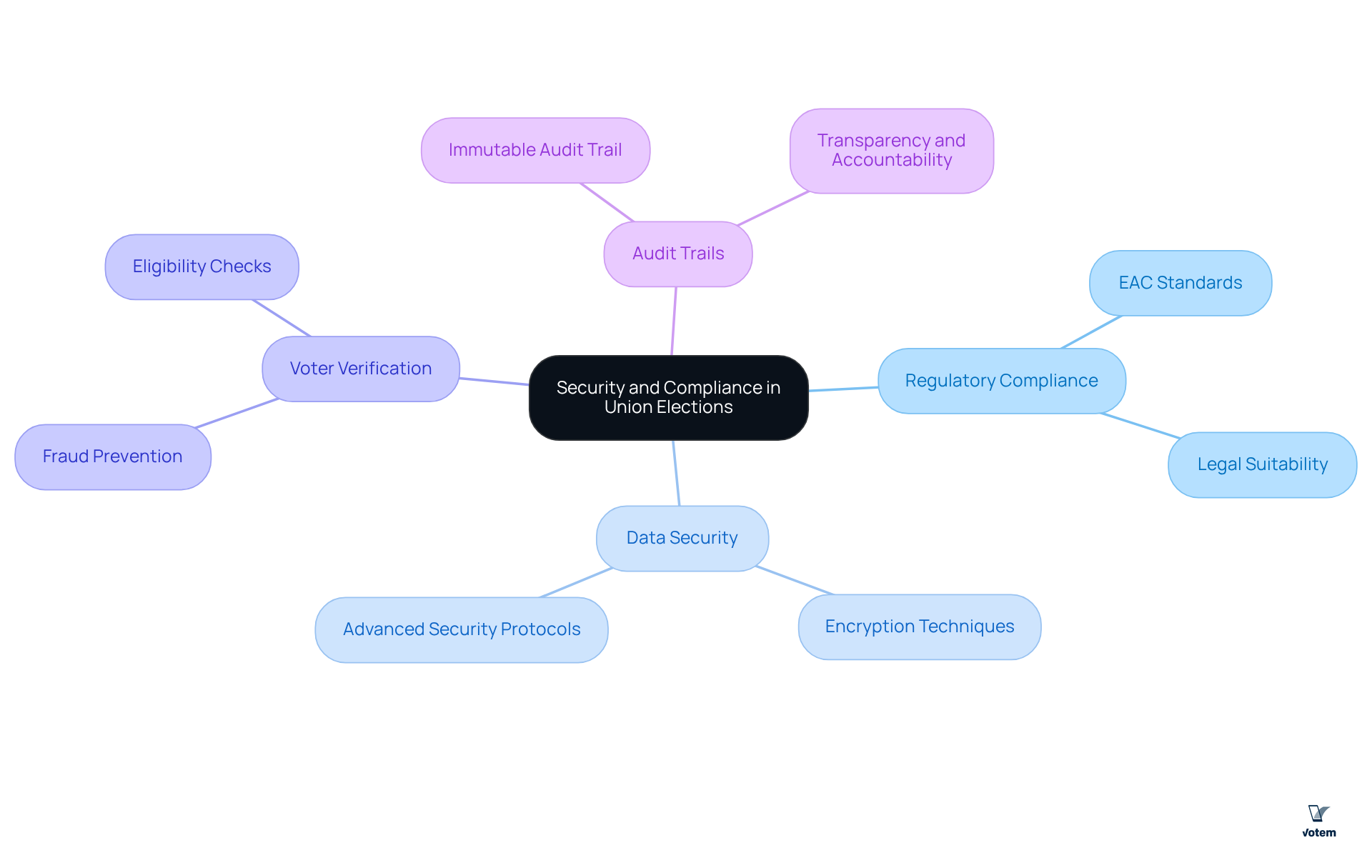
Cost-effectiveness is a crucial consideration when selecting voting machines, particularly for organizations operating within financial constraints. Key factors to evaluate include:
- Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Costs: While some voting devices may necessitate a higher initial investment, they frequently offer lower maintenance and operational expenses throughout their lifespan. This long-term perspective can yield significant savings, making it imperative to analyze the total cost of ownership of voting machines rather than focusing solely on the initial price.
- User Experience: Machines designed with accessible interfaces can significantly enhance participation, a vital goal for organizations striving to engage their members. For instance, Votem’s CastIron platform boasts a mobile-first user experience that can potentially increase turnout by up to three times on launch day. A positive user experience with voting machines not only fosters participation but also reduces the need for extensive training for poll workers, thereby streamlining the electoral process.
- Scalability: Selecting machines that can adapt to the organization’s evolving requirements is essential, particularly for larger entities that may conduct multiple votes. Scalable solutions ensure that organizations can efficiently manage varying voter volumes with voting machines without incurring excessive costs.
- Support and Maintenance: The caliber of vendor support services can significantly impact the overall cost-effectiveness of the voting machines solution. Votem’s commitment to delivering a ensures reliable support, which can reduce downtime and maintenance costs, further enhancing the value of the investment.
By meticulously balancing these factors, unions can make well-informed decisions that not only refine the electoral process but also promote greater member engagement and participation.
Conclusion
The landscape of voting machines is undergoing significant evolution, underscoring a critical focus on security, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. As organizations, particularly unions, navigate the complexities of electoral processes, grasping the distinctions between Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) units and optical scan systems is essential. Furthermore, the emergence of hybrid systems exemplifies a commitment to balancing efficiency with the paramount need for transparency and integrity in voting.
In this article, we delve into key features such as:
- Accessibility
- Security measures
- User experience
- Compliance with regulatory standards
The advantages of optical scan systems, especially their auditability and tangible paper trails, emphasize their increasing preference among organizations striving to cultivate trust and participation. In addition, recognizing the importance of long-term costs and vendor support in the decision-making process highlights the necessity for a holistic approach when selecting voting machines.
Ultimately, the choice of voting machines carries profound implications for the integrity of the electoral process. Organizations are urged to prioritize security and user experience to bolster voter turnout while ensuring adherence to established standards. By making informed decisions about voting technology, unions can not only protect the democratic process but also empower their members to engage actively and confidently in elections.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of voting machines?
Voting machines can be broadly categorized into two main types: Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) units and optical scan systems.
How do Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) units work?
DRE units allow individuals to submit their selections directly on a touchscreen or via buttons, documenting the choices electronically without a paper trail.
What are the concerns associated with DRE voting machines?
DRE voting machines raise significant concerns about security and reliability, as programming errors can result in lost votes and discrepancies in vote counts.
How do optical scan systems function?
Optical scan systems require individuals to mark paper ballots, which are then scanned and tallied by voting machines.
What are the advantages of optical scan systems?
Optical scan systems provide a tangible record of votes, enhancing transparency and auditability, making them a preferred option in many collective voting scenarios.
What percentage of labor elections are utilizing voting machines as of 2025?
As of 2025, approximately 70% of labor elections are utilizing voting machines, specifically optical scan systems.
Why are optical scan systems preferred in voting?
They are preferred because they bolster public confidence and election integrity by providing a secure and compliant voting method.
What are emerging hybrid voting systems?
Emerging hybrid systems integrate both electronic and paper methods, offering a compromise between speed and security while enhancing voter turnout.
Why is it important for organizations, particularly unions, to understand voting machine distinctions?
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations to prioritize secure and compliant voting machines, ensuring that their electoral practices meet high standards of transparency and accountability.
List of Sources
- Overview of Voting Machines: Types and Functions
- Electronic voting in the United States – Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_voting_in_the_United_States)
- Key Features and Benefits of Popular Voting Machines
- monroecounty.gov (https://monroecounty.gov/elections-voting-machines)
- tpgi.com (https://tpgi.com/accessible-voting-removing-barriers-for-voters-with-disabilities)
- Voting Equipment Database – ES&S AutoMARK (https://verifiedvoting.org/election-system/ess-automark)
- Post-Election Audits (https://ncsl.org/elections-and-campaigns/post-election-audits)
- Security and Compliance Considerations for Union Elections
- How Secure Are U.S. Electronic Voting Systems? | Econofact (https://econofact.org/how-secure-are-u-s-electronic-voting-systems)
- Election Security | Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency CISA (https://cisa.gov/topics/election-security)
- Cost-Effectiveness and User Experience: Making the Right Choice
- weforum.org (https://weforum.org/stories/2024/04/what-is-electronic-voting)

